A Circular Flow Diagram
... A. The diagram must have firms on the left side. B. Firms purchase final goods from households in return for cash. C. Households pay rent and interest to businesses in return for use of factors of production. D. Firms pay wages to households in return for labor. E. The money relationship between lab ...
... A. The diagram must have firms on the left side. B. Firms purchase final goods from households in return for cash. C. Households pay rent and interest to businesses in return for use of factors of production. D. Firms pay wages to households in return for labor. E. The money relationship between lab ...
Mysl EiP 1-2016.indd
... economies is the investment behavior of enterprises. Kornai considered the ‘expansion drive’ of all decision-makers in this system the basic reason for its irrational investment policy. The ‘expansion drive’ results from the political nature of all economic decisions, also from petty ambitions of en ...
... economies is the investment behavior of enterprises. Kornai considered the ‘expansion drive’ of all decision-makers in this system the basic reason for its irrational investment policy. The ‘expansion drive’ results from the political nature of all economic decisions, also from petty ambitions of en ...
GDP, CPI & Inflation Rate - VCC Library
... tax, interest, depreciation, and indirect taxes less subsidies. (see class notes for more) When GDP is calculated using current prices, it is called money GDP or nominal GDP. It is the sum of each good’s quantity (output) multiplied by the current price of the good. Money GDP= ...
... tax, interest, depreciation, and indirect taxes less subsidies. (see class notes for more) When GDP is calculated using current prices, it is called money GDP or nominal GDP. It is the sum of each good’s quantity (output) multiplied by the current price of the good. Money GDP= ...
PDF version
... All eligible prices are converted to a price per normalized quantity. These prices are then used to estimate a price for a defined fixed quantity. The average price per kilowatt-hour represents the total bill divided by the kilowatt-hour usage. The total bill is the sum of all items applicable to al ...
... All eligible prices are converted to a price per normalized quantity. These prices are then used to estimate a price for a defined fixed quantity. The average price per kilowatt-hour represents the total bill divided by the kilowatt-hour usage. The total bill is the sum of all items applicable to al ...
Power Point: Aggregate Supply
... Wages change when labor contracts expire. Workers are reluctant to accept lower wages. Employers prefer to fire unskilled workers to reduce wages of skilled workers: Wages ...
... Wages change when labor contracts expire. Workers are reluctant to accept lower wages. Employers prefer to fire unskilled workers to reduce wages of skilled workers: Wages ...
Materials Cost Calculation
... Tricky Part: We buy sheet goods by full sheets. Most are 4 feet by 8 feet so we need to calculate the cost per square foot for a whole sheet first. Seldom does the supplier tell you the cost per square foot. Width (4’) x Length (8’) = 32 square Cost per square foot is the total price ÷ 32 The formul ...
... Tricky Part: We buy sheet goods by full sheets. Most are 4 feet by 8 feet so we need to calculate the cost per square foot for a whole sheet first. Seldom does the supplier tell you the cost per square foot. Width (4’) x Length (8’) = 32 square Cost per square foot is the total price ÷ 32 The formul ...
Inflation and Interest Rates
... Problems in Measuring the Cost of Living • Unmeasured Quality Changes – If the quality of a good rises from one year to the next, the value of a dollar rises, even if the price of the good stays the same. – If the quality of a good falls from one year to the next, the value of a dollar falls, even ...
... Problems in Measuring the Cost of Living • Unmeasured Quality Changes – If the quality of a good rises from one year to the next, the value of a dollar rises, even if the price of the good stays the same. – If the quality of a good falls from one year to the next, the value of a dollar falls, even ...
Inflation and Interest Rates
... Problems in Measuring the Cost of Living • Unmeasured Quality Changes – If the quality of a good rises from one year to the next, the value of a dollar rises, even if the price of the good stays the same. – If the quality of a good falls from one year to the next, the value of a dollar falls, even ...
... Problems in Measuring the Cost of Living • Unmeasured Quality Changes – If the quality of a good rises from one year to the next, the value of a dollar rises, even if the price of the good stays the same. – If the quality of a good falls from one year to the next, the value of a dollar falls, even ...
SUBJECT 2
... l The economy’s absorption capacity of foreign resources l The economy’s capacity to execute projects l The performance of key economic variables in the face of an increase or impending reorientation of resources for reconstruction: interest rates, indebtedness, inputs and production means availabil ...
... l The economy’s absorption capacity of foreign resources l The economy’s capacity to execute projects l The performance of key economic variables in the face of an increase or impending reorientation of resources for reconstruction: interest rates, indebtedness, inputs and production means availabil ...
Consumer surplus
... • Producer surplus equals the amount sellers receive for their goods minus their costs of production. • Producer surplus measures the benefit sellers get from participating in a market. • Producer surplus can be computed by finding the area below the price and above the supply curve. ...
... • Producer surplus equals the amount sellers receive for their goods minus their costs of production. • Producer surplus measures the benefit sellers get from participating in a market. • Producer surplus can be computed by finding the area below the price and above the supply curve. ...
Chapter Three: Price Forecasting
... relationships. This process involves the following: – Determine the economic relationship. – Determine the mathematical expression of the economic model. – Determine what data to use and the time frame of analysis ...
... relationships. This process involves the following: – Determine the economic relationship. – Determine the mathematical expression of the economic model. – Determine what data to use and the time frame of analysis ...
Post Keynesian Pricing Theory: Alternative Foundations and
... suppliers as they balance the need to be competitive with the need to promote longerterm links needs investigation. In general, the message is that clearly psychological and behavioural analysis as much as technical concern is important in fleshing out how these forms of economic activity develop an ...
... suppliers as they balance the need to be competitive with the need to promote longerterm links needs investigation. In general, the message is that clearly psychological and behavioural analysis as much as technical concern is important in fleshing out how these forms of economic activity develop an ...
Inflation in Fiji The Reserve Bank of Fiji (RBF), like many central
... services. For example, if demand for a good or service is high but its supply is low, prices will tend to rise. Therefore, prices reflect the interaction between the demand and supply of goods and services. How is inflation measured? Inflation is a broad measure and is normally calculated as the ann ...
... services. For example, if demand for a good or service is high but its supply is low, prices will tend to rise. Therefore, prices reflect the interaction between the demand and supply of goods and services. How is inflation measured? Inflation is a broad measure and is normally calculated as the ann ...
Capital formation in post socialist countries
... should bring about adequately higher level of investments growth (the relation of consumption growth to investments growth equals the index: capital ratio outpu ), and if existing production capital is able to satisfy growing consumption, economy is able to react to the growth without investments, o ...
... should bring about adequately higher level of investments growth (the relation of consumption growth to investments growth equals the index: capital ratio outpu ), and if existing production capital is able to satisfy growing consumption, economy is able to react to the growth without investments, o ...
Forum for Social Economics Contemporary Capitalism as a New
... tendencies are developed in response to the crisis which marked the definitive end of the institutional forms that characterized the regulation of capitalism during the previous decades. First, there is the decomposition of the Fordist wage relation. In a context of increasing pressure exercised by ...
... tendencies are developed in response to the crisis which marked the definitive end of the institutional forms that characterized the regulation of capitalism during the previous decades. First, there is the decomposition of the Fordist wage relation. In a context of increasing pressure exercised by ...
Business Investment
... » Expand capacity to meet higher production levels These are highly cyclic sales, in that if construction is simply flat, no new equipment is required for expansion In other words, the level of such sales tracks the growth in customer production Equipment sales lag served markets by approximatel ...
... » Expand capacity to meet higher production levels These are highly cyclic sales, in that if construction is simply flat, no new equipment is required for expansion In other words, the level of such sales tracks the growth in customer production Equipment sales lag served markets by approximatel ...
International marketing theories
... Related and supporting industries – iternationally competitive suppliers and supporters existence or absence Firm strategy, structure and rivalry – the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized and managed and the nature of home rivalry ...
... Related and supporting industries – iternationally competitive suppliers and supporters existence or absence Firm strategy, structure and rivalry – the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized and managed and the nature of home rivalry ...
The Middle East
... Standard: Describe the factors that influence economic growth and examine their presence or absence in Israel, Saudi Arabia, and Iran E.Q. for Wednesday, 11/2/16: What is the definition for Natural Resources? List four examples of Natural Resources. Warm Up: What are the three things that investment ...
... Standard: Describe the factors that influence economic growth and examine their presence or absence in Israel, Saudi Arabia, and Iran E.Q. for Wednesday, 11/2/16: What is the definition for Natural Resources? List four examples of Natural Resources. Warm Up: What are the three things that investment ...
Price of Ice-Cream Cone - Class Notes for Mr.Guerriero
... the allocation of scarce resources to unlimited human wants. • Economics is broken down into: 1. Micro Economics: deals with the behaviour on individual basis (one person) 2. Macro Economics concerns itself with the economic situation as a whole, rather than the individual units (country) ...
... the allocation of scarce resources to unlimited human wants. • Economics is broken down into: 1. Micro Economics: deals with the behaviour on individual basis (one person) 2. Macro Economics concerns itself with the economic situation as a whole, rather than the individual units (country) ...
Interactive Tool
... knowledge to explain how their lives would be more difficult in a world with no money, or in a world where money sharply lost its value. 18. A nation's overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the interaction of spending and production decisions made by all households, firm ...
... knowledge to explain how their lives would be more difficult in a world with no money, or in a world where money sharply lost its value. 18. A nation's overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the interaction of spending and production decisions made by all households, firm ...
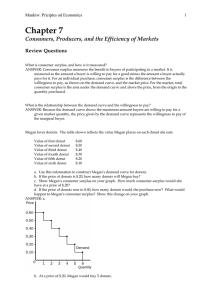
What is consumer surplus, and how is it measured
... c. Show Megan’s consumer surplus on your graph. How much consumer surplus would she have at a price of $.20? d. If the price of donuts rose to $.40, how many donuts would she purchase now? What would happen to Megan’s consumer surplus? Show this change on your graph. ANSWER: a. ...
... c. Show Megan’s consumer surplus on your graph. How much consumer surplus would she have at a price of $.20? d. If the price of donuts rose to $.40, how many donuts would she purchase now? What would happen to Megan’s consumer surplus? Show this change on your graph. ANSWER: a. ...