Coverdrive Ltd
... His first step was to consider the volume of production and its effect on cost behaviour. It is clear that the business incurs both fixed and variable costs which are defined as: Fixed Cost “The cost which is incurred for a period, and which, within certain output and turnover limits, tends to be un ...
... His first step was to consider the volume of production and its effect on cost behaviour. It is clear that the business incurs both fixed and variable costs which are defined as: Fixed Cost “The cost which is incurred for a period, and which, within certain output and turnover limits, tends to be un ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from... Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: NBER International Seminar on Macroeconomics
... frictions is not a clear solution either. Under the assumption of a small open economy, good news about future productivity will now lead to an increase in both consumption and investment, but it will create an even greater domestic recession since employment and production will decrease more signif ...
... frictions is not a clear solution either. Under the assumption of a small open economy, good news about future productivity will now lead to an increase in both consumption and investment, but it will create an even greater domestic recession since employment and production will decrease more signif ...
French circuit theory
... it, is to recoup their expenses, that is to say their production costs, and obtain a net yield (profit) that will allow them to pay interest and dividends on the funds invested. Therefore, the remuneration of capital is not formed in a specific market that is somehow pre-existent to the goods market ...
... it, is to recoup their expenses, that is to say their production costs, and obtain a net yield (profit) that will allow them to pay interest and dividends on the funds invested. Therefore, the remuneration of capital is not formed in a specific market that is somehow pre-existent to the goods market ...
CHAPTER 9 - Economics
... – supplies of capital, labor – technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. CHAPTER 9 ...
... – supplies of capital, labor – technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. CHAPTER 9 ...
Secular Stagnation and the Failed Growth Economy
... of limits. To begin with there is a set of biophysical limits imposed by the laws of the finite and nongrowing primary system in the second half of the age of hydrocarbons. These limits take the form of a declining resource base, for example peak oil, and myriad problems of the expansion of the huma ...
... of limits. To begin with there is a set of biophysical limits imposed by the laws of the finite and nongrowing primary system in the second half of the age of hydrocarbons. These limits take the form of a declining resource base, for example peak oil, and myriad problems of the expansion of the huma ...
A Different View on Pricing
... consumers process price information. It explains why consumers may not react in the same manner to prices that fall within an acceptable range as they do to prices outside that range, that consumers hold price thresholds that are measurable, and that we can use these notions to help explain why dema ...
... consumers process price information. It explains why consumers may not react in the same manner to prices that fall within an acceptable range as they do to prices outside that range, that consumers hold price thresholds that are measurable, and that we can use these notions to help explain why dema ...
Bubbles and Capital Flow Volatility: Causes and Risk Management
... capital requirements on real estate investment or liquidity requirements on such investment reduce bubbles. These policies are similar to those discussed in Caballero and Krishnamurthy (2004) in the context of overborrowing and the dollarization of liabilities problems. A more novel liquidity polic ...
... capital requirements on real estate investment or liquidity requirements on such investment reduce bubbles. These policies are similar to those discussed in Caballero and Krishnamurthy (2004) in the context of overborrowing and the dollarization of liabilities problems. A more novel liquidity polic ...
View/Open
... by wildlife-associated recreation activities. In particular, non-market valuation methods fail to account for implications of these activities for the rest of the economy (Loomis et al., 1989). While traditional I-O and social accounting based multiplier analyses account for inter-sectoral linkages, ...
... by wildlife-associated recreation activities. In particular, non-market valuation methods fail to account for implications of these activities for the rest of the economy (Loomis et al., 1989). While traditional I-O and social accounting based multiplier analyses account for inter-sectoral linkages, ...
Barcelona Summer School Lecture 2015
... There is an optimal steady state in which (C*, K*) = (70,45) From any initial level of capital stock, optimal decisions (of a benelovent social planner) at each point in time imply monotonic convergence to (C*, K*). However, if the economy is decentralized, there are two stationary rational expectat ...
... There is an optimal steady state in which (C*, K*) = (70,45) From any initial level of capital stock, optimal decisions (of a benelovent social planner) at each point in time imply monotonic convergence to (C*, K*). However, if the economy is decentralized, there are two stationary rational expectat ...
3/13-3/20 - David Friedman
... natural monopoly – Since it can make money selling at a price at which a smaller competitor would lose money – It ends up with the whole market ...
... natural monopoly – Since it can make money selling at a price at which a smaller competitor would lose money – It ends up with the whole market ...
What is Economics?
... • Regulated monopoly: Public utilities and the like – If forced to charge marginal cost they go broke – The usual policy is to try to force average cost--still inefficient, but not as inefficient as what the monopolist would do – But how do you know what average cost is? • If you ask the accountants ...
... • Regulated monopoly: Public utilities and the like – If forced to charge marginal cost they go broke – The usual policy is to try to force average cost--still inefficient, but not as inefficient as what the monopolist would do – But how do you know what average cost is? • If you ask the accountants ...
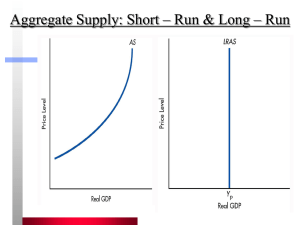
Aggregate Supply and AD
... and capital constant in the short-run) higher profit margins firms want to produce more. ...
... and capital constant in the short-run) higher profit margins firms want to produce more. ...
Property-Owning Democracy or Economic Democracy?
... adult populations. But these shares can be neither purchased nor sold. They can only be traded for other shares. The value of a share will deviate over time from its initial value, depending on how well the company is doing, so individual portfolios will, over time, shift in value. Those doing bette ...
... adult populations. But these shares can be neither purchased nor sold. They can only be traded for other shares. The value of a share will deviate over time from its initial value, depending on how well the company is doing, so individual portfolios will, over time, shift in value. Those doing bette ...
Inflation October 18
... their financial assets from inflation. The resources and time used to do so could be used to produce goods and services of value. Those goods and services given up are a true cost of inflation. 2. High rates of inflation discourage businesses planning and investment as inflation increases the diffic ...
... their financial assets from inflation. The resources and time used to do so could be used to produce goods and services of value. Those goods and services given up are a true cost of inflation. 2. High rates of inflation discourage businesses planning and investment as inflation increases the diffic ...
Russia`s protracted recession:
... in Russia look and behave more like those in other countries, which could mean that Moscow and some other cities will vary greatly from the rest of the country. In response to these changes, companies need to adapt their offerings (i.e. what to offer, how to offer it, at what price, and how to commu ...
... in Russia look and behave more like those in other countries, which could mean that Moscow and some other cities will vary greatly from the rest of the country. In response to these changes, companies need to adapt their offerings (i.e. what to offer, how to offer it, at what price, and how to commu ...
Openness in goods markets
... holdings of U.S. assets are greater (less) than U.S. holdings of foreign assets, in which case there is a capital account surplus (deficit). The numbers for current and capital account transactions are constructed using different sources; although they should give the same answers, they typically do ...
... holdings of U.S. assets are greater (less) than U.S. holdings of foreign assets, in which case there is a capital account surplus (deficit). The numbers for current and capital account transactions are constructed using different sources; although they should give the same answers, they typically do ...
Introduction to economic anlysis
... This is an introductory course to economic analysis. Its aims are, first, to familiarise the student with the topics that are normally covered by this discipline and, second, to introduce them to the way in which economists think to analyse real world problems and proceed to propose solutions for th ...
... This is an introductory course to economic analysis. Its aims are, first, to familiarise the student with the topics that are normally covered by this discipline and, second, to introduce them to the way in which economists think to analyse real world problems and proceed to propose solutions for th ...
Unlocking the Mystery of Economic Recessions Using a Multi-commodity Macroeconomic Model
... demand emphasized by Keynesian economists plays a key role in the short run (Sorensen and Whitta-Jacobsen, 2010). Thus, the dichotomy between Keynesian and Classical economics evolves as a dichotomy between the long run and the short run. That is, conflicting theories applying to the same economy bu ...
... demand emphasized by Keynesian economists plays a key role in the short run (Sorensen and Whitta-Jacobsen, 2010). Thus, the dichotomy between Keynesian and Classical economics evolves as a dichotomy between the long run and the short run. That is, conflicting theories applying to the same economy bu ...
state university - Высшая школа экономики
... The following methods and forms of study and control are used in the course: Lectures (2 hours a week) Attendance at lectures is optional, but it is recommended. Lectures offer a verbal presentation of the material to be mastered. More importantly, they indicate the relative importance of sub-topics ...
... The following methods and forms of study and control are used in the course: Lectures (2 hours a week) Attendance at lectures is optional, but it is recommended. Lectures offer a verbal presentation of the material to be mastered. More importantly, they indicate the relative importance of sub-topics ...
Economics Exit Exam Preparation
... this is possible depends on the elasticities of demand and supply. Generally, the more elastic (inelastic) demand is, the more difficult (easier) it is for the firm to pass the tax burden to the consumer. In contrast, the more inelastic (elastic) supply is, the more difficult (easier) it is to pass ...
... this is possible depends on the elasticities of demand and supply. Generally, the more elastic (inelastic) demand is, the more difficult (easier) it is for the firm to pass the tax burden to the consumer. In contrast, the more inelastic (elastic) supply is, the more difficult (easier) it is to pass ...
EIU proposal
... The main building blocks for the long-term forecasts of key market and macroeconomic variables are long-run real GDP growth projections. We have estimated growth regressions (based on cross-section, panel data for 86 countries for the 1970-2000 period) that link real growth in GDP per head to a larg ...
... The main building blocks for the long-term forecasts of key market and macroeconomic variables are long-run real GDP growth projections. We have estimated growth regressions (based on cross-section, panel data for 86 countries for the 1970-2000 period) that link real growth in GDP per head to a larg ...