Mankiw 5/e Chapter 9: Intro to Economic Fluctuations
... – supplies of capital, labor – technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. CHAPTER 9 ...
... – supplies of capital, labor – technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. CHAPTER 9 ...
Varieties of Keynesianism
... to light that allow the effective use of statistical inference to guide certain types of financial transactions, such as arbitrage. Unfortunately macroeconomic data does not seem to escape Keynes’ skeptical critique, since it is far less abundant, and subject to the historical vagaries Keynes diagno ...
... to light that allow the effective use of statistical inference to guide certain types of financial transactions, such as arbitrage. Unfortunately macroeconomic data does not seem to escape Keynes’ skeptical critique, since it is far less abundant, and subject to the historical vagaries Keynes diagno ...
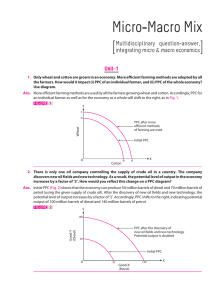
Micro-Macro Mix with solution
... Ans. No, is the answer. Because per capita change only indicates an average change. It does account for the distribution of income. It is possible that real GDP rises, but the distribution of income becomes more skewed. Benefit of higher GDP may not reach the poorest of the poor. It may just accrue ...
... Ans. No, is the answer. Because per capita change only indicates an average change. It does account for the distribution of income. It is possible that real GDP rises, but the distribution of income becomes more skewed. Benefit of higher GDP may not reach the poorest of the poor. It may just accrue ...
Introduction
... economic analysis of these methods is more complex, as in such cases direct net revenues will not be generated, so that this mechanism for influencing the incidence of benefits is not available. The economic effect will therefore tend to be determined by the precision with which the policies can be ...
... economic analysis of these methods is more complex, as in such cases direct net revenues will not be generated, so that this mechanism for influencing the incidence of benefits is not available. The economic effect will therefore tend to be determined by the precision with which the policies can be ...
Review Packet
... If the rate of inflation is less than 3 percent (and greater than 0 percent, of course), it is considered “acceptable”. Types of Inflation Demand-pull inflation: more spending than the economy’s capacity to produce. The excess demand increases the prices of the limited real output, causing prices to ...
... If the rate of inflation is less than 3 percent (and greater than 0 percent, of course), it is considered “acceptable”. Types of Inflation Demand-pull inflation: more spending than the economy’s capacity to produce. The excess demand increases the prices of the limited real output, causing prices to ...
Business Essentials 6e
... products has not been paid in full. In effect, therefore, it is borrowed money, and borrowed money costs more money in the form of interest. • The money that flows out of the country to pay off the deficit cannot be used to invest in productive enterprises, either at home or overseas. ...
... products has not been paid in full. In effect, therefore, it is borrowed money, and borrowed money costs more money in the form of interest. • The money that flows out of the country to pay off the deficit cannot be used to invest in productive enterprises, either at home or overseas. ...
CHAP18
... net investment responds to the incentive to invest. Total spending on business fixed investment equals net investment plus replacement of depreciated K: ...
... net investment responds to the incentive to invest. Total spending on business fixed investment equals net investment plus replacement of depreciated K: ...
Recommending a Strategy
... surplus further increases because of the movement of labor from the agricultural sector to the industrial sector (without a decline in agricultural output) Profits in the industrial sector are assumed to be saved and invested in the industrial sector Industrial workers consume only agricultural ...
... surplus further increases because of the movement of labor from the agricultural sector to the industrial sector (without a decline in agricultural output) Profits in the industrial sector are assumed to be saved and invested in the industrial sector Industrial workers consume only agricultural ...
Lecture 7. Classical monetary theory
... i.e. if there exists equilibrium in N markets, then there would also be equilibrium in the (N + 1)th market. In the absence of financial assets, Say’s law can be reformulated in the Walrasian setting to be: “If and only if the excess demand for money is zero, then Walras’ law ...
... i.e. if there exists equilibrium in N markets, then there would also be equilibrium in the (N + 1)th market. In the absence of financial assets, Say’s law can be reformulated in the Walrasian setting to be: “If and only if the excess demand for money is zero, then Walras’ law ...
benefit-cost analysis - University of Queensland
... • suppose that the country has a 100% tariff on imports of clothing i.e. in the domestic market 1 unit of food exchanges for 0.5 units of clothing; • suppose the economy is competitive with no distortions other than the tariff, and that labour is the only factor of production. The VMPL will be the s ...
... • suppose that the country has a 100% tariff on imports of clothing i.e. in the domestic market 1 unit of food exchanges for 0.5 units of clothing; • suppose the economy is competitive with no distortions other than the tariff, and that labour is the only factor of production. The VMPL will be the s ...
Supply & Demand
... economy functions it is important to understand the nation’s price system The forces that determine price are called the forces of supply and demand The place where these two forces meet is called the marketplace ...
... economy functions it is important to understand the nation’s price system The forces that determine price are called the forces of supply and demand The place where these two forces meet is called the marketplace ...
Factors of Production - Mankiw
... • The three most important factors of production are labor, land, and capital. • The demand for a factor, such as labor, is a derived demand that comes from firms that use the factors to produce goods and services. ...
... • The three most important factors of production are labor, land, and capital. • The demand for a factor, such as labor, is a derived demand that comes from firms that use the factors to produce goods and services. ...
LEERTEXT - Heterodox Economics Newsletter
... with changes in output levels, with some kind of fixed prices based upon the mark-up principle. This would, incidentally, require that Sraffa’s prices of production are no longer seen as conditions for reproduction (Roncaglia), but as a pure theory of prices of production, with applied prices of pro ...
... with changes in output levels, with some kind of fixed prices based upon the mark-up principle. This would, incidentally, require that Sraffa’s prices of production are no longer seen as conditions for reproduction (Roncaglia), but as a pure theory of prices of production, with applied prices of pro ...
Indeterminacy with Progressive Taxation and Sector
... and derive utility from consumption and leisure. In Model 1, the household utility is postulated to be additively separable between consumption and hours worked, as in Benhabib and Farmer (1994, 1996), Harrison (2001), and Guo and Harrison (2001, 2011). Model 2 examines a nonseparable preference spe ...
... and derive utility from consumption and leisure. In Model 1, the household utility is postulated to be additively separable between consumption and hours worked, as in Benhabib and Farmer (1994, 1996), Harrison (2001), and Guo and Harrison (2001, 2011). Model 2 examines a nonseparable preference spe ...
Y i - IES
... nominal wage, equilibrium • Keynes: – Does not dispute classical demand for labor – Refuses the construction of the labor supply • Workers do not adjust to real, but to nominal wage • Nominal wage much less flexible: – general political reasons after WWI (workers not ready to accept wage cuts) – dur ...
... nominal wage, equilibrium • Keynes: – Does not dispute classical demand for labor – Refuses the construction of the labor supply • Workers do not adjust to real, but to nominal wage • Nominal wage much less flexible: – general political reasons after WWI (workers not ready to accept wage cuts) – dur ...
National Production
... The main aim of a countryÊs economic activity is to ensure that all its peopleÊs needs for goods and services are satisfied. Nothing is more important than providing shelter, food, clothing, education and recreation for each and every citizen. Before you continue reading, think for just a moment abo ...
... The main aim of a countryÊs economic activity is to ensure that all its peopleÊs needs for goods and services are satisfied. Nothing is more important than providing shelter, food, clothing, education and recreation for each and every citizen. Before you continue reading, think for just a moment abo ...
5. Dynamics of a Small Open Economy y p y
... consumption of one country cannot exceed world output). Hence, only the constellation is ρ1=r (“world interest rate equals time preference rate of most patient country”)) is compatible with an equilibrium in the global economy ...
... consumption of one country cannot exceed world output). Hence, only the constellation is ρ1=r (“world interest rate equals time preference rate of most patient country”)) is compatible with an equilibrium in the global economy ...
6 Was the Great War a watershed? The economics of World War I in
... consequences for France were enormous, since the invaded region was among the richest: it had a highly productive agriculture (20 per cent of 1913 wheat production, 25 per cent of oats, 12 per cent of potatoes, 50 per cent of sugar beets); but most of the steel (80 per cent) and electricity (43 per ...
... consequences for France were enormous, since the invaded region was among the richest: it had a highly productive agriculture (20 per cent of 1913 wheat production, 25 per cent of oats, 12 per cent of potatoes, 50 per cent of sugar beets); but most of the steel (80 per cent) and electricity (43 per ...
Coverdrive Ltd
... His first step was to consider the volume of production and its effect on cost behaviour. It is clear that the business incurs both fixed and variable costs which are defined as: Fixed Cost “The cost which is incurred for a period, and which, within certain output and turnover limits, tends to be un ...
... His first step was to consider the volume of production and its effect on cost behaviour. It is clear that the business incurs both fixed and variable costs which are defined as: Fixed Cost “The cost which is incurred for a period, and which, within certain output and turnover limits, tends to be un ...