PDF Download
... This enables us to highlight positive output effects in some sectors and quantify potentially negative sectoral spillovers. These negative spillovers result from competition for scarce resources. In an innovative economy these resources will be attracted by innovative sectors and thus impose a negati ...
... This enables us to highlight positive output effects in some sectors and quantify potentially negative sectoral spillovers. These negative spillovers result from competition for scarce resources. In an innovative economy these resources will be attracted by innovative sectors and thus impose a negati ...
Driving North American Growth and Trade
... noting still healthy consumer fundamentals and broad strength in business investment, labour markets, and residential/commercial real estate markets. The statement should also affirm that the risks to the outlook “appear roughly balanced”, code for “we’re keeping the normalization door open”. This p ...
... noting still healthy consumer fundamentals and broad strength in business investment, labour markets, and residential/commercial real estate markets. The statement should also affirm that the risks to the outlook “appear roughly balanced”, code for “we’re keeping the normalization door open”. This p ...
executive summary - National Association of Wholesaler
... becoming a truly collaborative business partner; (2) develop a services strategy that is adopted and understood company-wide; and (3) actively manage their product and services portfolio to ensure they are providing the right solutions at the right prices with the right profit margins. Going forward ...
... becoming a truly collaborative business partner; (2) develop a services strategy that is adopted and understood company-wide; and (3) actively manage their product and services portfolio to ensure they are providing the right solutions at the right prices with the right profit margins. Going forward ...
0.1 Topics of Cognitive Economics 0.2 Introduction
... equacy between available means and pursued objectives. Its strong form assumes that the decision-maker chooses the action which maximizes his utility, for given beliefs (Bayesian rationality). Both forms of rationality intervene in the deliberation process, the first to frame the decision problem in ...
... equacy between available means and pursued objectives. Its strong form assumes that the decision-maker chooses the action which maximizes his utility, for given beliefs (Bayesian rationality). Both forms of rationality intervene in the deliberation process, the first to frame the decision problem in ...
Timmons Cartels and Their Consequences MWPSA 2006
... grew at a meager 0.2 percent per year in Latin America between 1950-95. 11 While post reform data is admittedly scarce, early indications are that productivity has increased slightly, but remain well-below the levels experienced elsewhere. In Mexico, for exa mple, TFP has been virtually stagnant sin ...
... grew at a meager 0.2 percent per year in Latin America between 1950-95. 11 While post reform data is admittedly scarce, early indications are that productivity has increased slightly, but remain well-below the levels experienced elsewhere. In Mexico, for exa mple, TFP has been virtually stagnant sin ...
LAND PRICES AND UNEMPLOYMENT
... The model consists of three types of agents: households, capitalists, and firms. The representative household consists of a continuum of workers—some are employed and others are not. All workers consume the same amount of goods and housing services, so that unemployment risks are pooled within the h ...
... The model consists of three types of agents: households, capitalists, and firms. The representative household consists of a continuum of workers—some are employed and others are not. All workers consume the same amount of goods and housing services, so that unemployment risks are pooled within the h ...
ThemeGallery PowerTemplate - United Nations Economic
... conducted, which allowed calculation of output, intermediate consumption and gross fixed capital formation by three groups: • market producers active on the market; • market producers which do not have sales (R&D development is performed at own expense); • units of general government sector. ...
... conducted, which allowed calculation of output, intermediate consumption and gross fixed capital formation by three groups: • market producers active on the market; • market producers which do not have sales (R&D development is performed at own expense); • units of general government sector. ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... much smaller for nondurable goods, and still smaller for most of the (nonstorable) services. Manufacturers' sales move with greater amplitudes than wholesalers' sales, and the latter with greater amplitudes than retailers' sales. In many industries, particularly manufacturing of durables, production ...
... much smaller for nondurable goods, and still smaller for most of the (nonstorable) services. Manufacturers' sales move with greater amplitudes than wholesalers' sales, and the latter with greater amplitudes than retailers' sales. In many industries, particularly manufacturing of durables, production ...
economic reforms and human capital development
... respect to the latter, they follow Barro (1999) in suggesting that the insignificant effect of female education may be a result of gender discrimination in some countries’ labour markets. The argument is that females receive education in these countries but are discouraged from participating in the ...
... respect to the latter, they follow Barro (1999) in suggesting that the insignificant effect of female education may be a result of gender discrimination in some countries’ labour markets. The argument is that females receive education in these countries but are discouraged from participating in the ...
Mankiw 5/e Chapter 3: National Income
... Demand: by households for consumption, government spending, and other firms demand them for investment ...
... Demand: by households for consumption, government spending, and other firms demand them for investment ...
Full Text 8 Uzor\374
... considered as the most radical industrial policy change in Nigeria 12 years after attaining independence. The objectives of the policy were theoretically a) to create an economically independent country with increased opportunities for indigenous Nigerian businessmen; b) to ensure greater retention ...
... considered as the most radical industrial policy change in Nigeria 12 years after attaining independence. The objectives of the policy were theoretically a) to create an economically independent country with increased opportunities for indigenous Nigerian businessmen; b) to ensure greater retention ...
Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL
... While GDP measures are informative and are widely used in many countries to summarize the state of the economy, it is important to realize that they are by no means perfect. be criticized f t RGDP can b iti i d as a measure of economic welfare because: 1. It does not include nonnon-market activities ...
... While GDP measures are informative and are widely used in many countries to summarize the state of the economy, it is important to realize that they are by no means perfect. be criticized f t RGDP can b iti i d as a measure of economic welfare because: 1. It does not include nonnon-market activities ...
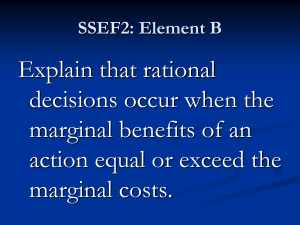
Marginal Costs and Benefits Notes
... one more unit (cost of processing one more item) The additional benefit gained from one more unit (benefit associated with that one additional item) ...
... one more unit (cost of processing one more item) The additional benefit gained from one more unit (benefit associated with that one additional item) ...
THE CLASSICAL MODEL OF THE MACROECONOMY
... The "Keynesian Revolution" means different things to different people. But even its critics have agreed that Keynes's General Theory triggered a series of analytical innovations and policy experiments that resulted in dramatically higher expectations about the government's ability to favorably influ ...
... The "Keynesian Revolution" means different things to different people. But even its critics have agreed that Keynes's General Theory triggered a series of analytical innovations and policy experiments that resulted in dramatically higher expectations about the government's ability to favorably influ ...
China`s gross domestic product estimation
... At first, Chinese GDP was only estimated from the production side. The NBS adopted the expenditure approach for GDP estimation as an experiment in 1989, and then formally in 1993. 1.2.2. From indirect to direct estimation At first, production-side GDP estimates were not calculated independently but ...
... At first, Chinese GDP was only estimated from the production side. The NBS adopted the expenditure approach for GDP estimation as an experiment in 1989, and then formally in 1993. 1.2.2. From indirect to direct estimation At first, production-side GDP estimates were not calculated independently but ...
Welfare Effects of Demand Management Policies: Impact Multipliers
... among intermediate inputs. Household demand functions permit substitution among commodities. Furthermore, imports may be substituted for domestic supplies in both intermediate use and in household consumption according to a system similar to that of Armington (1969). World prices for imports are giv ...
... among intermediate inputs. Household demand functions permit substitution among commodities. Furthermore, imports may be substituted for domestic supplies in both intermediate use and in household consumption according to a system similar to that of Armington (1969). World prices for imports are giv ...
Welfare Effects of Demand Management Policies: Impact Multipliers
... among intermediate inputs. Household demand functions permit substitution among commodities. Furthermore, imports may be substituted for domestic supplies in both intermediate use and in household consumption according to a system similar to that of Armington (1969). World prices for imports are giv ...
... among intermediate inputs. Household demand functions permit substitution among commodities. Furthermore, imports may be substituted for domestic supplies in both intermediate use and in household consumption according to a system similar to that of Armington (1969). World prices for imports are giv ...
Do Higher Wages Cause Inflation?
... A common view among economists is that higher wages lead to inflationary pressures; the argument is well articulated by Layard, Nickell and Jackman (1994): ”[...] when buoyant demand reduces unemployment (at least relative to recent experienced levels), inflationary pressure develops. Firms start bi ...
... A common view among economists is that higher wages lead to inflationary pressures; the argument is well articulated by Layard, Nickell and Jackman (1994): ”[...] when buoyant demand reduces unemployment (at least relative to recent experienced levels), inflationary pressure develops. Firms start bi ...
Dynamic Optimization Problems
... To construct these first-order conditions we used that E[h(xt )| It ] = h(xt ) when xt is an element of It and h(·) is a measurable function. Information set and state variables. Above we have been somewhat vague about the information set. In principle it could include current and lagged values, but ...
... To construct these first-order conditions we used that E[h(xt )| It ] = h(xt ) when xt is an element of It and h(·) is a measurable function. Information set and state variables. Above we have been somewhat vague about the information set. In principle it could include current and lagged values, but ...
Structure of the government accounts
... ownership or when economic value is created, transformed or extinguished. For example, debt repayment should be recorded when the debt expires, whether or not this coincides with an actual cash repayment. The recommendation to use accrual accounting for government financial statements was first made ...
... ownership or when economic value is created, transformed or extinguished. For example, debt repayment should be recorded when the debt expires, whether or not this coincides with an actual cash repayment. The recommendation to use accrual accounting for government financial statements was first made ...