PDF
... Proposition 1. In the free-market equilibrium, the welfare per capita, the amount of accumulated human capital, and the share of engineers in the population are below the socially desirable level if η ∈ (0,1) and α < 1 . Proof. The first part of the Proposition follows from a comparison of (15) and ...
... Proposition 1. In the free-market equilibrium, the welfare per capita, the amount of accumulated human capital, and the share of engineers in the population are below the socially desirable level if η ∈ (0,1) and α < 1 . Proof. The first part of the Proposition follows from a comparison of (15) and ...
3.5 Monopoly Power - New Prairie Press
... smaller, providing lower costs to consumers. There is a tradeoff for consumers who purchase goods from large firms: the cost is lower due to economies of scale, but the firm may have market power, which can result in higher prices. This tradeoff makes the economic analysis of large firms both fascin ...
... smaller, providing lower costs to consumers. There is a tradeoff for consumers who purchase goods from large firms: the cost is lower due to economies of scale, but the firm may have market power, which can result in higher prices. This tradeoff makes the economic analysis of large firms both fascin ...
Presentation Plus!
... Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 3 begins on page 150 of your textbook. ...
... Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 3 begins on page 150 of your textbook. ...
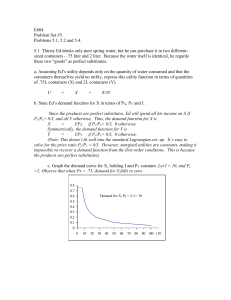
Overview Of Course - University of Texas at Dallas
... Average value of water is also greater. So what does price measure? ...
... Average value of water is also greater. So what does price measure? ...
PDF
... output of homogeneous commodities. Second, I present cite four empirical studies that verify that cartel behavior is associated with changes in transactions-price dispersion. Theory Stigler (1961) noted that significant price dispersion is typical of natural markets even for perfectly homogeneous go ...
... output of homogeneous commodities. Second, I present cite four empirical studies that verify that cartel behavior is associated with changes in transactions-price dispersion. Theory Stigler (1961) noted that significant price dispersion is typical of natural markets even for perfectly homogeneous go ...
expansion of fields of study
... demand for labour might different occupations do not change receive the same level of wage Suggest reasons why a firm may not be able to obtain the labour it requires Suggest factors which limit the total amount of labour available in the UK Understand the difference between wages and earnings Under ...
... demand for labour might different occupations do not change receive the same level of wage Suggest reasons why a firm may not be able to obtain the labour it requires Suggest factors which limit the total amount of labour available in the UK Understand the difference between wages and earnings Under ...
Rational-Choice Hermeneutics
... mental states. It should be noted, however, that these are not necessary differences; indeed, our whole purpose is to show that the distinctions can be overcome, and some analysts from both camps have already succeeded in doing so. Our purpose in this section is to describe how rational choice and ...
... mental states. It should be noted, however, that these are not necessary differences; indeed, our whole purpose is to show that the distinctions can be overcome, and some analysts from both camps have already succeeded in doing so. Our purpose in this section is to describe how rational choice and ...
ge11 Riezman 15002749 en
... sector a skilled worker needs to be matched with an entrepreneur. Initially, there are two type of agents, workers and entrepreneurs. Both populations are heterogeneous. Workers are distinguished by their potential ability as skilled workers and entrepreneurs by their potential ability to manage a ...
... sector a skilled worker needs to be matched with an entrepreneur. Initially, there are two type of agents, workers and entrepreneurs. Both populations are heterogeneous. Workers are distinguished by their potential ability as skilled workers and entrepreneurs by their potential ability to manage a ...
Chapter 1: PARADIGMS OF EXPLANATION
... narrowly economic to the broadly social. It also contains a distinct range of disagreement on what constitutes appropriate methodologies for the explanation of economic performance, however conceptualized and measured. That is a range that stretches from the isolation of discrete economic factors to ...
... narrowly economic to the broadly social. It also contains a distinct range of disagreement on what constitutes appropriate methodologies for the explanation of economic performance, however conceptualized and measured. That is a range that stretches from the isolation of discrete economic factors to ...
Social Provisioning, Embeddedness and Modeling the Economy
... production relations reinforce one another; it investigates the patterns of accumulation implicit in capitalist production; and it inquires into the relations connecting consumption, distribution and accumulation. The objectives are, first, to explain the rules that preserve the system’s viability, ...
... production relations reinforce one another; it investigates the patterns of accumulation implicit in capitalist production; and it inquires into the relations connecting consumption, distribution and accumulation. The objectives are, first, to explain the rules that preserve the system’s viability, ...
1 - people.vcu.edu
... Graphically, then, the demand curve would consist of a vertical line. At any price ratio where X was consumed, every increase or decrease in Px would have enough income added or subtracted to leave consumption at exactly the same point. The only change occurs when Px rises enough to cause a shift to ...
... Graphically, then, the demand curve would consist of a vertical line. At any price ratio where X was consumed, every increase or decrease in Px would have enough income added or subtracted to leave consumption at exactly the same point. The only change occurs when Px rises enough to cause a shift to ...
The Global Competitiveness Report 2014–2015: Country/Economy
... technical skills for companies are widely available and that skills match the needs of businesses. Germany’s economy could be more competitive if its labor markets were made even more efficient. In recent years, labor market efficiency has improved markedly, rising from the 53rd position in 2012 to ...
... technical skills for companies are widely available and that skills match the needs of businesses. Germany’s economy could be more competitive if its labor markets were made even more efficient. In recent years, labor market efficiency has improved markedly, rising from the 53rd position in 2012 to ...
Economics
... Unit 1: The behaviour of consumers and businesses Economics is a dynamic and constantly evolving field. As a social science, Economics is interested in the way humans behave and the decisions made to meet the needs and wants of society. In this unit students explore their role in the economy, how th ...
... Unit 1: The behaviour of consumers and businesses Economics is a dynamic and constantly evolving field. As a social science, Economics is interested in the way humans behave and the decisions made to meet the needs and wants of society. In this unit students explore their role in the economy, how th ...
Modeling the Economy as a Whole: An Integrative Approach
... service per se, neither is it a non-produced input with naturally given indestructible productive capabilities and talents that exist prior to production and externally to the structure of production as original factor input. Being producible within the structure of production, goods and services us ...
... service per se, neither is it a non-produced input with naturally given indestructible productive capabilities and talents that exist prior to production and externally to the structure of production as original factor input. Being producible within the structure of production, goods and services us ...
Sample
... Students are also interested in seeing what happens in the financial markets and to public opinion on the day a new GDP report comes out. 2. Market value: allows adding together unlike items by valuing them at their market prices a. Problem: misses nonmarket items such as homemaking, the value of en ...
... Students are also interested in seeing what happens in the financial markets and to public opinion on the day a new GDP report comes out. 2. Market value: allows adding together unlike items by valuing them at their market prices a. Problem: misses nonmarket items such as homemaking, the value of en ...
Document
... becomes nonbinding” to refer to the time point that the pre-shock condition is recovered. It is not correct to use this phrase to describe what is happening there. State-space and control constraints are used to restrict the movement of the respective variable above or below certain values at all ti ...
... becomes nonbinding” to refer to the time point that the pre-shock condition is recovered. It is not correct to use this phrase to describe what is happening there. State-space and control constraints are used to restrict the movement of the respective variable above or below certain values at all ti ...
Hibbard Presentation 2.17.12
... the 10 RGGI states together, and for each state participating in RGGI Across the region, the initial $0.9 billion in CO2 allowance auction proceeds translates to $1.6 billion in net economic value added ...
... the 10 RGGI states together, and for each state participating in RGGI Across the region, the initial $0.9 billion in CO2 allowance auction proceeds translates to $1.6 billion in net economic value added ...
Krugman_s Economics for AP
... too small for the number of students—some may be forced to sit on the floor or stand—despite the fact that a larger classroom nearby is empty during the same period. Economists would say that this is an inefficient use of resources because there is a way to make some people better off without making ...
... too small for the number of students—some may be forced to sit on the floor or stand—despite the fact that a larger classroom nearby is empty during the same period. Economists would say that this is an inefficient use of resources because there is a way to make some people better off without making ...
Investing in emerging markets: Evaluating the allure of
... overall U.S. economic productivity. As is well known, earnings growth is a fundamental building block when constructing estimates of expected stock returns. Hypothetically, if country A’s GDP is growing at 9% annually and country B’s is growing at 3% annually, isn’t it reasonable to expect the publi ...
... overall U.S. economic productivity. As is well known, earnings growth is a fundamental building block when constructing estimates of expected stock returns. Hypothetically, if country A’s GDP is growing at 9% annually and country B’s is growing at 3% annually, isn’t it reasonable to expect the publi ...
Negative Externalities
... Demand curve for firms in the market shifts downward to represent the net price of each unit sold. The net price, or Net Marginal Benefit (NMB), is the Marginal Benefit of consumers less the level of the sales tax (NMB = D - t*). Q*=Social Optimum output Pc*=Optimal Consumer price Ps*=Pc*-t=net prod ...
... Demand curve for firms in the market shifts downward to represent the net price of each unit sold. The net price, or Net Marginal Benefit (NMB), is the Marginal Benefit of consumers less the level of the sales tax (NMB = D - t*). Q*=Social Optimum output Pc*=Optimal Consumer price Ps*=Pc*-t=net prod ...
MICHAL KALECKI
... government, made up only of capitalists and workers, in which the latter spend all their wages, and where no unintended growth of inventories takes place. He then reaches the amazing conclusion encapsulated in the sentence popularized to sum up his theory of profits: when workers spend what they ear ...
... government, made up only of capitalists and workers, in which the latter spend all their wages, and where no unintended growth of inventories takes place. He then reaches the amazing conclusion encapsulated in the sentence popularized to sum up his theory of profits: when workers spend what they ear ...
Liquidity Premiums on Government Debt and the Fiscal Theory of
... of real future surpluses.1 Since the initial stock of nominal debt is given, for any …xed stream of surpluses, this theory argues that the price level must adjust to make the real value of the government debt satisfy the intertemporal government budget constraint. Furthermore, dynamic movements of t ...
... of real future surpluses.1 Since the initial stock of nominal debt is given, for any …xed stream of surpluses, this theory argues that the price level must adjust to make the real value of the government debt satisfy the intertemporal government budget constraint. Furthermore, dynamic movements of t ...
here - Heterodox Economics Newsletter
... instruments: that such instruments frequently only symbolize some underlying item of value without guaranteeing access to the item itself. The first two self-identified chapters of the book consider writing about money in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. The first chapter takes up the atte ...
... instruments: that such instruments frequently only symbolize some underlying item of value without guaranteeing access to the item itself. The first two self-identified chapters of the book consider writing about money in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. The first chapter takes up the atte ...