Preview Sample 1
... Explanation: B) Economics is the study of how a society uses its scarce resources to produce and distribute goods and services. Page Ref: 26 Difficulty: Easy Chapter LO: 1 Course LO: Compare and contrast different economic systems Classification: Concept 27) Microeconomics is the study of ________. ...
... Explanation: B) Economics is the study of how a society uses its scarce resources to produce and distribute goods and services. Page Ref: 26 Difficulty: Easy Chapter LO: 1 Course LO: Compare and contrast different economic systems Classification: Concept 27) Microeconomics is the study of ________. ...
E P conomic Statistics in apua New Guinea
... Standards/Classifications - SNA 1968 (2008 planned) - ISIC Rev. 3.1 (Rev. 4 planned) - COICOP - Plans to make BoP coherent with BPM6 ...
... Standards/Classifications - SNA 1968 (2008 planned) - ISIC Rev. 3.1 (Rev. 4 planned) - COICOP - Plans to make BoP coherent with BPM6 ...
Post Walrasian Macroeconomics and IS/LM Analysis
... planning horizons and dealing with such changes. (Others may be thinking about even more substantial changes—for example, using DNA computing, which involves a totally different type of information processing than that used by existing computers. For them, the long run would include switching from t ...
... planning horizons and dealing with such changes. (Others may be thinking about even more substantial changes—for example, using DNA computing, which involves a totally different type of information processing than that used by existing computers. For them, the long run would include switching from t ...
Russia: RenCap-NES Macro Monitor
... of cutting rates; and choose not to delve into the details here, as they are well-known and have been discussed ad nauseam over the past half-year or so. Suffice it to say that the key debate here has evolved around the differing monetary policy implications of the fact that the Russian economy has ...
... of cutting rates; and choose not to delve into the details here, as they are well-known and have been discussed ad nauseam over the past half-year or so. Suffice it to say that the key debate here has evolved around the differing monetary policy implications of the fact that the Russian economy has ...
Chapter 15: Explanations of Business Investment Spending
... Each of these automobiles is expected to sell for a certain price, say $20,000. The production of these automobiles will require a certain amount of raw materials (for example, steel) and a certain amount of parts (for example, tires). General Motors would need to estimate the costs of these items. ...
... Each of these automobiles is expected to sell for a certain price, say $20,000. The production of these automobiles will require a certain amount of raw materials (for example, steel) and a certain amount of parts (for example, tires). General Motors would need to estimate the costs of these items. ...
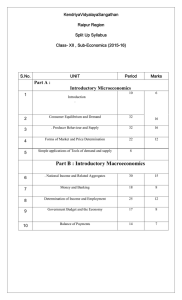
- Kendriya Vidyalaya No. 2 Raipur
... creates employment for large amount of labour also goods produced are cheap. But the quality & quantity of goods produced is less. 16-CAPITAL INTENSIVE TECHNIQUE:- Under this technique, capital is used more than labour. 17. production possibility frontier:- It is a boundary line which shows that max ...
... creates employment for large amount of labour also goods produced are cheap. But the quality & quantity of goods produced is less. 16-CAPITAL INTENSIVE TECHNIQUE:- Under this technique, capital is used more than labour. 17. production possibility frontier:- It is a boundary line which shows that max ...
chapter 4 class
... – Law of diminishing marginal utility marginal benefit of each additional unit declines as each unit is used ...
... – Law of diminishing marginal utility marginal benefit of each additional unit declines as each unit is used ...
Transportation and Development: Insights from the U.S. 1840–1860
... us to be skeptical about the potential of cross–country differences in transportation costs for accounting for the observed cross–country disparities in real GDP per capita. The intuition for the first effects comes from international trade theory. The principle of comparative advantage implies tha ...
... us to be skeptical about the potential of cross–country differences in transportation costs for accounting for the observed cross–country disparities in real GDP per capita. The intuition for the first effects comes from international trade theory. The principle of comparative advantage implies tha ...
A Primer on Economics: `X` Marks the Spot
... calculus are relevant. First it is assumed consumers and producers have perfect knowledge. This has profound implications for any knowledge-based economy which I will not explore at this time. Second, it is assumed human beings practice calculatory rationalism, i.e., they are constantly calculating ...
... calculus are relevant. First it is assumed consumers and producers have perfect knowledge. This has profound implications for any knowledge-based economy which I will not explore at this time. Second, it is assumed human beings practice calculatory rationalism, i.e., they are constantly calculating ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES CAPITAL DEEPENING AND NON-BALANCED ECONOMIC GROWTH Daron Acemoglu
... the demand-side reasons for non-balanced growth; the marginal rate of substitution between different goods changes as an economy grows, directly leading to a pattern of uneven growth between sectors. An alternative thesis, first proposed by Baumol (1967), emphasizes the potential non-balanced nature ...
... the demand-side reasons for non-balanced growth; the marginal rate of substitution between different goods changes as an economy grows, directly leading to a pattern of uneven growth between sectors. An alternative thesis, first proposed by Baumol (1967), emphasizes the potential non-balanced nature ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES CAN IT BE JAPAN’S SAVIOR Fumio Hayashi Koji Nomura
... Each sector utilizes many different capital assets. At the most detailed level of asset classification, the real capital stock and capital services are identical. However, when assets are aggregated into broader classes, the two are not the same, as first pointed out by Jorgenson and Griliches (1967 ...
... Each sector utilizes many different capital assets. At the most detailed level of asset classification, the real capital stock and capital services are identical. However, when assets are aggregated into broader classes, the two are not the same, as first pointed out by Jorgenson and Griliches (1967 ...
Housing markets and the economy: the assessment
... China, and India are quite different from Anglo economies in the role of housing. Section V discusses these issues and summarizes recent evidence on the size of the housing collateral effect and how it may have shifted with credit-market liberalization. The significance of credit markets and the pot ...
... China, and India are quite different from Anglo economies in the role of housing. Section V discusses these issues and summarizes recent evidence on the size of the housing collateral effect and how it may have shifted with credit-market liberalization. The significance of credit markets and the pot ...
Overborrowing and Systemic Externalities in the Business Cycle ∗
... by which declines in consumption, the real exchange rate, and access to foreign financing mutually reinforce one another, as in Mendoza’s work. In the model, private agents form rational expectations about the evolution of macroeconomic variables—in particular the real exchange rate—and correctly pe ...
... by which declines in consumption, the real exchange rate, and access to foreign financing mutually reinforce one another, as in Mendoza’s work. In the model, private agents form rational expectations about the evolution of macroeconomic variables—in particular the real exchange rate—and correctly pe ...
Chapter 14
... • Keynesian Sticky-Wage Theory: “The higher product prices cause a temporary decrease in real wages stimulating employment and output.” • Nominal wages are slow to adjust, or are “sticky” in the short-run, thus a higher price level makes employment and production more profitable, which induces firms ...
... • Keynesian Sticky-Wage Theory: “The higher product prices cause a temporary decrease in real wages stimulating employment and output.” • Nominal wages are slow to adjust, or are “sticky” in the short-run, thus a higher price level makes employment and production more profitable, which induces firms ...
FINANCIAL INTERMEDIATION AND REGIME SWITCHING IN
... orbit. Asymmetric cycles with m > n (expansions are longer and shallower than contractions) are found to exist if the "floor" of the economy is tighter than its "ceiling". What happens when these fluctuations occur? When the economy transits from an expansion phase to a contraction phase, resources ...
... orbit. Asymmetric cycles with m > n (expansions are longer and shallower than contractions) are found to exist if the "floor" of the economy is tighter than its "ceiling". What happens when these fluctuations occur? When the economy transits from an expansion phase to a contraction phase, resources ...
paper i - Madhya Pradesh Bhoj Open University
... of the people get satisfied and as such when income increases they save more than what they spend. This law may be considered as a rough indication of the actual macro behaviour of consumers in the short run. This is the fundamental principle upon which the Keynesian consumption function is based. I ...
... of the people get satisfied and as such when income increases they save more than what they spend. This law may be considered as a rough indication of the actual macro behaviour of consumers in the short run. This is the fundamental principle upon which the Keynesian consumption function is based. I ...
2A: ECONOMICS – MARKETS
... Students use economic information and data to communicate an understanding of economic events, issues and decisions. In achieving this outcome, students: locate, select and organise economic information and data; analyse and interpret economic information and data; and use economic terms, conc ...
... Students use economic information and data to communicate an understanding of economic events, issues and decisions. In achieving this outcome, students: locate, select and organise economic information and data; analyse and interpret economic information and data; and use economic terms, conc ...
E G conomic Statistics in uam
... ▪ Statistical law protects confidentiality and independence of statistical information ▪ Decentralized statistical system ○ Responsibilities are clearly defined for agencies involved in the production of the Core Set ○ No plans are currently being implemented to improve coordination of production of ...
... ▪ Statistical law protects confidentiality and independence of statistical information ▪ Decentralized statistical system ○ Responsibilities are clearly defined for agencies involved in the production of the Core Set ○ No plans are currently being implemented to improve coordination of production of ...
Sustainable Development: Between Moral Injunctions and Natural
... criterion in a growth model with exhaustible resources leads to null growth. For as long as growth remains positive, it is indeed always possible to increase the utility of the least favored generation (the first) by reducing its savings ratio, and an equilibrium is only achieved when this savings r ...
... criterion in a growth model with exhaustible resources leads to null growth. For as long as growth remains positive, it is indeed always possible to increase the utility of the least favored generation (the first) by reducing its savings ratio, and an equilibrium is only achieved when this savings r ...
Medium Term Business Cycles in Developing Countries
... very signi…cantly during this period, making the mechanisms emphasized by our model more relevant than before. Second, after 1990, FDI became the most signi…cant source of capital ‡ows from developed to developing economies, making our model’s assumptions about the nature of international capital ‡o ...
... very signi…cantly during this period, making the mechanisms emphasized by our model more relevant than before. Second, after 1990, FDI became the most signi…cant source of capital ‡ows from developed to developing economies, making our model’s assumptions about the nature of international capital ‡o ...
Economic Growth with Bubbles
... increase enough, bubbly episodes expand the capital stock and output. This turns out to be the case under a wide range of parameter values.10 To understand these effects of bubbly episodes, it is useful to analyze the set of transfers that bubbles implement. Remember that a bubble is nothing but a p ...
... increase enough, bubbly episodes expand the capital stock and output. This turns out to be the case under a wide range of parameter values.10 To understand these effects of bubbly episodes, it is useful to analyze the set of transfers that bubbles implement. Remember that a bubble is nothing but a p ...
Econ 809 Macro Jan 6, 2011 Page 1 of 54 Basic Review of Growth
... ), then there is no way to compare different consumption streams. ¾ The assumption we have made guarantee that is bounded. This is because is bounded, which follows from the fact that is bounded: Assume that . Then resource constraint is ...
... ), then there is no way to compare different consumption streams. ¾ The assumption we have made guarantee that is bounded. This is because is bounded, which follows from the fact that is bounded: Assume that . Then resource constraint is ...
Post Capitalist Society
... capital investment. Yet both were plentiful in the first hundred years of the capitalist age, before 1880, as they have been since. With respect to technology or to capital, the second hundred years differed very little from the first one hundred. But there was absolutely no increase in worker produ ...
... capital investment. Yet both were plentiful in the first hundred years of the capitalist age, before 1880, as they have been since. With respect to technology or to capital, the second hundred years differed very little from the first one hundred. But there was absolutely no increase in worker produ ...