Problem Areas in AP Economics Real Interest rate
... Real Interest rate – cost of borrowing the money to buy the capital goods (machinery) If rate of return is greater than the cost of the interest, the investment will be profitable Ex: 10% rate of return is greater than 7% interest = profitable decision Even if capital is financed by savings, it give ...
... Real Interest rate – cost of borrowing the money to buy the capital goods (machinery) If rate of return is greater than the cost of the interest, the investment will be profitable Ex: 10% rate of return is greater than 7% interest = profitable decision Even if capital is financed by savings, it give ...
Urban Geography - Loyola Blakefield
... • Economy: The production and exchange of goods and services among a group of people. Stuff and $!!! • Economic System: How people produce and goods and services. How do we get stuff and $!!! ...
... • Economy: The production and exchange of goods and services among a group of people. Stuff and $!!! • Economic System: How people produce and goods and services. How do we get stuff and $!!! ...
market economy - Public Schools of Robeson County
... World Trade Organization Exchange Rate ...
... World Trade Organization Exchange Rate ...
Chapter 2-1 Notes
... Because economic resources are limited, a country must answer three key economic questions: 1) What goods to produce? 2) How should these goods be produced? 3) Who consumes the goods? In answering these questions, societies must consider their economic goals, such as: economic freedom, economic effi ...
... Because economic resources are limited, a country must answer three key economic questions: 1) What goods to produce? 2) How should these goods be produced? 3) Who consumes the goods? In answering these questions, societies must consider their economic goals, such as: economic freedom, economic effi ...
The Factors of Production - Danville
... • This category includes all people except for entrepreneurs. • Unlike land, labor is a resource that may vary in size over time. ...
... • This category includes all people except for entrepreneurs. • Unlike land, labor is a resource that may vary in size over time. ...
Scarcity
... The fundamental economic problem facing all societies is Scarcity. Scarcity is the condition that results in society not having enough resources to produce all the things people would like to have. Even goods and services are scarce, because the resources we need to produce them are scarce ...
... The fundamental economic problem facing all societies is Scarcity. Scarcity is the condition that results in society not having enough resources to produce all the things people would like to have. Even goods and services are scarce, because the resources we need to produce them are scarce ...
Economic Ups and Downs
... Contraction-During this stage business activity slows down. IF this stage last to long the economy could head into a recession. Trough—this is the lowest point in the cycle, where business activity levels off. Expansion—The economy begins to recover. People spend more money. Peak-This period of pros ...
... Contraction-During this stage business activity slows down. IF this stage last to long the economy could head into a recession. Trough—this is the lowest point in the cycle, where business activity levels off. Expansion—The economy begins to recover. People spend more money. Peak-This period of pros ...
Economic Systems - mshsAmandaHanshew
... • Traditional Economy – Traditions and rituals answer the basic questions. Answers are often based on cultural or religious practices and ideals that have been passed down for generations. • Market Economy – In a pure market economy there is no government involvement in economic decisions. • Command ...
... • Traditional Economy – Traditions and rituals answer the basic questions. Answers are often based on cultural or religious practices and ideals that have been passed down for generations. • Market Economy – In a pure market economy there is no government involvement in economic decisions. • Command ...
the_return_to_the_market.14
... The peculiar character of the problem of a rational economic order is determined precisely by the fact that the knowledge of the circumstances of which we must make use never exists in concentrated or integrated form, but solely as the dispersed bits of incomplete and frequently contradictory knowle ...
... The peculiar character of the problem of a rational economic order is determined precisely by the fact that the knowledge of the circumstances of which we must make use never exists in concentrated or integrated form, but solely as the dispersed bits of incomplete and frequently contradictory knowle ...
A SUMMARY OF THE HISTORY OF ECONOMIC THEORIES Mgt. 704
... John Maynard Keynes was a reaction to the apparent failure of economics to explain the Great Depression. • He created the field of macroeconomics by viewing the economy in terms of aggregates rather than as a sum of markets. – Prices could be sticky so that aggregate demand determined aggregate supp ...
... John Maynard Keynes was a reaction to the apparent failure of economics to explain the Great Depression. • He created the field of macroeconomics by viewing the economy in terms of aggregates rather than as a sum of markets. – Prices could be sticky so that aggregate demand determined aggregate supp ...
Summary: The United States Economy
... GDP (gross domestic product). This tells the total value of the goods and services that a country produces. The U.S. economy is one of the world’s wealthiest. The U.S. government does not set prices, tell businesses what to produce, or tell people where to work. These are qualities of a free enterpr ...
... GDP (gross domestic product). This tells the total value of the goods and services that a country produces. The U.S. economy is one of the world’s wealthiest. The U.S. government does not set prices, tell businesses what to produce, or tell people where to work. These are qualities of a free enterpr ...
Economics Unit 1 PPT
... be seemingly unlimited and competing wants through the careful use of relatively scare resources ...
... be seemingly unlimited and competing wants through the careful use of relatively scare resources ...
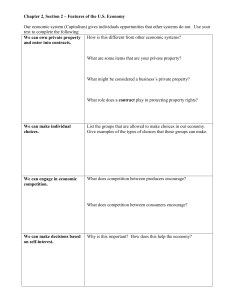
Chapter 2, Section 2 – Features of the U
... the chart: 1. Government (the regulators); 2. Business (producers); 3. Households (consumers). Let’s take a look at how it operates. ...
... the chart: 1. Government (the regulators); 2. Business (producers); 3. Households (consumers). Let’s take a look at how it operates. ...
EconPol.ppt
... Private property - people can obtain, control, use, and dispose of the property resources they own [subject to only minimal governmentimposed limitations] Freedom of enterprise and freedom of choice exist - individuals can become entrepreneurs; consumers can buy what they want [a.k.a., consumer sove ...
... Private property - people can obtain, control, use, and dispose of the property resources they own [subject to only minimal governmentimposed limitations] Freedom of enterprise and freedom of choice exist - individuals can become entrepreneurs; consumers can buy what they want [a.k.a., consumer sove ...
The Nature and Methods of Economics
... Social science concerned with how people satisfy unlimited wants w/ limited resources. ...
... Social science concerned with how people satisfy unlimited wants w/ limited resources. ...
Why government intervention in economy is necessary
... nism would either produce the wrong that there is soberness among the vari amounts of certain goods and services ous players in the industry thus mini or fail to allocate sufficient resources for mising conflicts. One major objective of the govern the production of certain other goods. This is us ...
... nism would either produce the wrong that there is soberness among the vari amounts of certain goods and services ous players in the industry thus mini or fail to allocate sufficient resources for mising conflicts. One major objective of the govern the production of certain other goods. This is us ...
GHSGT_Review_-_Economics
... unlimited wants exceed limited productive resources Trade-offs – alternatives that must be given up when one choice is made over another Opportunity cost – the next best alternative given up when individuals, businesses and governments confront scarcity by making choices ...
... unlimited wants exceed limited productive resources Trade-offs – alternatives that must be given up when one choice is made over another Opportunity cost – the next best alternative given up when individuals, businesses and governments confront scarcity by making choices ...
China
... Demography (internal migration) History Socialism (the appeal of socialist industrialization for developmental catch-up) Maoism (cult of personality and the emphasis on mass fervor and non-material incentives) ...
... Demography (internal migration) History Socialism (the appeal of socialist industrialization for developmental catch-up) Maoism (cult of personality and the emphasis on mass fervor and non-material incentives) ...
Slide 1
... • Individuals are free to do whatever they want as long as it is legal • Fluctuations in prices play a central role in coordinating individuals’ wants in a market economy Most economists believe the market is a good way to coordinate economic activity ...
... • Individuals are free to do whatever they want as long as it is legal • Fluctuations in prices play a central role in coordinating individuals’ wants in a market economy Most economists believe the market is a good way to coordinate economic activity ...
What Now, President-Elect Obama
... may complete the round of fiscal stimulus packages to support output and employment. The budget deficit for 2009 will easily exceed one trillion U.S. dollars. Then, they should implement a health care plan for the poor, grant tax relief to the middle-class and invest in projects for energy reliance. ...
... may complete the round of fiscal stimulus packages to support output and employment. The budget deficit for 2009 will easily exceed one trillion U.S. dollars. Then, they should implement a health care plan for the poor, grant tax relief to the middle-class and invest in projects for energy reliance. ...