Chapter 1: The nature of real estate (RE) and RE markets
... Land may include (a) the surface of the earth, (b) rights to air space above the land up to a certain height, (c) rights to the subsurface down to the center of the earth and to the minerals contained therein, and (d) the improvements to the land, e.g., walkways and water drainage systems. The impro ...
... Land may include (a) the surface of the earth, (b) rights to air space above the land up to a certain height, (c) rights to the subsurface down to the center of the earth and to the minerals contained therein, and (d) the improvements to the land, e.g., walkways and water drainage systems. The impro ...
Writing Assignment #1 - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... produce and what price to set for these goods. The desire to reap the highest possible profit requires businesses to sell as many goods as possible for the lowest possible cost to themselves. Businesses reinvest some of their profits to improve their goods or to create new ones. They also compete wi ...
... produce and what price to set for these goods. The desire to reap the highest possible profit requires businesses to sell as many goods as possible for the lowest possible cost to themselves. Businesses reinvest some of their profits to improve their goods or to create new ones. They also compete wi ...
Latin American Economies: Brazil and Cuba Let`s Review Do you
... a. People who provide the money to start and operate a business are called entrepreneurs i. These people risk their own money and time because they believe their business ideas will make a profit. b. Entrepreneurs must organize their businesses well for them to be successful. i. They bring together ...
... a. People who provide the money to start and operate a business are called entrepreneurs i. These people risk their own money and time because they believe their business ideas will make a profit. b. Entrepreneurs must organize their businesses well for them to be successful. i. They bring together ...
Lecture 7 Ecological & Environmental Economics
... - Are equal to expenses on the elimination of a problem. ...
... - Are equal to expenses on the elimination of a problem. ...
Folie 1
... Minsky, Hyman P. (1977), The Financial Instability Hypothesis: an Interpretation of Keynes and Alternative to “Standard” Theory, Nebraska Journal of Economics and Business, Vol. 16, No 1, pp. 5-16. ...
... Minsky, Hyman P. (1977), The Financial Instability Hypothesis: an Interpretation of Keynes and Alternative to “Standard” Theory, Nebraska Journal of Economics and Business, Vol. 16, No 1, pp. 5-16. ...
International Business
... environments of those countries in which it operates, as well as those of countries in which it does not, in order to predict how trends and events the world over will likely affect firm performance. ...
... environments of those countries in which it operates, as well as those of countries in which it does not, in order to predict how trends and events the world over will likely affect firm performance. ...
The End of the Classical Dichotomy
... which have been useful in analyzing the long term effects of economic policies and economic events on the employment, capital accumulation, production, terms of trade, inflation and the exchange rate. The primary assumption that we have made is that nominal prices, the prices of goods in terms of cu ...
... which have been useful in analyzing the long term effects of economic policies and economic events on the employment, capital accumulation, production, terms of trade, inflation and the exchange rate. The primary assumption that we have made is that nominal prices, the prices of goods in terms of cu ...
EOCT – What I know, you need to know!
... • Individuals, Businesses & Societies cannot satisfy all their needs & wants. • Result is specialization: to maximize ...
... • Individuals, Businesses & Societies cannot satisfy all their needs & wants. • Result is specialization: to maximize ...
Examen AIO Juni 2008
... emergence of the new downstream firm beneficial or harmful to consumers? Explain why. c2) Would you allow a merger between U1 and D1 from the consumers’ perspective? 5) A SSNIP-test on the cigarette market shows that because a 5% price raise isn’t profitable the market definition should be wider. ...
... emergence of the new downstream firm beneficial or harmful to consumers? Explain why. c2) Would you allow a merger between U1 and D1 from the consumers’ perspective? 5) A SSNIP-test on the cigarette market shows that because a 5% price raise isn’t profitable the market definition should be wider. ...
Economic Systems Notes
... HOW TO PRODUCE? (What productive resources are used to produce goods and services?) FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE? (Who gets to have the goods and services? The way a society answers these questions determines its economic system. ...
... HOW TO PRODUCE? (What productive resources are used to produce goods and services?) FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE? (Who gets to have the goods and services? The way a society answers these questions determines its economic system. ...
Brazil Cuba Economies classroom
... property needed by businesses to operate. • If a business is to be successful, it cannot let its equipment break down or have its buildings fall apart. • New technology can help a business produce more goods for a ...
... property needed by businesses to operate. • If a business is to be successful, it cannot let its equipment break down or have its buildings fall apart. • New technology can help a business produce more goods for a ...
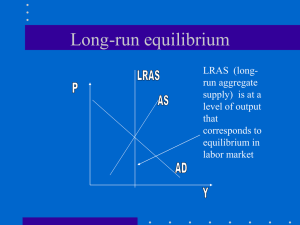
Long-run equilibrium
... market) • This means that AD and AS intersect LRAS and that the economy is operating at its potential level of RGDP (Real GDP). • Imagine now that the something happens to decrease AD. ...
... market) • This means that AD and AS intersect LRAS and that the economy is operating at its potential level of RGDP (Real GDP). • Imagine now that the something happens to decrease AD. ...
Chapter Test A What is Economics
... In the Answers column indicate which economic system is best described by each statement. ...
... In the Answers column indicate which economic system is best described by each statement. ...
What Economic Structure for Socialism?
... on market forces, the working of a market economy will eventually purge the society of any socialist features. These two problems will be considered in turn, although we will have to consider the first problem more briefly than the second due to space constraints. A competitive market system is supp ...
... on market forces, the working of a market economy will eventually purge the society of any socialist features. These two problems will be considered in turn, although we will have to consider the first problem more briefly than the second due to space constraints. A competitive market system is supp ...
Business and Economics
... In most countries, there is something called a poverty line. It is used to measure the extent to which people in the country live in poverty. In Britain, a couple with two children aged between 5-14 needs £346 per week in order to not fall below the poverty line. In the UK, the existence of the welf ...
... In most countries, there is something called a poverty line. It is used to measure the extent to which people in the country live in poverty. In Britain, a couple with two children aged between 5-14 needs £346 per week in order to not fall below the poverty line. In the UK, the existence of the welf ...
Tugan-Baranovsky, Mikhail Ivanovich (1865–1919)
... theories, and pointing out that ‘the process of production creates its own market’, especially for producers’ goods, he went on to stress that the simple model derived from J.-B. Say assumes that ‘that entrepreneur, before beginning production, has a wholly correct and accurate knowledge of the requ ...
... theories, and pointing out that ‘the process of production creates its own market’, especially for producers’ goods, he went on to stress that the simple model derived from J.-B. Say assumes that ‘that entrepreneur, before beginning production, has a wholly correct and accurate knowledge of the requ ...
Chapter 14 Economic Theories
... • Market success assumes that consumers can maximize their benefits and suppliers can maximize their profits under existing conditions. • In failed markets, competition is flawed, consumers and producers do not make optimal choices, and resources are not used optimally. • Allocation and cost control ...
... • Market success assumes that consumers can maximize their benefits and suppliers can maximize their profits under existing conditions. • In failed markets, competition is flawed, consumers and producers do not make optimal choices, and resources are not used optimally. • Allocation and cost control ...
Name:
... Answer: The dollar value of final goods includes the dollar value of intermediate goods. If intermediate goods were counted, then multiple counting would occur. The value of steel (intermediate good) used in autos is included in the price of the auto (the final product). This value is not included i ...
... Answer: The dollar value of final goods includes the dollar value of intermediate goods. If intermediate goods were counted, then multiple counting would occur. The value of steel (intermediate good) used in autos is included in the price of the auto (the final product). This value is not included i ...