Document
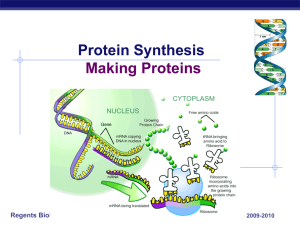
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
ch_42 gas exchange - Valhalla High School
... O2 & CO2 diffuse much faster through air respiratory surfaces exposed to air do not have to be ventilated as thoroughly as gills ...
... O2 & CO2 diffuse much faster through air respiratory surfaces exposed to air do not have to be ventilated as thoroughly as gills ...
Understanding the Food Chain and Natural Selection
... generations of a population of reproducing organisms. At the same time, unfavorable heritable traits become less common. Natural selection leads to evolutionary change. Some individuals have certain characteristics that give them a greater survival or reproductive rate than other individuals in a po ...
... generations of a population of reproducing organisms. At the same time, unfavorable heritable traits become less common. Natural selection leads to evolutionary change. Some individuals have certain characteristics that give them a greater survival or reproductive rate than other individuals in a po ...
goal 4 answers
... 4.05 Analyze the broad patterns of animal behavior as adaptations to the environment. 50. What is a stimulus? What is a response? (Page 871) any kind of signal that carries information and can be detected. Response – a reaction to a stimulus 51. Why is it important that organisms are able to respond ...
... 4.05 Analyze the broad patterns of animal behavior as adaptations to the environment. 50. What is a stimulus? What is a response? (Page 871) any kind of signal that carries information and can be detected. Response – a reaction to a stimulus 51. Why is it important that organisms are able to respond ...
Biology Spring Review
... 11. Why do viruses need a host cell? ___________________________ 12. Is a virus alive? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Why are viruses considered parasites? _________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 11. Why do viruses need a host cell? ___________________________ 12. Is a virus alive? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Why are viruses considered parasites? _________________________________________________________________________ ...
from a few genes lifes myriad shapes
... Scott F. Gilbert, a developmental biologist at Swarthmore College. By looking at what sorts of organisms are most likely or impossible to develop, he explained, “evo-devo looks at the arrival of the fittest.” Charles Darwin saw it first. He pointed out well over a century ago that developing forms o ...
... Scott F. Gilbert, a developmental biologist at Swarthmore College. By looking at what sorts of organisms are most likely or impossible to develop, he explained, “evo-devo looks at the arrival of the fittest.” Charles Darwin saw it first. He pointed out well over a century ago that developing forms o ...
Biol 2107K January 2015 (PRINCIPLES OF BIOLOGY I) Syllabus
... The primary goals of the two sequence of courses (BIOL 2107K / BIOL 2108 are to provide you with a foundation in biology so you'll be prepared to pursue further studies in science and to prepare you to function as a scientifically literate citizen within our society. We also hope that you become exc ...
... The primary goals of the two sequence of courses (BIOL 2107K / BIOL 2108 are to provide you with a foundation in biology so you'll be prepared to pursue further studies in science and to prepare you to function as a scientifically literate citizen within our society. We also hope that you become exc ...
MCAS Biology Review Packet Answer Key
... Double helix means 2 strands of nucleotides attached by hydrogen bonds in the middle and twisted together. 5. What is the base-pairing rule? Adenine hydrogen bonds with Thymine Guanine hydrogen bonds with Cytosine 6. What is the relationship between gene and DNA? Genes are sections of DNA that code ...
... Double helix means 2 strands of nucleotides attached by hydrogen bonds in the middle and twisted together. 5. What is the base-pairing rule? Adenine hydrogen bonds with Thymine Guanine hydrogen bonds with Cytosine 6. What is the relationship between gene and DNA? Genes are sections of DNA that code ...
The CNRS FRE 2846 (Plant Cellular and Molecular Physiology
... The CNRS-UPMC FRE 2846 Research Unit (Plant Cellular and Molecular Physiology Laboratory; http://pcmp.snv.jussieu.fr/) located at University Pierre et Marie Curie (University Paris 6) in Ivry-sur-Seine until 2007 (and on the Jussieu campus in Paris afterwards) wishes to host an ATIP team in 2006. A ...
... The CNRS-UPMC FRE 2846 Research Unit (Plant Cellular and Molecular Physiology Laboratory; http://pcmp.snv.jussieu.fr/) located at University Pierre et Marie Curie (University Paris 6) in Ivry-sur-Seine until 2007 (and on the Jussieu campus in Paris afterwards) wishes to host an ATIP team in 2006. A ...
June 26, 2007 - Esperanza High School
... rabbits and mice, among others, making them prime candidates for evolution via BMP4. “This is just the beginning,” Dr. Grant said. “These are exciting times for us all.” Used to lay out body plans, build beaks and alter fish jaws, BMP4 illustrates perfectly one of the major recurring themes of evo-d ...
... rabbits and mice, among others, making them prime candidates for evolution via BMP4. “This is just the beginning,” Dr. Grant said. “These are exciting times for us all.” Used to lay out body plans, build beaks and alter fish jaws, BMP4 illustrates perfectly one of the major recurring themes of evo-d ...
Chapter 42.
... O2 & CO2 diffuse much faster through air respiratory surfaces exposed to air do not have to be ventilated as thoroughly as gills ...
... O2 & CO2 diffuse much faster through air respiratory surfaces exposed to air do not have to be ventilated as thoroughly as gills ...
Kit of Parts - facilitator guide
... research to help solve these problems in the real world. This information can also be found on the back of each card. Synthetic biologists are currently working on all of these challenges. Next, let the visitor choose to try to solve one or more additional challenges. When they choose to use the sam ...
... research to help solve these problems in the real world. This information can also be found on the back of each card. Synthetic biologists are currently working on all of these challenges. Next, let the visitor choose to try to solve one or more additional challenges. When they choose to use the sam ...
Stage 3
... Lamarck’s Theory of Acquired Inheritance (early 1800s) • Jean Baptiste Lamarck • Observed fossil records and the current diversity of life • Suggested that organisms evolved by the process of adaptation • Traits gained during a lifetime could then be passed on to the next generation ...
... Lamarck’s Theory of Acquired Inheritance (early 1800s) • Jean Baptiste Lamarck • Observed fossil records and the current diversity of life • Suggested that organisms evolved by the process of adaptation • Traits gained during a lifetime could then be passed on to the next generation ...
TAKS - charleszaremba.com
... outside of a formal laboratory situation. They should include field trips in and around the campus and should closely simulate real time situations. Field work is no different than lab work in that certain safety and ethical practices must be applied. The students must understand that there are cert ...
... outside of a formal laboratory situation. They should include field trips in and around the campus and should closely simulate real time situations. Field work is no different than lab work in that certain safety and ethical practices must be applied. The students must understand that there are cert ...
Jolene Cogbill - BI205 - Chaminade University`s syllabus repository
... asked to leave class. ADA Accomodations: Students with special needs who meet criteria for the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provisions must provide written documentation of the need for accommodations from CUH Couseling Center (Dr. June Yasuhara, 735-4845) by the end of the third week of ...
... asked to leave class. ADA Accomodations: Students with special needs who meet criteria for the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provisions must provide written documentation of the need for accommodations from CUH Couseling Center (Dr. June Yasuhara, 735-4845) by the end of the third week of ...
File
... Scientist classify similar organisms in one group, and an organism that is very different from other known organisms is placed in a new. 2) Describe one advantage of having a classification system: A classification system makes it easier to communicate clearly because each organism has only one name ...
... Scientist classify similar organisms in one group, and an organism that is very different from other known organisms is placed in a new. 2) Describe one advantage of having a classification system: A classification system makes it easier to communicate clearly because each organism has only one name ...
Characteristics of Life Notes
... Autotrophs- make their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants. Chemoautotrophs- make their own food through chemicals / chemosynthesis. Heterotrophs- rely on others for food. Where do we get our energy from? i. Indirectly from photosynthesis and directly from cellular respiration, i ...
... Autotrophs- make their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants. Chemoautotrophs- make their own food through chemicals / chemosynthesis. Heterotrophs- rely on others for food. Where do we get our energy from? i. Indirectly from photosynthesis and directly from cellular respiration, i ...
Biology Review
... G. I am the scientists who erroneously came up with the idea that traits are acquired from animals from their use or disuse. H. I disproved the idea of spontaneous generation by using covered and uncovered jars of rotting meat. I. I am a researcher & primatologist studying African apes. J. I was fir ...
... G. I am the scientists who erroneously came up with the idea that traits are acquired from animals from their use or disuse. H. I disproved the idea of spontaneous generation by using covered and uncovered jars of rotting meat. I. I am a researcher & primatologist studying African apes. J. I was fir ...
Leaving Certificate Revision Notes Higher and Ordinary
... If it happens to contain correct information you forgot to put into your answer you will be awarded marks for it. Extra Questions Answer all required questions Read over your answers and check that they make sense [you would be amazed at the nonsense that can be written under exam pressure] ...
... If it happens to contain correct information you forgot to put into your answer you will be awarded marks for it. Extra Questions Answer all required questions Read over your answers and check that they make sense [you would be amazed at the nonsense that can be written under exam pressure] ...
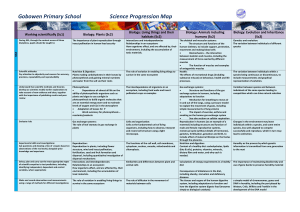
File - Gobowen Primary School
... cycle of flowering plants, including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal. ...
... cycle of flowering plants, including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal. ...
MCAS 2010 February Biology Released ITems
... The purpose of this document is to share with educators and the public all of the test items from the February 2010 MCAS Biology test on which student results are based. Local educators will be able to use this information to identify strengths and weaknesses in their curriculum and instruction, and ...
... The purpose of this document is to share with educators and the public all of the test items from the February 2010 MCAS Biology test on which student results are based. Local educators will be able to use this information to identify strengths and weaknesses in their curriculum and instruction, and ...
Living Things are Highly Organized
... Group of tissues that work together to perform closely related functions ...
... Group of tissues that work together to perform closely related functions ...
Biology EOC Review Packet
... 62. What is a transgenic organism? Explain how transgenic plants, animals and bacteria can be useful in both agriculture and the pharmaceutical industry. 63. What are some ethical issues associated with the study of genomics and biotechnology (like stem cell research and genetically modified organis ...
... 62. What is a transgenic organism? Explain how transgenic plants, animals and bacteria can be useful in both agriculture and the pharmaceutical industry. 63. What are some ethical issues associated with the study of genomics and biotechnology (like stem cell research and genetically modified organis ...
Biology EOC Review Packet
... 62. What is a transgenic organism? Explain how transgenic plants, animals and bacteria can be useful in both agriculture and the pharmaceutical industry. 63. What are some ethical issues associated with the study of genomics and biotechnology (like stem cell research and genetically modified organis ...
... 62. What is a transgenic organism? Explain how transgenic plants, animals and bacteria can be useful in both agriculture and the pharmaceutical industry. 63. What are some ethical issues associated with the study of genomics and biotechnology (like stem cell research and genetically modified organis ...
History of biology

The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to ayurveda, ancient Egyptian medicine and the works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world. This ancient work was further developed in the Middle Ages by Muslim physicians and scholars such as Avicenna. During the European Renaissance and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius and Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. The growing importance of natural theology, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (although it entrenched the argument from design).Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany and zoology became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics by Thomas Hunt Morgan and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the ""neo-Darwinian synthesis"". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson and Crick proposed the structure of DNA. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular and molecular biology. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics and proteomics were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.