File - Illinois Online High School
... 3.) Which of these is not a characteristic of living things? a) reproduction and heredity; b) metabolism; c) response to stimulus d) all of the are characteristics of life 4.) Control of homeostasis in the body is accomplished by ____. a) Nervous system; b) Circulatory system; c) Endocrine system; d ...
... 3.) Which of these is not a characteristic of living things? a) reproduction and heredity; b) metabolism; c) response to stimulus d) all of the are characteristics of life 4.) Control of homeostasis in the body is accomplished by ____. a) Nervous system; b) Circulatory system; c) Endocrine system; d ...
1 Living things - Macmillan English
... Living things can be classified into five groups called kingdoms. Living things, or organisms, in one kingdom share similarities and are different from organisms in other kingdoms. All the living things in the Monera Kingdom are unicellular, so they all consist of a single cell. Unicellular organism ...
... Living things can be classified into five groups called kingdoms. Living things, or organisms, in one kingdom share similarities and are different from organisms in other kingdoms. All the living things in the Monera Kingdom are unicellular, so they all consist of a single cell. Unicellular organism ...
Biology Standards Clarification
... Recognize and describe that both living and nonliving things are composed of compounds, which are themselves made up of elements joined by energy containing bonds, such as those in ATP. Explain that some structures in the modern eukaryotic cell developed from early prokaryotes, such as mitochondria, ...
... Recognize and describe that both living and nonliving things are composed of compounds, which are themselves made up of elements joined by energy containing bonds, such as those in ATP. Explain that some structures in the modern eukaryotic cell developed from early prokaryotes, such as mitochondria, ...
Cell Biology: Theory and Laboratory Skills
... Microtubules constructed of tubulin are polar structures that grow rapidly at the plus end. Flagella and Cilia of eukaryotes are composed of microtubules. Microtubules are used to transport organelles around the cell. Expression of intermediate filaments in a tissue specific manner with examples. Ke ...
... Microtubules constructed of tubulin are polar structures that grow rapidly at the plus end. Flagella and Cilia of eukaryotes are composed of microtubules. Microtubules are used to transport organelles around the cell. Expression of intermediate filaments in a tissue specific manner with examples. Ke ...
Understanding Our Environment
... separation can result in gametes carrying extra or missing chromosomes. - Aneuploid - Carries, or is missing, an extra chromosome(s). - Polyploid - Has at least one complete extra set of chromosomes. - Many cultivated plants are polyploid because they are bigger and produce more. Stern - Introductor ...
... separation can result in gametes carrying extra or missing chromosomes. - Aneuploid - Carries, or is missing, an extra chromosome(s). - Polyploid - Has at least one complete extra set of chromosomes. - Many cultivated plants are polyploid because they are bigger and produce more. Stern - Introductor ...
1 The diagram shows part of a pre-mRNA molecule. 1 (a) (i) Name
... Calculate the percentage increase from 1751 to 2007 in the number of people who survived to 70 years of age. Show your working. ...
... Calculate the percentage increase from 1751 to 2007 in the number of people who survived to 70 years of age. Show your working. ...
EOG Review Human Body and Genetics SI
... 5. The stomach and the intestines are parts of the digestive system. The digestive system breaks food down into small particles of nutrients that body cells can use. Food enters the digestive system through the mouth and travels down the esophagus to the stomach and the intestines, where it is diges ...
... 5. The stomach and the intestines are parts of the digestive system. The digestive system breaks food down into small particles of nutrients that body cells can use. Food enters the digestive system through the mouth and travels down the esophagus to the stomach and the intestines, where it is diges ...
BIOL 105 S 2013 Midterm Exam 1 Q 130311.5
... F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL ...
... F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL ...
01_Lecture_Presentation_PC
... Concept 1.3: In studying nature, scientists make observations and then form and test hypotheses • The word science is derived from Latin and means “to know” • Inquiry is the search for information and explanation • The scientific process includes making observations, forming logical hypotheses, and ...
... Concept 1.3: In studying nature, scientists make observations and then form and test hypotheses • The word science is derived from Latin and means “to know” • Inquiry is the search for information and explanation • The scientific process includes making observations, forming logical hypotheses, and ...
PDF
... tebrates, we tend to think of an individual but a negligible effect (commensalism) on invertebrate animal as just that: an individ- the other. Most commonly, the selective ual genome, a representative of a single effect on the host or endosymbiont is either taxon. But many invertebrate organisms are ...
... tebrates, we tend to think of an individual but a negligible effect (commensalism) on invertebrate animal as just that: an individ- the other. Most commonly, the selective ual genome, a representative of a single effect on the host or endosymbiont is either taxon. But many invertebrate organisms are ...
Protista and Fungi Notes
... C. Sporozoans (also known as Apicomplexans) are the non-motile parasites; Examples include Plasmodium (causes Malaria) and Trypanosome (causes sleeping sickness); both are carried by insects to a human host and must spend part of their life in a specific insect and then in a human host. D. Sarcodina ...
... C. Sporozoans (also known as Apicomplexans) are the non-motile parasites; Examples include Plasmodium (causes Malaria) and Trypanosome (causes sleeping sickness); both are carried by insects to a human host and must spend part of their life in a specific insect and then in a human host. D. Sarcodina ...
Human-Physiology-Lecture-IV-CellMembranes
... The cell membrane can also engulf structures that are much too large to fit through the pores in the membrane proteins this process is known as endocytosis. In this process the membrane itself wraps around the particle and pinches off a vesicle inside the cell. In this animation an ameba engulfs a f ...
... The cell membrane can also engulf structures that are much too large to fit through the pores in the membrane proteins this process is known as endocytosis. In this process the membrane itself wraps around the particle and pinches off a vesicle inside the cell. In this animation an ameba engulfs a f ...
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... nutrient or as a waste. Too much of a particular substance at a particular moment, even though it is usually an essential nutrient, can result in attempts at its removal. Excess amounts of vitamins or minerals taken by some people as supplements are generally removed with the urine. Excess water in ...
... nutrient or as a waste. Too much of a particular substance at a particular moment, even though it is usually an essential nutrient, can result in attempts at its removal. Excess amounts of vitamins or minerals taken by some people as supplements are generally removed with the urine. Excess water in ...
MODULE 1 FROM CELL TO ORGANISM
... Organ systems work together to help organisms meet their basic needs and to survive. The digestive system helps organisms get energy from the food they eat. The circulatory system moves the nutrients that come from digested food, along with blood, to the different parts of the body. How do you think ...
... Organ systems work together to help organisms meet their basic needs and to survive. The digestive system helps organisms get energy from the food they eat. The circulatory system moves the nutrients that come from digested food, along with blood, to the different parts of the body. How do you think ...
4 - King Edward VI School
... Content detail Describe the structure of the thorax, including the ribs, intercostal muscles, diaphragm, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and pleural membranes. ...
... Content detail Describe the structure of the thorax, including the ribs, intercostal muscles, diaphragm, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and pleural membranes. ...
Scheme of Work for IGCSE Biology
... Content detail Living organisms share the following basic characteristics: they require nutrition they respire they excrete their waste they respond to their surroundings they move they control their internal conditions they reproduce they grow and develop ...
... Content detail Living organisms share the following basic characteristics: they require nutrition they respire they excrete their waste they respond to their surroundings they move they control their internal conditions they reproduce they grow and develop ...
B1 Revision Checklist
... Describe sexual reproduction as the joining of male and female gametes. Define the term ‘clone’. Take plant cuttings and grow new plants. Interpret information about cloning techniques. Make informed judgements about the economic, social and ethical issues concerning cloning. Describe the ...
... Describe sexual reproduction as the joining of male and female gametes. Define the term ‘clone’. Take plant cuttings and grow new plants. Interpret information about cloning techniques. Make informed judgements about the economic, social and ethical issues concerning cloning. Describe the ...
Curriculum Guide Template DRAFT
... • Demonstrate the use of microscope techniques. • Calculate total magnification as well as steps in proper microscope usage. • Describe the hierarchy of cell organization: cells→tissues→organs→organ systems. • Describe the structure of cells as it relates to their specific functions. • Distinguish b ...
... • Demonstrate the use of microscope techniques. • Calculate total magnification as well as steps in proper microscope usage. • Describe the hierarchy of cell organization: cells→tissues→organs→organ systems. • Describe the structure of cells as it relates to their specific functions. • Distinguish b ...
biology 309 developmental biology
... whiteboard or blackboard to illustrate answers to questions is encouraged. Most people have difficulty drawing pictures in their minds while hearing spoken words. f. learn the conventions of evidence, format, usage, and documentation in their fields. In Developmental Biology, we are interested not o ...
... whiteboard or blackboard to illustrate answers to questions is encouraged. Most people have difficulty drawing pictures in their minds while hearing spoken words. f. learn the conventions of evidence, format, usage, and documentation in their fields. In Developmental Biology, we are interested not o ...
Document
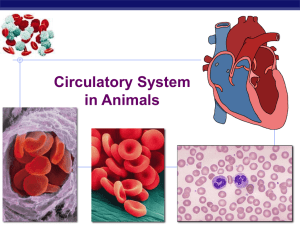
... Circulatory systems All animals have: muscular pump = heart tubes = blood vessels circulatory fluid = “blood” ...
... Circulatory systems All animals have: muscular pump = heart tubes = blood vessels circulatory fluid = “blood” ...
Grade Level / Course:
... diffusion, osmosis, passive transport, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, bacteria, Sexual, Asexual Common plant or animals cells: elodea leaf cells, onionskin cells, human cheek cells, paramecium, amoeba ...
... diffusion, osmosis, passive transport, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, bacteria, Sexual, Asexual Common plant or animals cells: elodea leaf cells, onionskin cells, human cheek cells, paramecium, amoeba ...
History of biology

The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to ayurveda, ancient Egyptian medicine and the works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world. This ancient work was further developed in the Middle Ages by Muslim physicians and scholars such as Avicenna. During the European Renaissance and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius and Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. The growing importance of natural theology, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (although it entrenched the argument from design).Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany and zoology became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics by Thomas Hunt Morgan and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the ""neo-Darwinian synthesis"". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson and Crick proposed the structure of DNA. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular and molecular biology. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics and proteomics were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.