Fall Exam Review 2016
... cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, nucleus, Golgi body, and ribosome. 2. Draw a plant cell and label the following organelles: cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and nucleus. 3. Create a chart for the following organelles, which includes a brief ...
... cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, nucleus, Golgi body, and ribosome. 2. Draw a plant cell and label the following organelles: cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and nucleus. 3. Create a chart for the following organelles, which includes a brief ...
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division
... plants and animals. – Mitotic reproduction can take several forms: ...
... plants and animals. – Mitotic reproduction can take several forms: ...
Comp 4c Packet
... solution with a lower solute concentration solution in which the solute concentration is the same condition plant cells require condition that animal cells require red blood cell bursts (cytolysis) plant cell loses turgor pressure (Plasmolysis) solution with a higher solute concentration plant cell ...
... solution with a lower solute concentration solution in which the solute concentration is the same condition plant cells require condition that animal cells require red blood cell bursts (cytolysis) plant cell loses turgor pressure (Plasmolysis) solution with a higher solute concentration plant cell ...
Cells - Peoria Public Schools
... plants and animals. – Mitotic reproduction can take several forms: ...
... plants and animals. – Mitotic reproduction can take several forms: ...
PASS_Review_Plants
... Which of the following best describes the function of the xylem? A. To transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. B. To absorb water from the soil and anchor the plant in the ground. C. To support the plant and hold the leaves up to the light. D. To protect the embryo fro ...
... Which of the following best describes the function of the xylem? A. To transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. B. To absorb water from the soil and anchor the plant in the ground. C. To support the plant and hold the leaves up to the light. D. To protect the embryo fro ...
Name
... exterior body surfaces. Connective tissue provides support for the body and connects its parts. Nervous tissue transmits nerve impulses throughout the body. And muscle tissue (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth), along with bones, enables the body to move. A group of different types of tissues that work ...
... exterior body surfaces. Connective tissue provides support for the body and connects its parts. Nervous tissue transmits nerve impulses throughout the body. And muscle tissue (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth), along with bones, enables the body to move. A group of different types of tissues that work ...
Cell Division: Shocking tails
... “Gotcha!” screeched the hawk as it swooped down and clamped its pointed beak on the lizard’s tail, catching it by surprise. “Oh no you don't!” hissed the lizard in reply, detaching its tail as it darted under a bush, leaving the hawk hungry and confused. Have you ever wondered why it is that a lizar ...
... “Gotcha!” screeched the hawk as it swooped down and clamped its pointed beak on the lizard’s tail, catching it by surprise. “Oh no you don't!” hissed the lizard in reply, detaching its tail as it darted under a bush, leaving the hawk hungry and confused. Have you ever wondered why it is that a lizar ...
Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs And Organ Systems
... This organizational concept (I-IV) is the way all living things are organized as well as humans. The hierarchy of structures starts with the smallest part (a cell) and works up to the largest structure which is the whole body of a living thing. This includes plants, animals, and other microscopi ...
... This organizational concept (I-IV) is the way all living things are organized as well as humans. The hierarchy of structures starts with the smallest part (a cell) and works up to the largest structure which is the whole body of a living thing. This includes plants, animals, and other microscopi ...
Cell and Human Body and Chemistry SC PASS Notes 17-16
... smallest unit of life that conducts life functions; organelles (parts) cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane, vacuole, chloroplasts**, mitochondria, cell wall** (**found only in plant cells); many organelles too small to be seen without aid of microscope; cells vary in size and shape 1) All living thing ...
... smallest unit of life that conducts life functions; organelles (parts) cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane, vacuole, chloroplasts**, mitochondria, cell wall** (**found only in plant cells); many organelles too small to be seen without aid of microscope; cells vary in size and shape 1) All living thing ...
1 - Port Fest Baltimore
... 10. A student observes a unicellular organism under a microscope. After a while, the organism begins to split into two cells, as shown in the diagram. ...
... 10. A student observes a unicellular organism under a microscope. After a while, the organism begins to split into two cells, as shown in the diagram. ...
BIOL 105 S 2012 QZ2 Q 120204.2
... 1. Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) grow and reproduce. B) respond and adapt to their environment. C) control the external environment. D) A and B only E) all of the above 2. The waste products of metabolism are eliminated through the process of A) assimilation. B) ...
... 1. Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) grow and reproduce. B) respond and adapt to their environment. C) control the external environment. D) A and B only E) all of the above 2. The waste products of metabolism are eliminated through the process of A) assimilation. B) ...
bio eoc powerpoint study guide
... the role of natural selection in the development of the theory of evolution. a. Trace the history of the theory. b. Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory. d. Relate natural selecti ...
... the role of natural selection in the development of the theory of evolution. a. Trace the history of the theory. b. Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory. d. Relate natural selecti ...
Slide 1
... • Animal cells lack cell walls that provide support to plants and fungi. • Animals are held together by extracellular proteins. • Most have muscle cells for movement and nerve cells for conducting impulses. ...
... • Animal cells lack cell walls that provide support to plants and fungi. • Animals are held together by extracellular proteins. • Most have muscle cells for movement and nerve cells for conducting impulses. ...
Membranes around cells provide separation
... the diffusion gradient, they carry electrical charges, etc. In active transport, specific carrier proteins bind to these molecules and bring them inside the cell. This requires the use of energy. Endocytosis is a form of active transport where large molecules are transported across a membrane. 3 typ ...
... the diffusion gradient, they carry electrical charges, etc. In active transport, specific carrier proteins bind to these molecules and bring them inside the cell. This requires the use of energy. Endocytosis is a form of active transport where large molecules are transported across a membrane. 3 typ ...
Notes on Levels of Organization
... tract in many animals • Function: to break down food, and store it to later be absorbed by the intestines ...
... tract in many animals • Function: to break down food, and store it to later be absorbed by the intestines ...
BIOLOGY SOL REVIEW PACKET IT`S TIME FOR YOU TO PASS
... experiment, a student stripped off all the leaves from a set of plants. In a second set of identical plants, the student allowed ants to strip off the plants’ leaves. In order to improve this experimental design, it is most important to add a set of plants — A exposed to a different ant species B of ...
... experiment, a student stripped off all the leaves from a set of plants. In a second set of identical plants, the student allowed ants to strip off the plants’ leaves. In order to improve this experimental design, it is most important to add a set of plants — A exposed to a different ant species B of ...
BiologyHonors-CourseExpectation
... 4. Anatomy and Physiology Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions ...
... 4. Anatomy and Physiology Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions ...
EVOLUTION
... In most cases, complex structures evolve by increments from simpler versions with the same basic functions. In the evolution of an eye or any other complex structure, behavior, or biochemical pathway, each step must bring a selective advantage to the organism possessing it and increase the o ...
... In most cases, complex structures evolve by increments from simpler versions with the same basic functions. In the evolution of an eye or any other complex structure, behavior, or biochemical pathway, each step must bring a selective advantage to the organism possessing it and increase the o ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1: From Cells to Organ Word Parts/meaning of word, if
... 1. Provides shape and support 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your internal organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. Stores certain material until your body needs them Muscular System: 1. Muscles are connected to your Skeletal System 2. Help you move your body parts. ...
... 1. Provides shape and support 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your internal organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. Stores certain material until your body needs them Muscular System: 1. Muscles are connected to your Skeletal System 2. Help you move your body parts. ...
Animalia
... BLASTULA (hollow ball of cells) GASTRULA (stage when layers that produce adult tissues form) GERM LAYER FORMATION ...
... BLASTULA (hollow ball of cells) GASTRULA (stage when layers that produce adult tissues form) GERM LAYER FORMATION ...
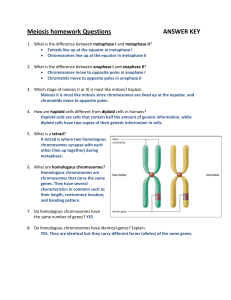
Meiosis homework Questions ANSWER KEY
... 9. What are the two key features of meiosis that contribute to genetic variations? 1. Pairing of homologous chromosomes allows for crossing over, resulting in exchange of chromosome sections between chromosomes. 2. Independent assortment of homologous maternal and paternal chromosomes during metaph ...
... 9. What are the two key features of meiosis that contribute to genetic variations? 1. Pairing of homologous chromosomes allows for crossing over, resulting in exchange of chromosome sections between chromosomes. 2. Independent assortment of homologous maternal and paternal chromosomes during metaph ...
Transport Systems and Solutions
... In which direction would water flow… between cells A and B? between cells A and D? between cells B and C? between cells C and A? Which cell has the greatest solute concentration? Which cell has the greatest solvent concentration? ...
... In which direction would water flow… between cells A and B? between cells A and D? between cells B and C? between cells C and A? Which cell has the greatest solute concentration? Which cell has the greatest solvent concentration? ...
Topic One: Chemistry of Living Things
... Organization: The human body is made up of ___________. A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a ______________ cell. 1. This single cell is called a ___________________. 2. The nucleus of this cell has _________ the genes needed to become a complete organism. ...
... Organization: The human body is made up of ___________. A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a ______________ cell. 1. This single cell is called a ___________________. 2. The nucleus of this cell has _________ the genes needed to become a complete organism. ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are