Plain Local Schools 5th Grade Science
... Class Copy – DO NOT WRITE! Use the following food web to answer question 29. 29. Short Answer: An herbicide (a chemical used to kill plants) was used on the plant shown in the diagram below. In your Answer Document, describe two ways the use of an herbicide can affect the food web. (2 points) ...
... Class Copy – DO NOT WRITE! Use the following food web to answer question 29. 29. Short Answer: An herbicide (a chemical used to kill plants) was used on the plant shown in the diagram below. In your Answer Document, describe two ways the use of an herbicide can affect the food web. (2 points) ...
Bone and Muscle Previous Exam Review
... Training produces a number of changes within your body that help to improve your endurance and performance. Respiratory/chest muscles become stronger which helps the lungs draw in more oxygen for ATP production. Training encourages the formation of new capillaries/blood vessels to the muscles. This ...
... Training produces a number of changes within your body that help to improve your endurance and performance. Respiratory/chest muscles become stronger which helps the lungs draw in more oxygen for ATP production. Training encourages the formation of new capillaries/blood vessels to the muscles. This ...
Learning Outcomes
... G8. demonstrate an understanding of the relationship and significance of surface area to volume, with reference to cell size ...
... G8. demonstrate an understanding of the relationship and significance of surface area to volume, with reference to cell size ...
WHITTIER UNION HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT
... Mutation and sexual reproduction lead to genetic variation in a population. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. Meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containin ...
... Mutation and sexual reproduction lead to genetic variation in a population. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. Meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containin ...
REPRODUCTION IN ANIMALS
... Also, there are other animals in the pond which may feed on eggs. Thus, production of large number of eggs and sperms is necessary to ensure fertilization of at least a few of them. Q.6. How could a single cell become such a big individual? Ans. The fusion of single sperm cell with single egg cell, ...
... Also, there are other animals in the pond which may feed on eggs. Thus, production of large number of eggs and sperms is necessary to ensure fertilization of at least a few of them. Q.6. How could a single cell become such a big individual? Ans. The fusion of single sperm cell with single egg cell, ...
Human Body Systems - walker2015
... Receives information about what is happening inside & outside of the body. Directs the way your body responds to this information. (Remember stimulus and response?). Helps maintain homeostasis. BrainPop Video – Nervous System ...
... Receives information about what is happening inside & outside of the body. Directs the way your body responds to this information. (Remember stimulus and response?). Helps maintain homeostasis. BrainPop Video – Nervous System ...
Middle East Jeopardy
... The organ that produces 3 digestive enzymes, then delivers the enzymes to the small intestine. What is the pancreas? ...
... The organ that produces 3 digestive enzymes, then delivers the enzymes to the small intestine. What is the pancreas? ...
Lecture Notes to Accompany Labs 8 and 9
... Sporophyte: Diploid (2N) spore producing body of the plant or algae. Undergoes meiosis to produce haplod (1N) gametes. Gametophyte: The haploid (1N), body in which gametes form during the life cycle via mitosis. Gymnosperms Have Vascular tissue No water needed for fertilization Have cuticle an ...
... Sporophyte: Diploid (2N) spore producing body of the plant or algae. Undergoes meiosis to produce haplod (1N) gametes. Gametophyte: The haploid (1N), body in which gametes form during the life cycle via mitosis. Gymnosperms Have Vascular tissue No water needed for fertilization Have cuticle an ...
Concept!Covered:!!Phylum!Platyhelminthes!
... 5. %Flatworms%do%not%have%circulatory%or%respiratory%systems.%%How% do%they%survive%without%these%body%systems?%_______________% ...
... 5. %Flatworms%do%not%have%circulatory%or%respiratory%systems.%%How% do%they%survive%without%these%body%systems?%_______________% ...
Asexual and sexual reproduction, two methods of
... offspring with novel combinations of genes. This can be an adaptive advantage in unstable or unpredictable environments. As humans, we are used to thinking of animals as having two separate sexes, male and female, determined at conception. However, in the animal kingdom, there are many variations on ...
... offspring with novel combinations of genes. This can be an adaptive advantage in unstable or unpredictable environments. As humans, we are used to thinking of animals as having two separate sexes, male and female, determined at conception. However, in the animal kingdom, there are many variations on ...
Derived copy of Epithelial Tissue
... By the end of this section, you will be able to: • Explain the structure and function of epithelial tissue • Distinguish between tight junctions, anchoring junctions, and gap junctions • Distinguish between simple epithelia and strati ed epithelia, as well as between squamous, cuboidal, and columnar ...
... By the end of this section, you will be able to: • Explain the structure and function of epithelial tissue • Distinguish between tight junctions, anchoring junctions, and gap junctions • Distinguish between simple epithelia and strati ed epithelia, as well as between squamous, cuboidal, and columnar ...
The Human Body
... epidermis – the upper layer of skin where nails grow and where melanin in located. dermis - middle layer of skin that contains nerves, blood vessels, sweat glands, oil glands and hair follicles. subcutaneous layer – acts as a fat storage to provide warmth and to absorb shock. Body systems that work ...
... epidermis – the upper layer of skin where nails grow and where melanin in located. dermis - middle layer of skin that contains nerves, blood vessels, sweat glands, oil glands and hair follicles. subcutaneous layer – acts as a fat storage to provide warmth and to absorb shock. Body systems that work ...
6 - SP Moodle
... 7. A major requirement of the body is to eliminate carbon dioxide (CO2). In the body, carbon dioxide exists in three forms: dissolved CO2, bound as the bicarbonate ion, and bound to proteins (e.g. haemoglobin in red blood cells or plasma proteins). The relative contribution of each of these forms to ...
... 7. A major requirement of the body is to eliminate carbon dioxide (CO2). In the body, carbon dioxide exists in three forms: dissolved CO2, bound as the bicarbonate ion, and bound to proteins (e.g. haemoglobin in red blood cells or plasma proteins). The relative contribution of each of these forms to ...
Simulation of Lung Conditions for Pea Plant Growth
... • Glycine and proline are components of the elastin and collagen fibers of the lungs. They may have affected the germination in ...
... • Glycine and proline are components of the elastin and collagen fibers of the lungs. They may have affected the germination in ...
What is Life? - bms8thgradescience
... outside of living or once living organisms, such as those in rocks, minerals, and ceramics. Most inorganic compounds lack carbon, such as salt (NaCl) and ammonia (NH 3 ); a few, such as carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), do contain it, but never attached to hydrogen atoms as in hydrocarbons. Inorganic molecule ...
... outside of living or once living organisms, such as those in rocks, minerals, and ceramics. Most inorganic compounds lack carbon, such as salt (NaCl) and ammonia (NH 3 ); a few, such as carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), do contain it, but never attached to hydrogen atoms as in hydrocarbons. Inorganic molecule ...
NORMAL TISSUE GROWTH AND CELL PROLIFERATION
... C to maintain self renewing capacity and also supply cells for replacement / regeneration, the stem cells must exhibit asymmetric replication; after division some of the clonal cell lines must become differentiated while others must remain as stem cells. a) Embryonic Stem Cells - embryonic stem (ES) ...
... C to maintain self renewing capacity and also supply cells for replacement / regeneration, the stem cells must exhibit asymmetric replication; after division some of the clonal cell lines must become differentiated while others must remain as stem cells. a) Embryonic Stem Cells - embryonic stem (ES) ...
Circulatory and Gas Exchange Systems
... Open circulatory systems greatly increase the efficiency of transport of substances within a body relative to diffusion ...
... Open circulatory systems greatly increase the efficiency of transport of substances within a body relative to diffusion ...
study guide - SchoolNotes
... -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Identify the basic characteristics of a cnidarian. o Body structure all cnidarians have tentacles with stinging cells and have radial symmetry – all organisms with radial symmetry lack a head. o Die ...
... -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Identify the basic characteristics of a cnidarian. o Body structure all cnidarians have tentacles with stinging cells and have radial symmetry – all organisms with radial symmetry lack a head. o Die ...
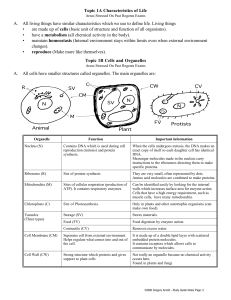
Topic 1A Characteristics of Life A. All living things have similar
... There are many different types of cells in the body. These body cells coordinate their activities with one another to maintain homeostasis by using two systems for communication: - The nervous system uses special nerve cells (neurons) to pass information from one part of the organism to another. Ner ...
... There are many different types of cells in the body. These body cells coordinate their activities with one another to maintain homeostasis by using two systems for communication: - The nervous system uses special nerve cells (neurons) to pass information from one part of the organism to another. Ner ...
Fungi
... • Out of the spore wall grows a hypha • The body of the fungus is made up of hyphal threads collectively called the mycelium • The mycelium grows in soil or within dead wood or living organisms • When growing conditions are favorable, the mycelium develops fruiting bodies, e.g. mushrooms • Fruiting ...
... • Out of the spore wall grows a hypha • The body of the fungus is made up of hyphal threads collectively called the mycelium • The mycelium grows in soil or within dead wood or living organisms • When growing conditions are favorable, the mycelium develops fruiting bodies, e.g. mushrooms • Fruiting ...
Phylum Cnidaria
... OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0† ...
... OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0† ...
Organ Systems in Plants and Animals
... the lung. Interaction with other systems: Each cell in your body requires oxygen to carry out various life processes including growth, movement, and reproduction. It is transported around in the circulatory system. Oxygen is also required to break down food to produce energy: this chemical proce ...
... the lung. Interaction with other systems: Each cell in your body requires oxygen to carry out various life processes including growth, movement, and reproduction. It is transported around in the circulatory system. Oxygen is also required to break down food to produce energy: this chemical proce ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are