Chapter 5
... Serous membranes line body cavities. Mucous membranes line the cavities and tubes that open to the outside of the body. 5.5 Muscle Tissues 26. Describe the general characteristics of muscle tissues. (p. 163) Muscle tissues are contractile. Muscle fibers within the tissue change shape to become short ...
... Serous membranes line body cavities. Mucous membranes line the cavities and tubes that open to the outside of the body. 5.5 Muscle Tissues 26. Describe the general characteristics of muscle tissues. (p. 163) Muscle tissues are contractile. Muscle fibers within the tissue change shape to become short ...
... 4. Whether the seeds are enclosed within fruits. Q5. How are the criteria for deciding divisions in plants different from the criteria for deciding the subgroups among the animals? Ans. The characteristics used to classify plants is different from animals because thebasic design are different, based ...
learning outcomes for biology 12 and ib biology 12
... chromosomes A2. Identify the functional interrelationships of cell structures p. 51 A3. Define the four main tissue types of the body and give their functions p. 156-162 A4. Differentiate between tissue, organ and organ systems p. 156-164 A5. Define homeostasis and describe at least four examples p. ...
... chromosomes A2. Identify the functional interrelationships of cell structures p. 51 A3. Define the four main tissue types of the body and give their functions p. 156-162 A4. Differentiate between tissue, organ and organ systems p. 156-164 A5. Define homeostasis and describe at least four examples p. ...
FUNGI
... have centrioles and histone proteins Acquire nutrition through: capable of sexual & asexual reproduction Cells that undergo meiosis are ingestion external digestion/absorption diploid adult cells photosynthesis zygotes; only diploid life cycle stage Circulation Organism body heart & vessels little o ...
... have centrioles and histone proteins Acquire nutrition through: capable of sexual & asexual reproduction Cells that undergo meiosis are ingestion external digestion/absorption diploid adult cells photosynthesis zygotes; only diploid life cycle stage Circulation Organism body heart & vessels little o ...
Section 8 - DigitalWebb.com
... Created by Julia Hsu Levy – Version 1.5 * * * Animal Structure and Function * * * Anatomy: study of the structures of an organism Physiology: study of the functions of an organism Atoms molecules molecular structures cell tissues organs organ ...
... Created by Julia Hsu Levy – Version 1.5 * * * Animal Structure and Function * * * Anatomy: study of the structures of an organism Physiology: study of the functions of an organism Atoms molecules molecular structures cell tissues organs organ ...
CHAPTER 5: TISSUES
... surface that is made up of squamous (flat) cells. – The other layers have different shapes, but the name is based on the apical layer. – The many layers are ideal for ...
... surface that is made up of squamous (flat) cells. – The other layers have different shapes, but the name is based on the apical layer. – The many layers are ideal for ...
Third Grade Science Vocabulary
... A tough, elastic connective tissue found in reduces friction and imparts flexibility Cartilage Permanent cartilage remains throughout life, various parts of the body, such as the joints, as in the external ear, nose, larynx, and windpipe (or trachea) R23 Muscles attached to and move bones (part of P ...
... A tough, elastic connective tissue found in reduces friction and imparts flexibility Cartilage Permanent cartilage remains throughout life, various parts of the body, such as the joints, as in the external ear, nose, larynx, and windpipe (or trachea) R23 Muscles attached to and move bones (part of P ...
Chapter 35-1 - Human Body Systems
... • Can you name the 11 organ systems found in the human body? • What are the main functions of each organ system? ...
... • Can you name the 11 organ systems found in the human body? • What are the main functions of each organ system? ...
Homeostasis and Human Organ Systems Test (M)
... The nonspecific line of defense for the body includes the MARCOPHAGES which are cells that seek out and engulf foreign invaders by PHAGOCYTOSIS (a type of active transport) and push the invader’s antigens out its cell membrane. The specific line of defense starts with HELPER T CELLS which are the ce ...
... The nonspecific line of defense for the body includes the MARCOPHAGES which are cells that seek out and engulf foreign invaders by PHAGOCYTOSIS (a type of active transport) and push the invader’s antigens out its cell membrane. The specific line of defense starts with HELPER T CELLS which are the ce ...
Body System Structures Function
... broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and distributed to cells. The blood stream transports molecules to the cells. The main organ systems that interact in nutrient absorption are the digestive and circulatory systems. Regulation is the process of body systems working together to m ...
... broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and distributed to cells. The blood stream transports molecules to the cells. The main organ systems that interact in nutrient absorption are the digestive and circulatory systems. Regulation is the process of body systems working together to m ...
What is the Digestive System?
... in – some foods are too large and not water soluble The digestive system breaks down the food we eat into small pieces that can be metabolized by individual cells in our body GLUCOSE + 6H2O 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36ATP ATP is the form of energy out body can use to perform ...
... in – some foods are too large and not water soluble The digestive system breaks down the food we eat into small pieces that can be metabolized by individual cells in our body GLUCOSE + 6H2O 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36ATP ATP is the form of energy out body can use to perform ...
Chapter-6-Cell-membrane-and-transport-of
... from the outside by engulfing it with cell membrane. • This involves the PM folding inwards to form a pouch. When this becomes closed off and detached from the cell membrane, it is called an INTRACELLULAR VESICLE. • It is used by all cells of the body because most substances important to them are la ...
... from the outside by engulfing it with cell membrane. • This involves the PM folding inwards to form a pouch. When this becomes closed off and detached from the cell membrane, it is called an INTRACELLULAR VESICLE. • It is used by all cells of the body because most substances important to them are la ...
Human Body Systems
... coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules. Sperm cells are produced by meiosis in the seminiferous tubules. In addition, the testes produce testosterone. ...
... coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules. Sperm cells are produced by meiosis in the seminiferous tubules. In addition, the testes produce testosterone. ...
32 Lung Respiratory Tissue
... branching into alveolar ducts. Alveolar ducts are thin walled tubes from which numerous alveoli or clusters of alveoli open around its circumference so that the wall becomes little more than a succession of alveolar openings. Appearances of a tube persist only in a few places, where small groups of ...
... branching into alveolar ducts. Alveolar ducts are thin walled tubes from which numerous alveoli or clusters of alveoli open around its circumference so that the wall becomes little more than a succession of alveolar openings. Appearances of a tube persist only in a few places, where small groups of ...
Internal Anatomy
... • Crayfish have separate male and female animals ~ in other words, they are not hermaphrodites • External Fertilization = eggs are fertilized outside of the female’s body • Fertilized eggs are stored on the last three abdominal sections on the female ...
... • Crayfish have separate male and female animals ~ in other words, they are not hermaphrodites • External Fertilization = eggs are fertilized outside of the female’s body • Fertilized eggs are stored on the last three abdominal sections on the female ...
CONNECTIVE TISSUE I
... fibroblasts, chrondroblasts, osteoblasts, smooth muscle, endothelial and epithelial cells. It is the most abundant protein in the body. Synthesis (intracellular and extracellular components): In the RER, polypeptide chains (procollagen), are transported outside the cell, and cleaved by proteases to ...
... fibroblasts, chrondroblasts, osteoblasts, smooth muscle, endothelial and epithelial cells. It is the most abundant protein in the body. Synthesis (intracellular and extracellular components): In the RER, polypeptide chains (procollagen), are transported outside the cell, and cleaved by proteases to ...
Dedham Middle School MCAS Science Review Book
... energy for the cell. A common form in which energy is stored in living systems; consists of a nucleotide (with ribose sugar) with three phosphate groups. The energy coin of the cell. organic compound that are the building blocks of proteins. The subunits (monomers) from which proteins (polymers) are ...
... energy for the cell. A common form in which energy is stored in living systems; consists of a nucleotide (with ribose sugar) with three phosphate groups. The energy coin of the cell. organic compound that are the building blocks of proteins. The subunits (monomers) from which proteins (polymers) are ...
LECTURE OUTLINE 1
... -retention of water, glucose -use of ions to conserve water -loop of Henle -water retention under control of hypothalamus ...
... -retention of water, glucose -use of ions to conserve water -loop of Henle -water retention under control of hypothalamus ...
Tissues and Membranes
... cytoplasm is lost. Example: salivary glands • Apocrine glands – Product accumulates in an area of the gland, then is pinched off – a small portion of the cell is lost. Example: sweat ...
... cytoplasm is lost. Example: salivary glands • Apocrine glands – Product accumulates in an area of the gland, then is pinched off – a small portion of the cell is lost. Example: sweat ...
Unit2-KA4
... Unit2 – Key area 4: Notes for Reproduction - Copy what is in bold and follow instructions DO NOT GLUE THIS SHEET ON YOUR JOTTER ...
... Unit2 – Key area 4: Notes for Reproduction - Copy what is in bold and follow instructions DO NOT GLUE THIS SHEET ON YOUR JOTTER ...
vet ch 1 and 2
... 2. The female not only provides the ovum for fertilization, but she also cares for the young ...
... 2. The female not only provides the ovum for fertilization, but she also cares for the young ...
1.1 Where organisms live 1.2 - Pearson-Global
... for photosynthesis without the cactus losing too much water. The stem has a small surface area which cuts down water loss. The roots are usually long and spread over a wide area so that if it rains water can be absorbed quickly and stored within the stem. These are just two examples of the ways orga ...
... for photosynthesis without the cactus losing too much water. The stem has a small surface area which cuts down water loss. The roots are usually long and spread over a wide area so that if it rains water can be absorbed quickly and stored within the stem. These are just two examples of the ways orga ...
2 December, 1998
... called phospholipids. It is VERY important that this layer be soft an malleable. Here's why. Scattered through this bilayer of phospholipids are all kinds of important proteins that control many of the special characteristics of a cell that enable it to do its function. Specialized carrier proteins ...
... called phospholipids. It is VERY important that this layer be soft an malleable. Here's why. Scattered through this bilayer of phospholipids are all kinds of important proteins that control many of the special characteristics of a cell that enable it to do its function. Specialized carrier proteins ...
The Animal Kingdom PowerPoint
... cuttlefish, and chambered nautilus. Muscular foot is divided into tentacles for swimming. They are very complex and intelligent. Range in size from 160 feet. Most are predators of other small invertebrates. ...
... cuttlefish, and chambered nautilus. Muscular foot is divided into tentacles for swimming. They are very complex and intelligent. Range in size from 160 feet. Most are predators of other small invertebrates. ...
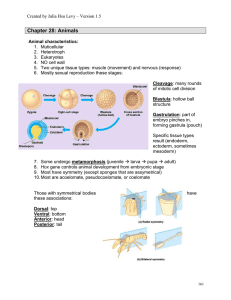
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are