mc2 Chromatin - WordPress.com
... from Talbert and Henikoff, Nature Rev.Mol.Cell Biol. 11, 264 (2010) ...
... from Talbert and Henikoff, Nature Rev.Mol.Cell Biol. 11, 264 (2010) ...
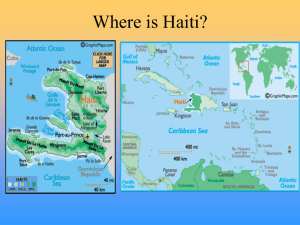
Study Material - Class- XI - Biology
... -Objects having characteristics of cellular organisation, growth & development, reproduction, ability to sense environment & give response, metabolism etc. All organisms grow: -Increase in mass or number of cells characterise growth. -Plants grow throughout life but Animals grow to certain age. -Gro ...
... -Objects having characteristics of cellular organisation, growth & development, reproduction, ability to sense environment & give response, metabolism etc. All organisms grow: -Increase in mass or number of cells characterise growth. -Plants grow throughout life but Animals grow to certain age. -Gro ...
Chapter 1: Animal Agriculture
... • Gross anatomy: structures can be seen with unaided eye • Microscopic anatomy: tissues are studied using a microscope (magnification of 401000 times), also called histology • Comparative anatomy: comparisons between species ...
... • Gross anatomy: structures can be seen with unaided eye • Microscopic anatomy: tissues are studied using a microscope (magnification of 401000 times), also called histology • Comparative anatomy: comparisons between species ...
Slide 1
... • Gene probes are used to test for some ‘faulty’ genes • Faulty genes stick to the probe. These can be seen by • UV – a fluorescent molecule sticks to the DNA and glows under UV light • Autoradiography – gene probe made from radioactive DNA which blacken Xray film ...
... • Gene probes are used to test for some ‘faulty’ genes • Faulty genes stick to the probe. These can be seen by • UV – a fluorescent molecule sticks to the DNA and glows under UV light • Autoradiography – gene probe made from radioactive DNA which blacken Xray film ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... Chapter 9 Notes: Life Functions Common to Living Things 9.1 Life Functions Common All Living Things -life functions (aka life processes) – seven activities carried out by cells and organ systems 1. transportation 2. nutrition 3. growth and repair 4. reproduction 5. regulation 6. metabolism 7. synthe ...
... Chapter 9 Notes: Life Functions Common to Living Things 9.1 Life Functions Common All Living Things -life functions (aka life processes) – seven activities carried out by cells and organ systems 1. transportation 2. nutrition 3. growth and repair 4. reproduction 5. regulation 6. metabolism 7. synthe ...
Sexual reproduction in Human beings
... Identify on diagrams of the male reproductive system and give the functions of testes, scrotum, sperm ducts, prostate gland, urethra and penis Identify on diagrams of the female reproductive system and give the functions of ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix and vagina Compare male and female gametes ...
... Identify on diagrams of the male reproductive system and give the functions of testes, scrotum, sperm ducts, prostate gland, urethra and penis Identify on diagrams of the female reproductive system and give the functions of ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix and vagina Compare male and female gametes ...
Chapter-23
... • Multicelled heterotrophs (ingest other organisms) • Grow and develop through a series of stages • Actively move about during all or part of life cycle ...
... • Multicelled heterotrophs (ingest other organisms) • Grow and develop through a series of stages • Actively move about during all or part of life cycle ...
Keystone Review Packet #1 File - Dallastown Area School District
... a. ability to store hereditary information b. use of organelles to control cell processes c. use of cellular respiration for energy release d. ability to move in response to environmental stimuli 2. Living organisms can be classified as prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Which two structures are common to b ...
... a. ability to store hereditary information b. use of organelles to control cell processes c. use of cellular respiration for energy release d. ability to move in response to environmental stimuli 2. Living organisms can be classified as prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Which two structures are common to b ...
Part 1 Answers
... a. ability to store hereditary information b. use of organelles to control cell processes c. use of cellular respiration for energy release d. ability to move in response to environmental stimuli 2. Living organisms can be classified as prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Which two structures are common to b ...
... a. ability to store hereditary information b. use of organelles to control cell processes c. use of cellular respiration for energy release d. ability to move in response to environmental stimuli 2. Living organisms can be classified as prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Which two structures are common to b ...
Chapter 18 - San Diego Mesa College
... the radiation of diversity in the kingdom Animalia proceeded based on the evolution of a number of distinct "hallmark" features or characteristics ...
... the radiation of diversity in the kingdom Animalia proceeded based on the evolution of a number of distinct "hallmark" features or characteristics ...
Unit 2, Module 2 Biochemistry - rev 2012
... to occur. Enzymes regulate metabolism, allowing life to continue. Enzymes speed up reactions, making an enzyme a biological catalyst. Metabolism (each reaction) has a small range of temperature and pH at which it can proceed. Each reaction also needs some energy to begin. This is called activation e ...
... to occur. Enzymes regulate metabolism, allowing life to continue. Enzymes speed up reactions, making an enzyme a biological catalyst. Metabolism (each reaction) has a small range of temperature and pH at which it can proceed. Each reaction also needs some energy to begin. This is called activation e ...
Additional Science Biology Summary
... 10. Explain the term diffusion and some factors that affect the speed of diffusion Environment and sampling can you??? 1. Suggest some factors that affect the distribution of organisms and explain why?? 2. Explain how to randomly sample (quadrats) and systematically sample (transect)? In the topics ...
... 10. Explain the term diffusion and some factors that affect the speed of diffusion Environment and sampling can you??? 1. Suggest some factors that affect the distribution of organisms and explain why?? 2. Explain how to randomly sample (quadrats) and systematically sample (transect)? In the topics ...
pregnancy - Holy Family Catholic Regional Division No. 37
... – Approximately 500,000 new cases of this incurable viral infection develop annually. – Caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV). – painful blisters or open sores in the genital area. – These may be preceded by a tingling or burning sensation in the legs, buttocks, or genital region. – The herpes sores ...
... – Approximately 500,000 new cases of this incurable viral infection develop annually. – Caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV). – painful blisters or open sores in the genital area. – These may be preceded by a tingling or burning sensation in the legs, buttocks, or genital region. – The herpes sores ...
File
... Relationship with other systems: • All other systems: The brain is responsible for sending information signals to all other systems in order for them to function. Interesting Facts: • Only four percent of the brain's cells work while the remaining cells are kept in reserve. • There are more nerve ce ...
... Relationship with other systems: • All other systems: The brain is responsible for sending information signals to all other systems in order for them to function. Interesting Facts: • Only four percent of the brain's cells work while the remaining cells are kept in reserve. • There are more nerve ce ...
Organ
... 1. Cells in multi-cellular organisms have a specific job. Unicellular organism must carry on all 7 characteristics of life in one cell. 2. Multi-cellular organisms have tissues, organs, and organ systems. Unicellular organisms DO NOT. ...
... 1. Cells in multi-cellular organisms have a specific job. Unicellular organism must carry on all 7 characteristics of life in one cell. 2. Multi-cellular organisms have tissues, organs, and organ systems. Unicellular organisms DO NOT. ...
Human Body Vocabulary
... two tubes at the end of the trachea, brings in air from trachea and helps clean lungs; one tube goes to right lung, one to left ...
... two tubes at the end of the trachea, brings in air from trachea and helps clean lungs; one tube goes to right lung, one to left ...
Readiness— Knowledge and Skills Science 8— STAAR
... (B) The student will identify that protons determine an element's identity and valence electors determine its chemical properties including reactivity. (D) The student will recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical ...
... (B) The student will identify that protons determine an element's identity and valence electors determine its chemical properties including reactivity. (D) The student will recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical ...
Homeostasis - WordPress.com
... environment that need to be held within narrow limits Integrate this information with other relevant information Make appropriate adjustments in order to restore factor to its desired value ...
... environment that need to be held within narrow limits Integrate this information with other relevant information Make appropriate adjustments in order to restore factor to its desired value ...
E - Power PowerPoint Presentation - Julie Herbert
... • As we get older, the bones resist PTH from the parathyroid gland (Thyroid) to make more bone-forming cells. Negative fields increase this function. ...
... • As we get older, the bones resist PTH from the parathyroid gland (Thyroid) to make more bone-forming cells. Negative fields increase this function. ...
Blood 1 - biologyonline.us
... enzyme in RBC (carbonic anhydrase) catalyzes a reaction that joins CO2 and water CO2 + H2O ===> HCO3 (carbonic acid) carbonic acid dissolved in water forms bicarbonate ions ( HCO3-) bicarbonate ion diffuses out of the RBC and serves to transport CO 2 in the blood plasma bicarbonate ions are also imp ...
... enzyme in RBC (carbonic anhydrase) catalyzes a reaction that joins CO2 and water CO2 + H2O ===> HCO3 (carbonic acid) carbonic acid dissolved in water forms bicarbonate ions ( HCO3-) bicarbonate ion diffuses out of the RBC and serves to transport CO 2 in the blood plasma bicarbonate ions are also imp ...
Five Kingdoms of Living Things
... a. the act of placing objects in groups based on characteristics 3. Scientists use both of these to organize living organisms. 4. The largest group living things are placed in is a kingdom (there are 5). 5. The smallest classification group is the species. The second smallest is the genus. ...
... a. the act of placing objects in groups based on characteristics 3. Scientists use both of these to organize living organisms. 4. The largest group living things are placed in is a kingdom (there are 5). 5. The smallest classification group is the species. The second smallest is the genus. ...
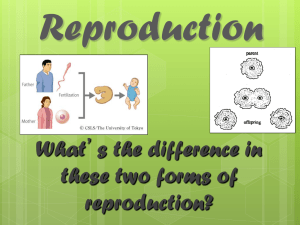
Reproduction Notes
... A parent organism produces one or more new organisms that are identical to the parent and live independently of the parent ...
... A parent organism produces one or more new organisms that are identical to the parent and live independently of the parent ...
Seaweed Notes II
... Marine Flowering Plants • There are many terrestrial flowering plants, but only a few marine flowering plants. • These do have true roots, stems and leaves. –They need specialized tissues to transport water, nutrients, and food. ...
... Marine Flowering Plants • There are many terrestrial flowering plants, but only a few marine flowering plants. • These do have true roots, stems and leaves. –They need specialized tissues to transport water, nutrients, and food. ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are