Biology (SPA)
... Overview A basic characteristic of life is the hierarchy of structural order within the organism. Robert Hooke (1635–1703), one of the first scientists to use a microscope to examine pond water, cork and other things, was the first to refer to the cavities he saw in cork as ‘cells’, Latin for chambe ...
... Overview A basic characteristic of life is the hierarchy of structural order within the organism. Robert Hooke (1635–1703), one of the first scientists to use a microscope to examine pond water, cork and other things, was the first to refer to the cavities he saw in cork as ‘cells’, Latin for chambe ...
Equine I - Internal Organs
... • Major organs include: • Male reproductive organs which lie toward the back and at the base of the pelvic cavity; OR, • Female reproductive organs extending from the back of the cavity to near the abdominal cavity. ...
... • Major organs include: • Male reproductive organs which lie toward the back and at the base of the pelvic cavity; OR, • Female reproductive organs extending from the back of the cavity to near the abdominal cavity. ...
Biology Class IX for SA-I 2016-17
... respected sir Shri. K. L. Nagaraju, Retd-AC, KVS RO Bangalore and respected sir Shri M.K. Kulshreshtha, Retd-AC, KVS RO Chandigarh for their blessings, motivation and encouragement in bringing out this project in such an excellent form. I also extend my special thanks to respected sir Shri. P. S. Ra ...
... respected sir Shri. K. L. Nagaraju, Retd-AC, KVS RO Bangalore and respected sir Shri M.K. Kulshreshtha, Retd-AC, KVS RO Chandigarh for their blessings, motivation and encouragement in bringing out this project in such an excellent form. I also extend my special thanks to respected sir Shri. P. S. Ra ...
Chapter 29 - Palm Beach State College
... • Polyspermy—fertilization by two or more sperm which would produce a doomed fertilized egg • Two mechanisms to prevent polyspermy – Fast block: binding of the sperm to the egg opens Na+ channels in egg membrane • Inflow of Na+ depolarizes membrane and inhibits the attachment of any more sperm ...
... • Polyspermy—fertilization by two or more sperm which would produce a doomed fertilized egg • Two mechanisms to prevent polyspermy – Fast block: binding of the sperm to the egg opens Na+ channels in egg membrane • Inflow of Na+ depolarizes membrane and inhibits the attachment of any more sperm ...
Chapter 26
... This evolutionary tree will show our best understanding of the way in which animal phyla are related to one another. For now, focus on tracing a few important evolutionary trends and pat¬ terns as you move from one animal phylum to the next. The levels of organization become higher as animals be¬ co ...
... This evolutionary tree will show our best understanding of the way in which animal phyla are related to one another. For now, focus on tracing a few important evolutionary trends and pat¬ terns as you move from one animal phylum to the next. The levels of organization become higher as animals be¬ co ...
Critical Content/Concept Web
... Students will Know… 1. The anatomical structure of the heart. 2. The major vessels traveling into and away from the heart. 3. The arteries carry blood away from the heart. 4. The veins carry blood toward the heart. 5. Blood components and their function. 6. The anatomical structure of the respirator ...
... Students will Know… 1. The anatomical structure of the heart. 2. The major vessels traveling into and away from the heart. 3. The arteries carry blood away from the heart. 4. The veins carry blood toward the heart. 5. Blood components and their function. 6. The anatomical structure of the respirator ...
Chapter 42 Respiration
... • Overview: Trading with the Environment • Every organism must exchange materials with its environment –And this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level ...
... • Overview: Trading with the Environment • Every organism must exchange materials with its environment –And this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level ...
COMPLETE BIOLOGY Table of contents I. Chemistry II. Cells III
... Cell doctrine/theory: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure, function, and organization in all organisms. 3. All cells come from preexisting, living cells. 4. Cells carry hereditary information RNA world hypothesis proposes that self-re ...
... Cell doctrine/theory: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure, function, and organization in all organisms. 3. All cells come from preexisting, living cells. 4. Cells carry hereditary information RNA world hypothesis proposes that self-re ...
Renal Physiology - part 2
... are also glucose co-transporters (sodium glucose transporters, SGLTs). These couple the movement of Na+ ions down their concentration gradient into the cells with the movement of glucose molecules against their concentration gradient into the cells. This is an example of secondary active transport. ...
... are also glucose co-transporters (sodium glucose transporters, SGLTs). These couple the movement of Na+ ions down their concentration gradient into the cells with the movement of glucose molecules against their concentration gradient into the cells. This is an example of secondary active transport. ...
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... The occurrence of both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, even though they are likely taking place at different rates at different times, also sets up cycles not possible in animals. Waste materials released by one process could become nutrients for the other. For instance, oxygen released by ...
... The occurrence of both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, even though they are likely taking place at different rates at different times, also sets up cycles not possible in animals. Waste materials released by one process could become nutrients for the other. For instance, oxygen released by ...
5 REASONS WHY THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM IS IMPORTANT TO
... and F and all our essential fatty acids. This is all needed to maintain good health, eyesight, bone and skin structure, and more! 4. HEALTHY SINUSES A healthy lymphatic system performs drainage functions in the body, as it drains out accumulated fluid in the sinuses and thus relief the sinus pressur ...
... and F and all our essential fatty acids. This is all needed to maintain good health, eyesight, bone and skin structure, and more! 4. HEALTHY SINUSES A healthy lymphatic system performs drainage functions in the body, as it drains out accumulated fluid in the sinuses and thus relief the sinus pressur ...
2.germ disc differentiation(20160108).
... In general terms it may be stated that the ectoderm gives rise to those organs and structures that maintain contact with the outside world. ...
... In general terms it may be stated that the ectoderm gives rise to those organs and structures that maintain contact with the outside world. ...
heart muscle
... the human body. Each type of tissue has its own special function but joins with others to serve a larger common purpose. * The human body is made of many kinds of tissue. * The heart is an example of an organ. It has a pump made mostly of tissue. * The heart is part of a system. The circulatory syst ...
... the human body. Each type of tissue has its own special function but joins with others to serve a larger common purpose. * The human body is made of many kinds of tissue. * The heart is an example of an organ. It has a pump made mostly of tissue. * The heart is part of a system. The circulatory syst ...
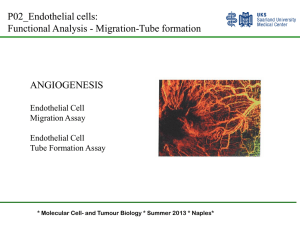
Microvascular Endothelial Cells
... • Response of Macrophage Chemoattractant Protein 1 (MCP-1)-induced chemotaxis in monocytic cells: • Calcein-prelabeled cells (top chamber) were incubated with 25 nM MCP-1 (bottom chamber) • Bottom fluorescence was measured at varying time points • Data on the graph are representative for a typical e ...
... • Response of Macrophage Chemoattractant Protein 1 (MCP-1)-induced chemotaxis in monocytic cells: • Calcein-prelabeled cells (top chamber) were incubated with 25 nM MCP-1 (bottom chamber) • Bottom fluorescence was measured at varying time points • Data on the graph are representative for a typical e ...
The Respiratory System
... – Alveolar macrophages (dust cells) - removal of particulates and debris – Fibroblasts - surrounding reticular and elastic connective tissue • Alveolar wall plus capillary wall about 0.5 m - four layers – respiratory membrane – Alveolar wall, epithelial basement membrane, capillary basement membran ...
... – Alveolar macrophages (dust cells) - removal of particulates and debris – Fibroblasts - surrounding reticular and elastic connective tissue • Alveolar wall plus capillary wall about 0.5 m - four layers – respiratory membrane – Alveolar wall, epithelial basement membrane, capillary basement membran ...
The Respiratory System Respiration • Exchange of O2 and CO2
... – Alveolar macrophages (dust cells) - removal of particulates and debris – Fibroblasts - surrounding reticular and elastic connective tissue • Alveolar wall plus capillary wall about 0.5 µm - four layers – respiratory membrane – Alveolar wall, epithelial basement membrane, capillary basement membran ...
... – Alveolar macrophages (dust cells) - removal of particulates and debris – Fibroblasts - surrounding reticular and elastic connective tissue • Alveolar wall plus capillary wall about 0.5 µm - four layers – respiratory membrane – Alveolar wall, epithelial basement membrane, capillary basement membran ...
Unit C: Body Systems
... Scott, Ann Senisi and Elizabeth Fong. Body Structures & Functions. Delmar Publishers, Latest ...
... Scott, Ann Senisi and Elizabeth Fong. Body Structures & Functions. Delmar Publishers, Latest ...
histology blood vascular system
... • They are found where free exchange of substances or even cells between bloodstream and organ is advantageous. ARTERIES Depending on their size, the arteries are classified into the following three main types: • Arterioles and small arteries. • Medium size arteries. • Large arteries. The structure ...
... • They are found where free exchange of substances or even cells between bloodstream and organ is advantageous. ARTERIES Depending on their size, the arteries are classified into the following three main types: • Arterioles and small arteries. • Medium size arteries. • Large arteries. The structure ...
Introduction - Harris Training Institute, Inc.
... Cell Theory – Overview Basic unit of all living tissues or organisms All living organisms made of cells Cellular function is essential process of living things Cells have several functioning structures called organelle, that carry on work of cell Structure and Function – Cells Are building ...
... Cell Theory – Overview Basic unit of all living tissues or organisms All living organisms made of cells Cellular function is essential process of living things Cells have several functioning structures called organelle, that carry on work of cell Structure and Function – Cells Are building ...
Implantation
... Formation of chorionic cavity or extraembryonic cavity Development of connecting stalk (umbilical cord) Trophoblast forms villous structures - „Primary chorionic villi‟ • Prechordal plate develop as thickening of hypoblast (14days) ...
... Formation of chorionic cavity or extraembryonic cavity Development of connecting stalk (umbilical cord) Trophoblast forms villous structures - „Primary chorionic villi‟ • Prechordal plate develop as thickening of hypoblast (14days) ...
File - Mizzou Pre
... Cell doctrine/theory: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure, function, and organization in all organisms. 3. All cells come from preexisting, living cells. 4. Cells carry hereditary information RNA world hypothesis proposes that self-re ...
... Cell doctrine/theory: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure, function, and organization in all organisms. 3. All cells come from preexisting, living cells. 4. Cells carry hereditary information RNA world hypothesis proposes that self-re ...