Intro TOC, etc. FINAL 7/12 - South Carolina Sea Grant Consortium
... pigments present in the phytoplankton living there. “Red tides” get their name from dinoflagellates that may impart a reddish color to the water whenever there is a bloom, or rapid increase in abundance, of these organisms. In the absence of large amounts of phytoplankton, as is often the case in tr ...
... pigments present in the phytoplankton living there. “Red tides” get their name from dinoflagellates that may impart a reddish color to the water whenever there is a bloom, or rapid increase in abundance, of these organisms. In the absence of large amounts of phytoplankton, as is often the case in tr ...
File - Ms. Daley Science
... NATURE OF SCIENCE/SCIENCE AS A PROCESS (Chapter 1) The Nature of Science 1. Describe the steps of the scientific method. Use and define the following terms in your explanation: control group (positive and negative), hypothesis, variable (independent, dependent, and controlled), and experimental set- ...
... NATURE OF SCIENCE/SCIENCE AS A PROCESS (Chapter 1) The Nature of Science 1. Describe the steps of the scientific method. Use and define the following terms in your explanation: control group (positive and negative), hypothesis, variable (independent, dependent, and controlled), and experimental set- ...
2013 - SAASTA
... strand of a DNA double helix, relaxation occurs, and then the cut strand is reannealed. Cutting one strand allows the part of the molecule on one side of the cut to rotate around the uncut strand, thereby reducing stress from too much or too little twist in the helix. Topoisomerase II cuts both stra ...
... strand of a DNA double helix, relaxation occurs, and then the cut strand is reannealed. Cutting one strand allows the part of the molecule on one side of the cut to rotate around the uncut strand, thereby reducing stress from too much or too little twist in the helix. Topoisomerase II cuts both stra ...
Regulating the Internal Environment
... freshwater hypotonic water flow into cells & salt loss ...
... freshwater hypotonic water flow into cells & salt loss ...
the cell cycle
... Cell differentiation and Stem Cells We have seen that cells specialize in order to perform different functions in our bodies. The process that produces these specialized cells is called ________________________________. It is a process that is directed by the ___________________________ of the cell ...
... Cell differentiation and Stem Cells We have seen that cells specialize in order to perform different functions in our bodies. The process that produces these specialized cells is called ________________________________. It is a process that is directed by the ___________________________ of the cell ...
YES NC - WordPress.com
... organism as a whole system comprised of many parts that work together to keep the body stable through the process of homeostasis. Students will then explore homeostasis through stimulus and response—how organisms respond to internal or external changes in order to maintain internal balance. Througho ...
... organism as a whole system comprised of many parts that work together to keep the body stable through the process of homeostasis. Students will then explore homeostasis through stimulus and response—how organisms respond to internal or external changes in order to maintain internal balance. Througho ...
Biology 20 Year Review
... Survival of the Fittest – surviving organisms are ones better able to compete, survive and reproduce. The others die without leaving offspring (natural selection) Speciation – over numerous generations, new species arise by accumulation of inherited variations of traits; considered new species when ...
... Survival of the Fittest – surviving organisms are ones better able to compete, survive and reproduce. The others die without leaving offspring (natural selection) Speciation – over numerous generations, new species arise by accumulation of inherited variations of traits; considered new species when ...
Cell Structure
... than the dot on this i. A human red blood cell is about one-tenth the size of a human egg cell. A bacterium is even smaller-8,OOO of the smallest bacteria can fit inside one of your red blood cells. A cell's shape might tell you something about its function. The nerve cell in Figure 1 has many fine ...
... than the dot on this i. A human red blood cell is about one-tenth the size of a human egg cell. A bacterium is even smaller-8,OOO of the smallest bacteria can fit inside one of your red blood cells. A cell's shape might tell you something about its function. The nerve cell in Figure 1 has many fine ...
2001 AP Biology Scoring Guidelines - AP Central
... Competition — intraspecific struggle for existence Differential Reproduction — reproductive success of variants Generations — time needed for evolution to occur Elaboration — expansion of Darwin’s ideas such as the effects of environmental change or artificial selection or good, linked example ...
... Competition — intraspecific struggle for existence Differential Reproduction — reproductive success of variants Generations — time needed for evolution to occur Elaboration — expansion of Darwin’s ideas such as the effects of environmental change or artificial selection or good, linked example ...
Phylum Cnidaria
... After prey is hit with a nematocysts or cnidocytes (tentacles) the cnidarian brings it to its mouth (it’s only opening). It then eventually makes it’s way to the gastrovascular cavity. ...
... After prey is hit with a nematocysts or cnidocytes (tentacles) the cnidarian brings it to its mouth (it’s only opening). It then eventually makes it’s way to the gastrovascular cavity. ...
CnidariaNotes
... After prey is hit with a nematocysts or cnidocytes (tentacles) the cnidarian brings it to its mouth (it’s only opening). It then eventually makes it’s way to the gastrovascular cavity. ...
... After prey is hit with a nematocysts or cnidocytes (tentacles) the cnidarian brings it to its mouth (it’s only opening). It then eventually makes it’s way to the gastrovascular cavity. ...
Biology Exam Review
... A DNA molecule with the base sequence A-G-C-T-C-A was used as a template for the synthesis of a messenger RNA molecule. Which base sequence correctly represents the corresponding portion of this RNA molecule? A. ...
... A DNA molecule with the base sequence A-G-C-T-C-A was used as a template for the synthesis of a messenger RNA molecule. Which base sequence correctly represents the corresponding portion of this RNA molecule? A. ...
Respiration
... center that detects the concentration of CO2 in the blood. When CO2 increases as a result of exercise, for example, the breathing rate and heart rate increase. When there is little CO2 in the blood, the nervous system slows the breathing rate. Gas exchange in the lungs—the little picture Gases are e ...
... center that detects the concentration of CO2 in the blood. When CO2 increases as a result of exercise, for example, the breathing rate and heart rate increase. When there is little CO2 in the blood, the nervous system slows the breathing rate. Gas exchange in the lungs—the little picture Gases are e ...
Bio 20 Year Review Key
... Survival of the Fittest – surviving organisms are ones better able to compete, survive and reproduce. The others die without leaving offspring (natural selection) Speciation – over numerous generations, new species arise by accumulation of inherited variations of traits; considered new species when ...
... Survival of the Fittest – surviving organisms are ones better able to compete, survive and reproduce. The others die without leaving offspring (natural selection) Speciation – over numerous generations, new species arise by accumulation of inherited variations of traits; considered new species when ...
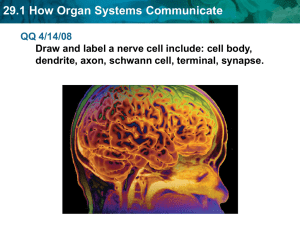
29.1 How Organ Systems Communicate - Morales Biology
... The nervous and endocrine systems have different methods and rates of communication. • The nervous system works quickly, using chemical and electrical signals. – interconnected network of cells – signals move through cells – divided into central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PN ...
... The nervous and endocrine systems have different methods and rates of communication. • The nervous system works quickly, using chemical and electrical signals. – interconnected network of cells – signals move through cells – divided into central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PN ...
Alan`s DAT Biology Notes edited by scsc7211
... i. Bulbs- split to form several bulbs (tulips and daffodils) ii. Tubers- underground stems with buds (eyes of potatoes) iii. Runners- stems running above and along ground that produce new roots and upright stems (strawberry and lawn grasses) iv. Rhizomes (stolons): woody, underground stems (ferns an ...
... i. Bulbs- split to form several bulbs (tulips and daffodils) ii. Tubers- underground stems with buds (eyes of potatoes) iii. Runners- stems running above and along ground that produce new roots and upright stems (strawberry and lawn grasses) iv. Rhizomes (stolons): woody, underground stems (ferns an ...
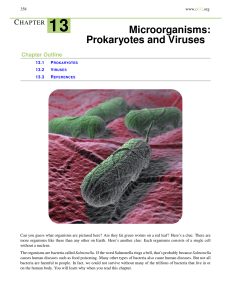
13 Microorganisms: Prokaryotes and Viruses
... Scientists still know relatively little about Archaea. This is partly because they are hard to grow in the lab. Many live inside the bodies of animals, including humans. However, none are known for certain to cause disease. Archaea were first discovered in extreme environments. For example, some wer ...
... Scientists still know relatively little about Archaea. This is partly because they are hard to grow in the lab. Many live inside the bodies of animals, including humans. However, none are known for certain to cause disease. Archaea were first discovered in extreme environments. For example, some wer ...
The Hierarchy of Structural Organization
... Homeostasis and Negative Feedback • Receptor—senses change in the body (e.g., stretch receptors that monitor blood pressure) • Integrating (control) center—control center that processes the sensory information, “makes a decision,” and directs the response (e.g., cardiac center of the brain) ...
... Homeostasis and Negative Feedback • Receptor—senses change in the body (e.g., stretch receptors that monitor blood pressure) • Integrating (control) center—control center that processes the sensory information, “makes a decision,” and directs the response (e.g., cardiac center of the brain) ...
Cell Structure - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... Use a genetic diagram to show how they could have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use the symbol A for the dominant allele and the symbol a for the recessive allele. ...
... Use a genetic diagram to show how they could have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use the symbol A for the dominant allele and the symbol a for the recessive allele. ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... itself and be resistant to it. Next time if the same antibiotic is used on an infection by this ...
... itself and be resistant to it. Next time if the same antibiotic is used on an infection by this ...
File
... 3. The terms in order of increasing complexity are tissue, organ, and system. 4. Answers will vary. Examples of tissue include nerve tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue. Examples of organs include skin, heart, liver, lungs, stomach, and intestines. Examples of systems include the circulator ...
... 3. The terms in order of increasing complexity are tissue, organ, and system. 4. Answers will vary. Examples of tissue include nerve tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue. Examples of organs include skin, heart, liver, lungs, stomach, and intestines. Examples of systems include the circulator ...
Grade Level / Course:
... Outcomes and Components Grade Level / Course: 7th Grade Life Science Subject: Science Course Purpose: Students will apply scientific knowledge to support explanations while designing and conducting experiments including analyzing and interpreting data. Students will develop and use models to suppor ...
... Outcomes and Components Grade Level / Course: 7th Grade Life Science Subject: Science Course Purpose: Students will apply scientific knowledge to support explanations while designing and conducting experiments including analyzing and interpreting data. Students will develop and use models to suppor ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... • As the glycoproteins pass from layer to layer of the Golgi, they are modified chemically. • When they reach the outermost layer, they are packaged in bits of Golgi membrane, which bud off and form transport vesicles. • Vesicles may move to the cell membrane and release its contents to the outside ...
... • As the glycoproteins pass from layer to layer of the Golgi, they are modified chemically. • When they reach the outermost layer, they are packaged in bits of Golgi membrane, which bud off and form transport vesicles. • Vesicles may move to the cell membrane and release its contents to the outside ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.