Unit 2 - Cells and Systems Learning Pack (Science In Action 8
... inside the organism to sustain its life are called the organism’s metabolism. Responding To The Environment A stimulus is anything that causes a response in an organism. The organism’s reaction to this stimulus is called a response. Growth and Development Organisms have the ability to replace some c ...
... inside the organism to sustain its life are called the organism’s metabolism. Responding To The Environment A stimulus is anything that causes a response in an organism. The organism’s reaction to this stimulus is called a response. Growth and Development Organisms have the ability to replace some c ...
Life Science
... ● Identify the factors that affect the number and types of organisms an ecosystem can support are food availability, abiotic factors such as quantity of light and water, temperature and temperature range, soil composition, disease, competitions from other organisms, and predation (DOK 2) Response to ...
... ● Identify the factors that affect the number and types of organisms an ecosystem can support are food availability, abiotic factors such as quantity of light and water, temperature and temperature range, soil composition, disease, competitions from other organisms, and predation (DOK 2) Response to ...
Plant Cell
... • Specialized cells have physical and chemical differences that allow each type to perform one job very well. • These cells help keep dirt out of the lungs. – The orange goblet cells secrete mucus ...
... • Specialized cells have physical and chemical differences that allow each type to perform one job very well. • These cells help keep dirt out of the lungs. – The orange goblet cells secrete mucus ...
revision cards - Thomas Clarkson Academy
... there must therefore be considerable competition for survival between the organisms Survival - those with advantageous characteristics are more likely to survive this struggle Advantageous characteristics inherited – better adapted organisms are more likely to reproduce successfully passing on the a ...
... there must therefore be considerable competition for survival between the organisms Survival - those with advantageous characteristics are more likely to survive this struggle Advantageous characteristics inherited – better adapted organisms are more likely to reproduce successfully passing on the a ...
Revised NEW Item Specifications October 2007 Biology
... Look at the list of organism characteristics below. Which two statements correctly differentiate Archaebacteria from other bacteria? ...
... Look at the list of organism characteristics below. Which two statements correctly differentiate Archaebacteria from other bacteria? ...
Kingdom Animalia
... circulatory system, in which blood-like circulatory fluid is pumped from vessels in the body into the body cavity, and then is returned to the vessels in the body into the body cavity, and then is returned to the vessels. In a closed circulatory system, blood circulates through the body in tubular v ...
... circulatory system, in which blood-like circulatory fluid is pumped from vessels in the body into the body cavity, and then is returned to the vessels in the body into the body cavity, and then is returned to the vessels. In a closed circulatory system, blood circulates through the body in tubular v ...
16photosynthesis2009..
... Like animals, plants need energy to live Unlike animals, plants don’t need to eat ...
... Like animals, plants need energy to live Unlike animals, plants don’t need to eat ...
Unit 1 Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... of organisms that look more or less like their parents. How are these characteristics passed on from generation to generation? You have already learned that the characteristics of organisms vary greatly within a species. How does reproduction allow for variation? Not only do the physical traits of o ...
... of organisms that look more or less like their parents. How are these characteristics passed on from generation to generation? You have already learned that the characteristics of organisms vary greatly within a species. How does reproduction allow for variation? Not only do the physical traits of o ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Jones
... of organisms that look more or less like their parents. How are these characteristics passed on from generation to generation? You have already learned that the characteristics of organisms vary greatly within a species. How does reproduction allow for variation? Not only do the physical traits of o ...
... of organisms that look more or less like their parents. How are these characteristics passed on from generation to generation? You have already learned that the characteristics of organisms vary greatly within a species. How does reproduction allow for variation? Not only do the physical traits of o ...
Cell Simulation Paper - Engineering Computing Facility
... The E-Cell project was initiated in 1996 at the ShonanFujisawa Campus of Keio University in Fujisawa, Japan. The aim was to directly address the challenging task of whole-cell modeling [3]. E-Cell is essentially a computer software environment for modeling and simulation of the cell. It is a generic ...
... The E-Cell project was initiated in 1996 at the ShonanFujisawa Campus of Keio University in Fujisawa, Japan. The aim was to directly address the challenging task of whole-cell modeling [3]. E-Cell is essentially a computer software environment for modeling and simulation of the cell. It is a generic ...
Ninth Grade Biology
... Main ideas: A habitat differs from a niche. Section 14.2: Community Interactions Key concept: Organisms interact as individuals and as populations. Main ideas: Competition and predation are two important ways in which organisms interact. Symbiosis is a close relationship between species. Section 14. ...
... Main ideas: A habitat differs from a niche. Section 14.2: Community Interactions Key concept: Organisms interact as individuals and as populations. Main ideas: Competition and predation are two important ways in which organisms interact. Symbiosis is a close relationship between species. Section 14. ...
Molecular Genetics
... when in fact Wilkins and Franklin were peers in the Randall laboratory. And it was Franklin alone whom Randall had given the task of elucidating DNA's structure. The technique with which Rosalind Franklin set out to do this is called X-ray crystallography. With this technique, the locations of atoms ...
... when in fact Wilkins and Franklin were peers in the Randall laboratory. And it was Franklin alone whom Randall had given the task of elucidating DNA's structure. The technique with which Rosalind Franklin set out to do this is called X-ray crystallography. With this technique, the locations of atoms ...
Yaron Fuchs, Ph.D. - Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine
... - Perez-Garijo A., Fuchs Y. and Steller H., (2013): Apoptotic cells can induce non-autonomous apoptosis through the TNF-pathway. eLife 2013, 2, e01004. (Impact factor 8.3) - Fuchs Y., Brunwasser M., Haif S., Hadad J., Shneyer B., Goldshmidt-Tran O., Korsensky L., Abed M., Zisman-Rosen S., Koren L., ...
... - Perez-Garijo A., Fuchs Y. and Steller H., (2013): Apoptotic cells can induce non-autonomous apoptosis through the TNF-pathway. eLife 2013, 2, e01004. (Impact factor 8.3) - Fuchs Y., Brunwasser M., Haif S., Hadad J., Shneyer B., Goldshmidt-Tran O., Korsensky L., Abed M., Zisman-Rosen S., Koren L., ...
What is an Animal? Animals: General Characteristics 1. by far, the
... most multicellular forms have ways to protect themselves against pathogens and disease (plants: sap protects damaged areas and prevents invasion; also produce many compounds that discourage herbivores and parasites) animals are much more active and much more likely to encounter pathogens and parasit ...
... most multicellular forms have ways to protect themselves against pathogens and disease (plants: sap protects damaged areas and prevents invasion; also produce many compounds that discourage herbivores and parasites) animals are much more active and much more likely to encounter pathogens and parasit ...
content.njctl.org
... 1. The human heart pumps blood through the circulatory system, delivering oxygen and other molecules to body’s cells and removing waste. a. Relate the process of diffusion, osmosis, and cellular respiration to the circulatory system. b. The circulatory system, like all other body systems, is interco ...
... 1. The human heart pumps blood through the circulatory system, delivering oxygen and other molecules to body’s cells and removing waste. a. Relate the process of diffusion, osmosis, and cellular respiration to the circulatory system. b. The circulatory system, like all other body systems, is interco ...
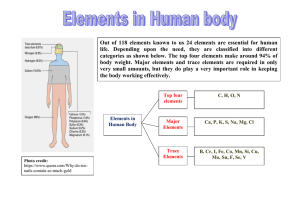
Elements in the Human Body
... Biological role: The heme group present in hemoglobin binds with oxygen and transport it from lungs to tissues. Molecular oxygen is essential for cellular respiration in all organisms. It is used as an electron acceptor in mitochondria present ...
... Biological role: The heme group present in hemoglobin binds with oxygen and transport it from lungs to tissues. Molecular oxygen is essential for cellular respiration in all organisms. It is used as an electron acceptor in mitochondria present ...
Cellular Respiration PPt
... Autotrophs are organisms that use energy from sunlight or from chemical bonds in inorganic substances to make organic compounds. Heterotrophs are organisms that must consume other organisms as food to get their energy. Regents Biology ...
... Autotrophs are organisms that use energy from sunlight or from chemical bonds in inorganic substances to make organic compounds. Heterotrophs are organisms that must consume other organisms as food to get their energy. Regents Biology ...
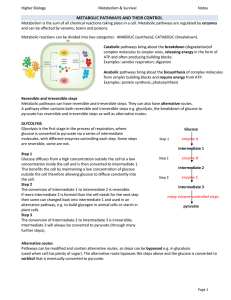
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... a substance out of a body is egestion or elimination. Removal of urine or feces from a body is egestion. Many references use the term excretion for this process as well. On occasion, it may be difficult to choose the best term to describe the removal of a particular substance. Tears in many marine o ...
... a substance out of a body is egestion or elimination. Removal of urine or feces from a body is egestion. Many references use the term excretion for this process as well. On occasion, it may be difficult to choose the best term to describe the removal of a particular substance. Tears in many marine o ...
Unit 2 – pupil notes
... Cells have different areas or compartments (organelles) for different functions, increasing efficiency. The cell itself, and all its organelles, are bounded by membranes. The cell membrane separates the internal contents of the cell from its surroundings and regulates entry and exit of materials. Th ...
... Cells have different areas or compartments (organelles) for different functions, increasing efficiency. The cell itself, and all its organelles, are bounded by membranes. The cell membrane separates the internal contents of the cell from its surroundings and regulates entry and exit of materials. Th ...
SI 10/19/08 Exam 2 Review 1. Which of the following phylogenetic
... 26. Which of the following is the best description of human evolution: a. Humans did not evolve from gorillas b. Humans did not evolve from chimps c. Humans did not evolve from any extant (still living) primates d. Last common ancestor (a primate) was 5-7 million years ago e. All of the above are co ...
... 26. Which of the following is the best description of human evolution: a. Humans did not evolve from gorillas b. Humans did not evolve from chimps c. Humans did not evolve from any extant (still living) primates d. Last common ancestor (a primate) was 5-7 million years ago e. All of the above are co ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.