Homeostasis - thephysicsteacher.ie
... Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment in an organism. Homeostasis allows cells, and therefore organisms, to function at their most efficient rate e.g. 37oC for humans; to function independently of external conditions e.g. humans in winter (frogs can’t control internal ...
... Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment in an organism. Homeostasis allows cells, and therefore organisms, to function at their most efficient rate e.g. 37oC for humans; to function independently of external conditions e.g. humans in winter (frogs can’t control internal ...
Module3_Student
... algae grow to lengths of up to 50 m. This species includes a number of large plants generally called kelp. Most species of kelp can be divided into three parts: holdfast, stipe and frond. Many brown algae have floats, or pneumatocysts, located either on the fronds or stipe. Pneumatocysts are filled ...
... algae grow to lengths of up to 50 m. This species includes a number of large plants generally called kelp. Most species of kelp can be divided into three parts: holdfast, stipe and frond. Many brown algae have floats, or pneumatocysts, located either on the fronds or stipe. Pneumatocysts are filled ...
Body System Checklist
... –T-cells attack invaded body cells –Each B-cell, T-cell, and antibody is specific to what it attacks ...
... –T-cells attack invaded body cells –Each B-cell, T-cell, and antibody is specific to what it attacks ...
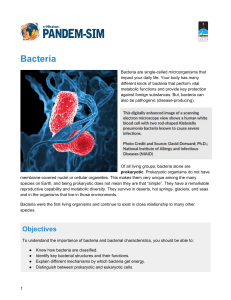
Bacteria - Pandem-Sim
... 3) flagella—a whip-like structure used for movement. Some, but not all, bacteria have one or more flagella. These structures move in a circular motion to propel the bacteria forward. Bacteria can have multiple flagella that surround the cell, a few flagella on one or both ends of the cell, or a sin ...
... 3) flagella—a whip-like structure used for movement. Some, but not all, bacteria have one or more flagella. These structures move in a circular motion to propel the bacteria forward. Bacteria can have multiple flagella that surround the cell, a few flagella on one or both ends of the cell, or a sin ...
Human Body Systems Lesson Guide
... that perform different functions. These cells join together to form tissues that give organs their structure and enable the organs to perform specialized functions within organ systems ...
... that perform different functions. These cells join together to form tissues that give organs their structure and enable the organs to perform specialized functions within organ systems ...
FINAL REVIEW GUIDE
... Vestigial examples What is phylogeny and cladograms Classification Know who was responsible for our current classification system Who is Linnaeus, Aristotle What is Taxonomy and what language do we use What is a taxa and how do we separate organisms from Domain to species Bacteria/Viruse ...
... Vestigial examples What is phylogeny and cladograms Classification Know who was responsible for our current classification system Who is Linnaeus, Aristotle What is Taxonomy and what language do we use What is a taxa and how do we separate organisms from Domain to species Bacteria/Viruse ...
Most animals are invertebrates.
... are animals that do not have backbones. In fact, invertebrates do not have any bone tissue at all. Invertebrates can be found just about everywhere, from frozen tundra to tropical forests. Some invertebrates live in water, while others survive in deserts where there is almost no water. Many inverteb ...
... are animals that do not have backbones. In fact, invertebrates do not have any bone tissue at all. Invertebrates can be found just about everywhere, from frozen tundra to tropical forests. Some invertebrates live in water, while others survive in deserts where there is almost no water. Many inverteb ...
3 | biological macromolecules
... smaller organic molecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that wate ...
... smaller organic molecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that wate ...
What are the major organ systems found in vertebrate animals?
... How is the animal body organized in terms of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems? Animals are very complex organisms; yet, the structural basis of all animals begins with cells. A. A cell is the most basic structure of an animal and is considered the building block from which an animal’s bo ...
... How is the animal body organized in terms of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems? Animals are very complex organisms; yet, the structural basis of all animals begins with cells. A. A cell is the most basic structure of an animal and is considered the building block from which an animal’s bo ...
Fluid dynamics of self-propelled microorganisms, from individuals to
... are not analogs. The viscous forces are described by Slender Body Theory and extensions of Faxén’s and Stokes’ laws (Pozrikidis 1997). A key feature of these dynamics is that for an isolated swimmer the net propulsive force of the flagella must equal the opposing drag force of the body connected to ...
... are not analogs. The viscous forces are described by Slender Body Theory and extensions of Faxén’s and Stokes’ laws (Pozrikidis 1997). A key feature of these dynamics is that for an isolated swimmer the net propulsive force of the flagella must equal the opposing drag force of the body connected to ...
Patterns in nature
... Lysosomes were first described in the 1950s. They are smaller than mitochondria and are enclosed by single membranes. The membrane does not permit the movement of enzymes from within and is capable of resisting their digestive action. Lysosomes are more commonly found in animal cells. The lysosome i ...
... Lysosomes were first described in the 1950s. They are smaller than mitochondria and are enclosed by single membranes. The membrane does not permit the movement of enzymes from within and is capable of resisting their digestive action. Lysosomes are more commonly found in animal cells. The lysosome i ...
Sickle Cell Workshop
... Research in cognition has demonstrated that learning is most effective when topics are of human interest, relate to one another (theme-oriented), and relate to previously learned concepts (scaffolding). A focus on sickle cell anemia satisfies these criteria and can facilitate the teaching of a varie ...
... Research in cognition has demonstrated that learning is most effective when topics are of human interest, relate to one another (theme-oriented), and relate to previously learned concepts (scaffolding). A focus on sickle cell anemia satisfies these criteria and can facilitate the teaching of a varie ...
attached example
... Discuss the standard growth curve for a bacterial population Compare the use of heat and chemical agents in controlling bacteria Select appropriate techniques for sterilizing microbiological materials ...
... Discuss the standard growth curve for a bacterial population Compare the use of heat and chemical agents in controlling bacteria Select appropriate techniques for sterilizing microbiological materials ...
as a PDF
... in the right types of cells in the right numbers in the right places in the organism. Another functional requirement is that multicellular function be restored rapidly. The urgency depends on the vulnerability of the embryo. Planktonic embryos receive less protection than brooded or encapsulated emb ...
... in the right types of cells in the right numbers in the right places in the organism. Another functional requirement is that multicellular function be restored rapidly. The urgency depends on the vulnerability of the embryo. Planktonic embryos receive less protection than brooded or encapsulated emb ...
AP Biology Unit 9 Animal Structure and Function
... changing external conditions while maintaining a constant internal environment. To accomplish these tasks, animal cells are organized into systems that are specialized for particular functions. This unit focuses on the structure of these various systems and how they accomplish particular tasks. Cell ...
... changing external conditions while maintaining a constant internal environment. To accomplish these tasks, animal cells are organized into systems that are specialized for particular functions. This unit focuses on the structure of these various systems and how they accomplish particular tasks. Cell ...
2002 AP Biology Form B Scoring Guidelines - AP Central
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progra ...
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progra ...
8 - Hatboro
... like baking a layer cake," says Atala. "You're layering the cells one layer at a time, spreading these toppings." The bladder-to-be is then incubated at body temperature until the cells form functioning tissue. The whole process takes six to eight weeks. Solid organs with lots of blood vessels, such ...
... like baking a layer cake," says Atala. "You're layering the cells one layer at a time, spreading these toppings." The bladder-to-be is then incubated at body temperature until the cells form functioning tissue. The whole process takes six to eight weeks. Solid organs with lots of blood vessels, such ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... material. Contents of the vesicle can dump into the cytoplasm to be used for metabolic reactions, or be expelled from the cell (exocytosis). Some cells, especially some white blood cells, are phagocytes that conduct phagocytosis as a major function. This provides a major defense against invasion by ...
... material. Contents of the vesicle can dump into the cytoplasm to be used for metabolic reactions, or be expelled from the cell (exocytosis). Some cells, especially some white blood cells, are phagocytes that conduct phagocytosis as a major function. This provides a major defense against invasion by ...
Bio Diversity Project - Pleasantville High School
... consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer outside the plasma membrane of bacteria (but not Archaea), Eukaryotic cell walls made up of cellulose or chitin. Gram positive bacteria: have large amounts of peptidoglycan Gram negative bacteria have less peptidoglycan but more lip ...
... consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer outside the plasma membrane of bacteria (but not Archaea), Eukaryotic cell walls made up of cellulose or chitin. Gram positive bacteria: have large amounts of peptidoglycan Gram negative bacteria have less peptidoglycan but more lip ...
Cells and reproduction Jordanhill School S1 Science
... The sex cells are the cells that fuse together during sexual reproduction to form a new cell that will eventually form a new organism. The female sex cell is called the egg or ovum and is produced in the ovary. These round cells are the largest in the human body. They have a cell membrane, cytoplasm ...
... The sex cells are the cells that fuse together during sexual reproduction to form a new cell that will eventually form a new organism. The female sex cell is called the egg or ovum and is produced in the ovary. These round cells are the largest in the human body. They have a cell membrane, cytoplasm ...
1 Classification - Assets - Cambridge University Press
... c State one feature, visible on all of the animals in the drawings, which indicates that they are all reptiles. ...
... c State one feature, visible on all of the animals in the drawings, which indicates that they are all reptiles. ...
Release of February 2017 MCAS Biology Test Items
... The Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education is committed to working in partnership with schools to support a system that will prepare all students to succeed as productive and contributing members of our democratic society and the global economy. To assist in achieving this go ...
... The Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education is committed to working in partnership with schools to support a system that will prepare all students to succeed as productive and contributing members of our democratic society and the global economy. To assist in achieving this go ...
Class Introduction - Cedarville University
... – Central Metabolic cycle (A) • Basic replication • Pathway for fatty acid production ...
... – Central Metabolic cycle (A) • Basic replication • Pathway for fatty acid production ...
Homeostasis Across Body Systems
... likely to see a question centered on a theme like “transport of amterials” via the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems than a pure question on the excretory system for example. This rule is not iron-clad as 2 pure immune questions have been asked recently (2007 form B and 2005). The AP e ...
... likely to see a question centered on a theme like “transport of amterials” via the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems than a pure question on the excretory system for example. This rule is not iron-clad as 2 pure immune questions have been asked recently (2007 form B and 2005). The AP e ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.