a previous Learning Experience
... mass of M = 15 kg, a radius of R = 0.5 m, and a moment of inertia I = 15.0 kgm2 . What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the disk about its axis of rotation? ...
... mass of M = 15 kg, a radius of R = 0.5 m, and a moment of inertia I = 15.0 kgm2 . What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the disk about its axis of rotation? ...
Problem set 11
... Suppose the axis of the top makes an angle θ , 0 with the fixed direction of L. (a) h6i Find the angle α between the angular velocity vector Ω and angular momentum vector L (α is half the opening angle of the cone swept out by Ω). Express α in terms of θ , the principal moments of inertia and the ma ...
... Suppose the axis of the top makes an angle θ , 0 with the fixed direction of L. (a) h6i Find the angle α between the angular velocity vector Ω and angular momentum vector L (α is half the opening angle of the cone swept out by Ω). Express α in terms of θ , the principal moments of inertia and the ma ...
Physics 2414, Spring 2005 Group Exercise 10, Apr 28, 2005
... where τnet is the sum of all the torques acting on the rigid body, and α is the angular acceleration of the rigid body about the axis. ...
... where τnet is the sum of all the torques acting on the rigid body, and α is the angular acceleration of the rigid body about the axis. ...
Ch8-9
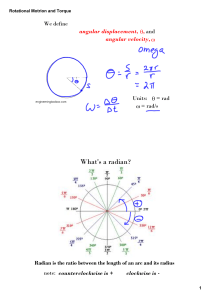
... • Torque, , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about some axis • F is the force • d is the lever arm (or moment arm) Fig 8.1, p.221 Slide 1 ...
... • Torque, , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about some axis • F is the force • d is the lever arm (or moment arm) Fig 8.1, p.221 Slide 1 ...
Click here for a short consolidation presentation on the basics of
... The centre of mass is the point where all of the mass of the object is concentrated. When an object is supported at its centre of mass it will remain in equilibrium. If the object is uniform, for example a meter stick, the center of mass will be at the exact geometric center; if the object is irreg ...
... The centre of mass is the point where all of the mass of the object is concentrated. When an object is supported at its centre of mass it will remain in equilibrium. If the object is uniform, for example a meter stick, the center of mass will be at the exact geometric center; if the object is irreg ...
TORQUE AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM 73. (11.3) Angular
... (In other words, the center of a force is such a point that the effect of the total torque about any given point, exerted on the system by another body, is as if the total force acted on the center of the force.) Example. Center of gravity. ...
... (In other words, the center of a force is such a point that the effect of the total torque about any given point, exerted on the system by another body, is as if the total force acted on the center of the force.) Example. Center of gravity. ...
Rotational Motrion and Torque - Parkway C-2
... Rotation - the object rotates about a fixed point. Every point on the object moves in a circle. ...
... Rotation - the object rotates about a fixed point. Every point on the object moves in a circle. ...
Rotational Inertia and Angular Momentum
... Because the direction of something rotating is hard to determine, physicists say that the direction of angular momentum is in the plane of the rotation. If this wheel was rotating, we would say its angular momentum is pointed in this direction. So it would want to stay rotating in that direction. ...
... Because the direction of something rotating is hard to determine, physicists say that the direction of angular momentum is in the plane of the rotation. If this wheel was rotating, we would say its angular momentum is pointed in this direction. So it would want to stay rotating in that direction. ...
Simple Biomechanical Models
... only if the effort force is applied to the axle. If the effort force is on the wheel (resistive on the axis) reverse this fraction. Nearly all musculoskeletal systems in the human body are third class levers. Systems like rotator cuff muscles and other muscles responsible for longitudinal rotati ...
... only if the effort force is applied to the axle. If the effort force is on the wheel (resistive on the axis) reverse this fraction. Nearly all musculoskeletal systems in the human body are third class levers. Systems like rotator cuff muscles and other muscles responsible for longitudinal rotati ...
Review Notes on Angular Momentum, Correspondence Between
... Conservation of Angular Momentum In the absence of an external torque (isolated system) angular momentum is conserved regardless of what change takes place within the system. ...
... Conservation of Angular Momentum In the absence of an external torque (isolated system) angular momentum is conserved regardless of what change takes place within the system. ...