Chapter 7 Gravitation - REDIRECT TO NEW SITE
... period of time or a small force over a long period of time. An airbag reduces the force by increasing the time ...
... period of time or a small force over a long period of time. An airbag reduces the force by increasing the time ...
... Answer [B]: By Newton’s third law, the force exerted by the rod on the hinge is the same as the force exerted by the hinge on the rod, G which I will denote Fh . From the geometry of the problem, since the rope is at a 45° angle from the rod, in the coordinate system shown, Tx = −Ty The rod is in eq ...
Chapter 14 - Illinois State University
... not only on the magnitude and direction of acting external torques, but also on the length of the time interval over which each torque acts. ...
... not only on the magnitude and direction of acting external torques, but also on the length of the time interval over which each torque acts. ...
Rotational Motion - My Teacher Pages
... •Forces do not have to be perpendicular to an object to cause the object to rotate ...
... •Forces do not have to be perpendicular to an object to cause the object to rotate ...
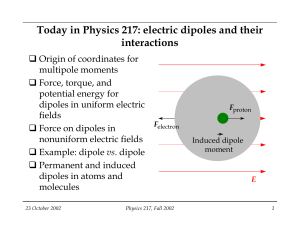
Today in Physics 217: electric dipoles and their interactions
... If the dipole moment is constant, the net force is zero, because the charges get pulled equally and oppositely. There is a torque, though, that tends to align the dipole moment vector with the applied field: x ...
... If the dipole moment is constant, the net force is zero, because the charges get pulled equally and oppositely. There is a torque, though, that tends to align the dipole moment vector with the applied field: x ...
Ch 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium
... • The figure on the left below shows that a force acting in a direction that is directly toward or away from the axis of rotation will cause no rotation. That is, radial forces produce zero torque. • The figure on the right below shows that if the force is at an angle θ relative to the radial line, ...
... • The figure on the left below shows that a force acting in a direction that is directly toward or away from the axis of rotation will cause no rotation. That is, radial forces produce zero torque. • The figure on the right below shows that if the force is at an angle θ relative to the radial line, ...
Translational_Equilibrium
... • Equilibrium is the state of a body in which there is no change in its motion. • A body is in equilibrium when the net force acting on it is zero; there is no acceleration (a = 0 m/s2), the body is either at rest or is moving at a constant velocity. • The study of objects in equilibrium is called ...
... • Equilibrium is the state of a body in which there is no change in its motion. • A body is in equilibrium when the net force acting on it is zero; there is no acceleration (a = 0 m/s2), the body is either at rest or is moving at a constant velocity. • The study of objects in equilibrium is called ...
The first condition of equilibrium is that the net force in all
... This car is in dynamic equilibrium because it is moving at constant velocity. There are horizontal and vertical forces, but the net external force in any direction is zero. The applied force Fapp between the tires and the road is balanced by air friction, and the weight of the car is supported by th ...
... This car is in dynamic equilibrium because it is moving at constant velocity. There are horizontal and vertical forces, but the net external force in any direction is zero. The applied force Fapp between the tires and the road is balanced by air friction, and the weight of the car is supported by th ...
Chapter 21 Rigid Body Dynamics: Rotation and Translation
... We shall analyze the motion of systems of particles and rigid bodies that are undergoing translational and rotational motion about a fixed direction. Because the body is translating, the axis of rotation is no longer fixed in space. We shall describe the motion by a translation of the center of mass ...
... We shall analyze the motion of systems of particles and rigid bodies that are undergoing translational and rotational motion about a fixed direction. Because the body is translating, the axis of rotation is no longer fixed in space. We shall describe the motion by a translation of the center of mass ...
CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM
... conserved about a given axis Another classic example of conservation of angular momentum. When the spinning wheel is moved so its axis of rotation is vertical, the frictionless turntable spins in a direction opposite to the wheel ...
... conserved about a given axis Another classic example of conservation of angular momentum. When the spinning wheel is moved so its axis of rotation is vertical, the frictionless turntable spins in a direction opposite to the wheel ...
AP Physics - eLearning
... 10. A skater extends her arms horizontally, holding a 5-kg mass in each hand. She is rotating about a vertical axis with an angular velocity of one revolution per second. If she drops her hands to her sides, what will the final angular velocity (in rev sec ) be if her moment of inertia remains appr ...
... 10. A skater extends her arms horizontally, holding a 5-kg mass in each hand. She is rotating about a vertical axis with an angular velocity of one revolution per second. If she drops her hands to her sides, what will the final angular velocity (in rev sec ) be if her moment of inertia remains appr ...