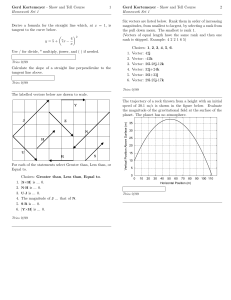
Physics I. :: 2. Dynamics of point masses
... long rope, then the constraint is that their distance cannot be more than 3 m. The tension in the rope will be whatever is needed to ensure that this remains true (as long as the rope does not break, of course). i) Inertial forces: These forces only appear when the frame of reference is not inertial ...
... long rope, then the constraint is that their distance cannot be more than 3 m. The tension in the rope will be whatever is needed to ensure that this remains true (as long as the rope does not break, of course). i) Inertial forces: These forces only appear when the frame of reference is not inertial ...
form 4- 32 circular motion - kcpe-kcse
... The direction of the resultant force and the acceleration must be the same. Therefore centripetal acceleration requires a resultant force directed towards the centre of the circular path – this is CENTRIPETAL FORCE. ...
... The direction of the resultant force and the acceleration must be the same. Therefore centripetal acceleration requires a resultant force directed towards the centre of the circular path – this is CENTRIPETAL FORCE. ...
AP Physics Summer Packet
... In science, all numbers involve units, because all numbers are measurements of a quantity. Numbers without units mean nothing in physics, unless they are referring to a ratio. In this class, we emphasize the system of units known as SI units. By agreement of the scientific world, a set of units are ...
... In science, all numbers involve units, because all numbers are measurements of a quantity. Numbers without units mean nothing in physics, unless they are referring to a ratio. In this class, we emphasize the system of units known as SI units. By agreement of the scientific world, a set of units are ...
centripetal force
... What will be the rotational and tangential speed of a penny placed at 3 cm away from the center? ...
... What will be the rotational and tangential speed of a penny placed at 3 cm away from the center? ...
Circular Motion
... accelerating. The acceleration due to its change in direction is called centripetal acceleration. For uniform circular motion, the acceleration vector has a constant magnitude and always points toward the center of the circle. ...
... accelerating. The acceleration due to its change in direction is called centripetal acceleration. For uniform circular motion, the acceleration vector has a constant magnitude and always points toward the center of the circle. ...
Part I
... • Energy: Traditionally defined as the ability to do work. We now know that not all forces are able to do work; however, we are dealing in these chapters with mechanical energy, which does follow this definition. • Kinetic Energy The energy of motion “Kinetic” Greek word for motion An object in ...
... • Energy: Traditionally defined as the ability to do work. We now know that not all forces are able to do work; however, we are dealing in these chapters with mechanical energy, which does follow this definition. • Kinetic Energy The energy of motion “Kinetic” Greek word for motion An object in ...
Force Vectors 1
... • When the resultant of all forces acting on a particle is zero, the particle is in equilibrium. • Newton’s First Law: If the resultant force on a particle is zero, the particle will remain at rest or will continue at constant speed in a straight line. ...
... • When the resultant of all forces acting on a particle is zero, the particle is in equilibrium. • Newton’s First Law: If the resultant force on a particle is zero, the particle will remain at rest or will continue at constant speed in a straight line. ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... (or equilibrium) position under the influence of a restoring force which is always directed towards the mean position and whose magnitude at any instant of time is directly proportional to the displacement of the particle from the mean position at that instant. • Let x be the displacement of a parti ...
... (or equilibrium) position under the influence of a restoring force which is always directed towards the mean position and whose magnitude at any instant of time is directly proportional to the displacement of the particle from the mean position at that instant. • Let x be the displacement of a parti ...