5. Potential Energy
... point in space. It can still be thought of as constant for a small displacement dl so that the work done is dW = F·dl. If the particle moves along a path connecting r1 to r2 the work done can be found by breaking up the path into small steps and adding up the work done in each step. This is the inte ...
... point in space. It can still be thought of as constant for a small displacement dl so that the work done is dW = F·dl. If the particle moves along a path connecting r1 to r2 the work done can be found by breaking up the path into small steps and adding up the work done in each step. This is the inte ...
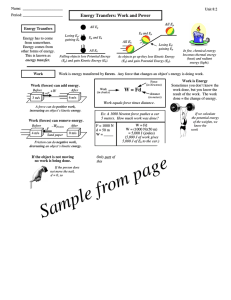
Energy, Work, and Simple Machines
... • The faster we do Work… the more powerful our action is • The slower we do that same Work… the less powerful our action is What makes the backhoe loader more POWERFUL? ...
... • The faster we do Work… the more powerful our action is • The slower we do that same Work… the less powerful our action is What makes the backhoe loader more POWERFUL? ...
Workbooklet 2.5 exercises page 14
... 6. A body of mass 2.5 kg is projected vertically with an initial speed of 40 m/s. (a) What is the initial kinetic energy of the body? (b) What is the kinetic energy of the body when it reaches its maximum height? (c) How much potential energy does the body gain as it rises from the point of project ...
... 6. A body of mass 2.5 kg is projected vertically with an initial speed of 40 m/s. (a) What is the initial kinetic energy of the body? (b) What is the kinetic energy of the body when it reaches its maximum height? (c) How much potential energy does the body gain as it rises from the point of project ...
Physics I - Rose
... where aA is directed toward the left and aB, is directed toward the right. To find the maximum speeds vfA and vfB it is easier to use the conservation of momentum and conservation of energy equations than kinematics. The momentum conservation equation along x-direction pafter pbefore 0 kg m/s me ...
... where aA is directed toward the left and aB, is directed toward the right. To find the maximum speeds vfA and vfB it is easier to use the conservation of momentum and conservation of energy equations than kinematics. The momentum conservation equation along x-direction pafter pbefore 0 kg m/s me ...
24-2: Electric potential energy
... Introduction: Why will we be introducing the electrostatic potential (V) and electric potential energy (U)? Because they are scalars!! not vectors like F and E. ...
... Introduction: Why will we be introducing the electrostatic potential (V) and electric potential energy (U)? Because they are scalars!! not vectors like F and E. ...
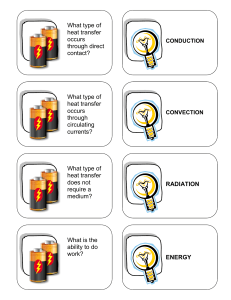
Energy and Forces
... D3h Describe several different types of energy forms including heat energy, chemical energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or destroyed E2D Describe how matter and energy change from one form to anot ...
... D3h Describe several different types of energy forms including heat energy, chemical energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or destroyed E2D Describe how matter and energy change from one form to anot ...
Forces and COM - K
... Homework: Calculating Power on a Treadmill • Problem: What is workload (power) of a 100 kg man running on a treadmill at 10% grade at 4 m/s? • Solution: – Power = force x velocity – Force is simply body weight, or 100 x 9.8 = 980 N – Velocity is vertical velocity, or rate of climbing • Rate of clim ...
... Homework: Calculating Power on a Treadmill • Problem: What is workload (power) of a 100 kg man running on a treadmill at 10% grade at 4 m/s? • Solution: – Power = force x velocity – Force is simply body weight, or 100 x 9.8 = 980 N – Velocity is vertical velocity, or rate of climbing • Rate of clim ...
File - 5th Grade Rocks!
... The energy an object has because it is in a position where it is affected by a force is called what? ...
... The energy an object has because it is in a position where it is affected by a force is called what? ...
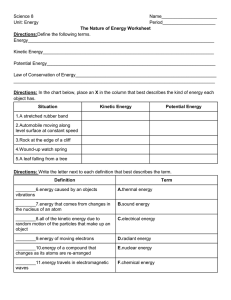
Chapter 13 Section 2 pg. 447-451
... Mechanical energy is energy associated with the POSTION and MOTION. Mechanical energy is a COMBINATION of the objects potential and kinetic energy. ...
... Mechanical energy is energy associated with the POSTION and MOTION. Mechanical energy is a COMBINATION of the objects potential and kinetic energy. ...