Chapter Fourteen The Electric Field and the Electric Potential
... The Electric Field • The electric field, with symbol , at a point in space as the vector resultant force experienced by a positive test charge of magnitude 1 C placed at that point. • If an arbitrary test charge is placed at that point, the charge experience a force • The magnitude of the force bet ...
... The Electric Field • The electric field, with symbol , at a point in space as the vector resultant force experienced by a positive test charge of magnitude 1 C placed at that point. • If an arbitrary test charge is placed at that point, the charge experience a force • The magnitude of the force bet ...
PHYS_2326_020309
... if the exact distribution is known. If we know the electric field as a function of position, we integrate the field. b ...
... if the exact distribution is known. If we know the electric field as a function of position, we integrate the field. b ...
El Energy Syllabus Summary Blank
... describe the production of a magnetic field by an electric current in a straight current-carrying conductor and describe how the right hand grip rule can determine the direction of current and field ...
... describe the production of a magnetic field by an electric current in a straight current-carrying conductor and describe how the right hand grip rule can determine the direction of current and field ...
r - Personal.psu.edu
... Negative charge moves in opposite direction to electric field Positive charge moves in the same direction as an electric field ...
... Negative charge moves in opposite direction to electric field Positive charge moves in the same direction as an electric field ...
2005 - The Physics Teacher
... In an experiment to verify the principle of conservation of momentum, a body A was set in motion with a constant velocity. It was then allowed to collide with a second body B, which was initially at rest and the bodies moved off together at constant velocity. The following data was recorded. Mass of ...
... In an experiment to verify the principle of conservation of momentum, a body A was set in motion with a constant velocity. It was then allowed to collide with a second body B, which was initially at rest and the bodies moved off together at constant velocity. The following data was recorded. Mass of ...
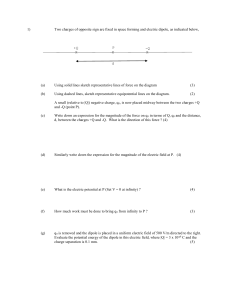
1) Two charges of opposite sign are fixed in space forming and
... The charging battery is disconnected and the plates are pulled apart until their separation is d. Derive expressions, in terms of A,d,V and 0, for, (b) ...
... The charging battery is disconnected and the plates are pulled apart until their separation is d. Derive expressions, in terms of A,d,V and 0, for, (b) ...
t299-1-03f
... A small (relative to |Q|) negative charge, q0, is now placed midway between the two charges +Q and -Q (point P). (c) ...
... A small (relative to |Q|) negative charge, q0, is now placed midway between the two charges +Q and -Q (point P). (c) ...
POTENTIAL 1. A uniform electric field with a magnitude of 500 N/C is
... Use the following to answer questions 14-25: The sketch below shows cross sections of equipotential surfaces between two charged conductors that are shown in solid black. Various points on the equipotential surfaces near the conductors are labeled A, B, C, ..., I. ...
... Use the following to answer questions 14-25: The sketch below shows cross sections of equipotential surfaces between two charged conductors that are shown in solid black. Various points on the equipotential surfaces near the conductors are labeled A, B, C, ..., I. ...
Lesson Plan
... Remind students that objects with zero velocity have zero kinetic energy. Does this mean that objects at rest have no energy? No, this type of energy is sometimes called potential energy and does not depend on the velocity of an object. Potential energy is the energy an object has because of its pos ...
... Remind students that objects with zero velocity have zero kinetic energy. Does this mean that objects at rest have no energy? No, this type of energy is sometimes called potential energy and does not depend on the velocity of an object. Potential energy is the energy an object has because of its pos ...
electric potential
... two or more charged particles, we can assign an ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY U to the system. The change in potential energy of a charge is the amount of work that is done by an external force in moving the charge from its initial position to its new position. It is the negative of the work done by the ...
... two or more charged particles, we can assign an ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY U to the system. The change in potential energy of a charge is the amount of work that is done by an external force in moving the charge from its initial position to its new position. It is the negative of the work done by the ...