Chapter 12: Light
... Section 1: The Behavior of Light The Nature of Light A basic question: Is light a wave or a particle? • General properties of waves: Propagation within a uniform medium is along straight lines Reflection occurs at a surface or boundary (known for at least 2,000 years) Refraction occurs where ...
... Section 1: The Behavior of Light The Nature of Light A basic question: Is light a wave or a particle? • General properties of waves: Propagation within a uniform medium is along straight lines Reflection occurs at a surface or boundary (known for at least 2,000 years) Refraction occurs where ...
Refraction - fwiatrowskimbhs
... A ray of light is approaching a set of three mirrors as shown in the diagram. The light ray is approaching the first mirror at an angle of 45-degrees with the mirror surface. Trace the path of the light ray as it bounces off the mirror. Continue tracing the ray until it finally exits from the mirror ...
... A ray of light is approaching a set of three mirrors as shown in the diagram. The light ray is approaching the first mirror at an angle of 45-degrees with the mirror surface. Trace the path of the light ray as it bounces off the mirror. Continue tracing the ray until it finally exits from the mirror ...
Chapter 21
... -- absorbs higher energy visible light (blue, violet), -- Red/yellow/orange is transmitted and gives it color. -- Sapphire is colorless (i.e., Egap > 3.1eV) ...
... -- absorbs higher energy visible light (blue, violet), -- Red/yellow/orange is transmitted and gives it color. -- Sapphire is colorless (i.e., Egap > 3.1eV) ...
Figures from Lecture 12 - University of Texas Astronomy
... Light as waves associated with electric and magnetic fields James Clerk Maxwell (1831 – 1879) showed that light can be viewed as electromagnetic waves, which are waves associated with vibrating electric and magnetic fields (see Fig. 1 in class) ...
... Light as waves associated with electric and magnetic fields James Clerk Maxwell (1831 – 1879) showed that light can be viewed as electromagnetic waves, which are waves associated with vibrating electric and magnetic fields (see Fig. 1 in class) ...
To understand the basics of reflection and refraction
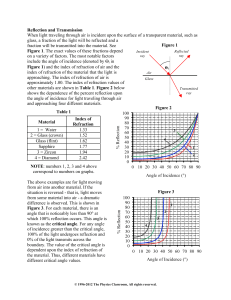
... • A surface is defined to be a point where the index of refraction changes. • The most common form of this is when you have 2 different types of materials – such as air, glass, water, ect. • For each the speed of light is different. • When the light enters the material the speed changes but the rest ...
... • A surface is defined to be a point where the index of refraction changes. • The most common form of this is when you have 2 different types of materials – such as air, glass, water, ect. • For each the speed of light is different. • When the light enters the material the speed changes but the rest ...
Document
... Open water phytoplankton and bacteria Ice-edge phytoplankton and bacteria Under-ice phytoplankton and bacteria Melt pond algae and bacteria Marine aggregates at the sea surface (e.g. the centric diatom Melosira sp.) ...
... Open water phytoplankton and bacteria Ice-edge phytoplankton and bacteria Under-ice phytoplankton and bacteria Melt pond algae and bacteria Marine aggregates at the sea surface (e.g. the centric diatom Melosira sp.) ...
Refraction and its uses
... • The process of vision begins when light rays that reflect off objects and travel through the eye's optical system are refracted and focused into a point of sharp focus. • For good vision, this focus point must be on the retina. The retina is the tissue that lines the inside of the back of the eye, ...
... • The process of vision begins when light rays that reflect off objects and travel through the eye's optical system are refracted and focused into a point of sharp focus. • For good vision, this focus point must be on the retina. The retina is the tissue that lines the inside of the back of the eye, ...
Bioluminescence

Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by a living organism. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria and terrestrial invertebrates such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is produced by symbiotic organisms such as Vibrio bacteria.The principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves the light-emitting pigment luciferin and the enzyme luciferase, assisted by other proteins such as aequorin in some species. The enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin. In some species, the type of luciferin requires cofactors such as calcium or magnesium ions, and sometimes also the energy-carrying molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In evolution, luciferins vary little: one in particular, coelenterazine, is found in nine different animal (phyla), though in some of these, the animals obtain it through their diet. Conversely, luciferases vary widely in different species. Bioluminescence has arisen over forty times in evolutionary history.Both Aristotle and Pliny the Elder mentioned that damp wood sometimes gives off a glow and many centuries later Robert Boyle showed that oxygen was involved in the process, both in wood and in glow-worms. It was not until the late nineteenth century that bioluminescence was properly investigated. The phenomenon is widely distributed among animal groups, especially in marine environments where dinoflagellates cause phosphorescence in the surface layers of water. On land it occurs in fungi, bacteria and some groups of invertebrates, including insects.The uses of bioluminescence by animals include counter-illumination camouflage, mimicry of other animals, for example to lure prey, and signalling to other individuals of the same species, such as to attract mates. In the laboratory, luciferase-based systems are used in genetic engineering and for biomedical research. Other researchers are investigating the possibility of using bioluminescent systems for street and decorative lighting, and a bioluminescent plant has been created.