Designing Active Band Pass Filter using Double Layers
... MOSFET filter and a single gain amplifier. Herein, α and K parameters of the circuit are used to improve the magnitude response. From the experimental results of the frequency characteristics give us a good agreement with theoretical values. It is showed that the behaviour of the proposed band pass ...
... MOSFET filter and a single gain amplifier. Herein, α and K parameters of the circuit are used to improve the magnitude response. From the experimental results of the frequency characteristics give us a good agreement with theoretical values. It is showed that the behaviour of the proposed band pass ...
September 20th, 2012 World Mining Congress Montreal, Quebec
... satisfactorily with experimental results. Following this rigorous validation approach, BS band pull-out simulations were conducted on the validated model. For comparison purposes, the proposed threadedconnection design was next incorporated into the validated FE model and the BS band pull-out test w ...
... satisfactorily with experimental results. Following this rigorous validation approach, BS band pull-out simulations were conducted on the validated model. For comparison purposes, the proposed threadedconnection design was next incorporated into the validated FE model and the BS band pull-out test w ...
OpAmp_Lab_II
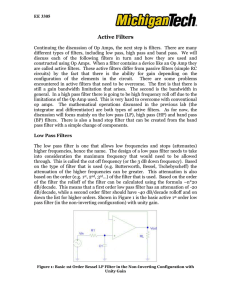
... Continuing the discussion of Op Amps, the next step is filters. There are many different types of filters, including low pass, high pass and band pass. We will discuss each of the following filters in turn and how they are used and constructed using Op Amps. When a filter contains a device like an O ...
... Continuing the discussion of Op Amps, the next step is filters. There are many different types of filters, including low pass, high pass and band pass. We will discuss each of the following filters in turn and how they are used and constructed using Op Amps. When a filter contains a device like an O ...
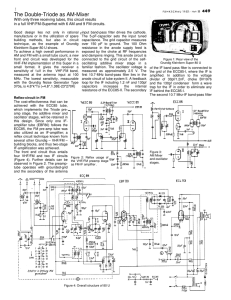
Question 1 – Transfer Functions
... c) The voltage and phase vs frequency for each of these filters is shown on the following two pages. Identify which plot goes with each transfer function. Show your work below for partial credit: (12 points) The easiest way to distinguish between the plots is as follows: F is the only band pass filt ...
... c) The voltage and phase vs frequency for each of these filters is shown on the following two pages. Identify which plot goes with each transfer function. Show your work below for partial credit: (12 points) The easiest way to distinguish between the plots is as follows: F is the only band pass filt ...
Title Limit Cycle Behavior in a Class-AB Second
... In internally-linear fully-differential circuits it is usual to replace any pair of equal-value capacitors, each connected between a node and ground, with a single half-sized floating capacitor, placed between those nodes. This standard linear IC design technique reduces by a factor of 4 the total a ...
... In internally-linear fully-differential circuits it is usual to replace any pair of equal-value capacitors, each connected between a node and ground, with a single half-sized floating capacitor, placed between those nodes. This standard linear IC design technique reduces by a factor of 4 the total a ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... at the point of common coupling and makes the source current sinusoidal. This paper presents a performance comparison of different methods of estimating reference-compensating current for a three-phase shunt active power filter. The control strategy considers the presence of harmonics in the system ...
... at the point of common coupling and makes the source current sinusoidal. This paper presents a performance comparison of different methods of estimating reference-compensating current for a three-phase shunt active power filter. The control strategy considers the presence of harmonics in the system ...
PDF
... higher frequencies. The job of filters is to include the desired frequencies that make up the important components of the waveform while excluding the undesired frequencies outside the frequencies of interest. A high-frequency filter (also called a low-pass filter) is designed to limit the amount of ...
... higher frequencies. The job of filters is to include the desired frequencies that make up the important components of the waveform while excluding the undesired frequencies outside the frequencies of interest. A high-frequency filter (also called a low-pass filter) is designed to limit the amount of ...
closer
... electronic or structural, impairs the ability of these instruments to gather accurate readings, a problem that has been previously addressed through linear filtering technology. An internally funded Southwest Research Institute project h as shown, however, that even greater accuracy is possible thro ...
... electronic or structural, impairs the ability of these instruments to gather accurate readings, a problem that has been previously addressed through linear filtering technology. An internally funded Southwest Research Institute project h as shown, however, that even greater accuracy is possible thro ...
Transducer
... This 180 degree phase shift can be used to determine the direction of the core from the null point by means of appropriate circuitry. As this diagram shows, the polarity of the output signal represents the core's positional relationship to the null point. ...
... This 180 degree phase shift can be used to determine the direction of the core from the null point by means of appropriate circuitry. As this diagram shows, the polarity of the output signal represents the core's positional relationship to the null point. ...
Experiment 3 - Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
... We can have the circuit respond to a broad band or narrow band frequencies. There are uses for both. The TV channel is 6 MHz wide in order to contain the picture, sound, and color information. A broad-band circuit is necessary to pass all these frequencies. In AM radio you only want a signal station ...
... We can have the circuit respond to a broad band or narrow band frequencies. There are uses for both. The TV channel is 6 MHz wide in order to contain the picture, sound, and color information. A broad-band circuit is necessary to pass all these frequencies. In AM radio you only want a signal station ...
Lab-15-datasheet-new
... to make a LPF with wo of 20 Rad/sec List components used for your LPF How are these components to be arranged? Calculated wo using nominal values ...
... to make a LPF with wo of 20 Rad/sec List components used for your LPF How are these components to be arranged? Calculated wo using nominal values ...
HAS 600-S
... Caution, risk of electrical shock When operating the transducer, certain parts of the module can carry hazardous voltage (eg. primary busbar, power supply). Ignoring this warning can lead to injury and/or cause serious damage. This transducer is a build-in device, whose conducting parts must be inac ...
... Caution, risk of electrical shock When operating the transducer, certain parts of the module can carry hazardous voltage (eg. primary busbar, power supply). Ignoring this warning can lead to injury and/or cause serious damage. This transducer is a build-in device, whose conducting parts must be inac ...
Automotive-grade low voltage NPN power transistor
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
Mechanical filter

A mechanical filter is a signal processing filter usually used in place of an electronic filter at radio frequencies. Its purpose is the same as that of a normal electronic filter: to pass a range of signal frequencies, but to block others. The filter acts on mechanical vibrations which are the analogue of the electrical signal. At the input and output of the filter, transducers convert the electrical signal into, and then back from, these mechanical vibrations.The components of a mechanical filter are all directly analogous to the various elements found in electrical circuits. The mechanical elements obey mathematical functions which are identical to their corresponding electrical elements. This makes it possible to apply electrical network analysis and filter design methods to mechanical filters. Electrical theory has developed a large library of mathematical forms that produce useful filter frequency responses and the mechanical filter designer is able to make direct use of these. It is only necessary to set the mechanical components to appropriate values to produce a filter with an identical response to the electrical counterpart.Steel and nickel–iron alloys are common materials for mechanical filter components; nickel is sometimes used for the input and output couplings. Resonators in the filter made from these materials need to be machined to precisely adjust their resonance frequency before final assembly.While the meaning of mechanical filter in this article is one that is used in an electromechanical role, it is possible to use a mechanical design to filter mechanical vibrations or sound waves (which are also essentially mechanical) directly. For example, filtering of audio frequency response in the design of loudspeaker cabinets can be achieved with mechanical components. In the electrical application, in addition to mechanical components which correspond to their electrical counterparts, transducers are needed to convert between the mechanical and electrical domains. A representative selection of the wide variety of component forms and topologies for mechanical filters are presented in this article.The theory of mechanical filters was first applied to improving the mechanical parts of phonographs in the 1920s. By the 1950s mechanical filters were being manufactured as self-contained components for applications in radio transmitters and high-end receivers. The high ""quality factor"", Q, that mechanical resonators can attain, far higher than that of an all-electrical LC circuit, made possible the construction of mechanical filters with excellent selectivity. Good selectivity, being important in radio receivers, made such filters highly attractive. Contemporary researchers are working on microelectromechanical filters, the mechanical devices corresponding to electronic integrated circuits.