EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGY
... however, refers to the ability to make large quantities of ATP. Power and capacity are inversely related. Metabolic pathways that are the most powerful also have the least capacity, and vice versa. The anaerobic pathways are far more powerful than the aerobic pathways, but have a very limited capac ...
... however, refers to the ability to make large quantities of ATP. Power and capacity are inversely related. Metabolic pathways that are the most powerful also have the least capacity, and vice versa. The anaerobic pathways are far more powerful than the aerobic pathways, but have a very limited capac ...
2.1 Living organisms 2.1.1 Useful products Scientists are looking for
... the soil, for healthy growth; state that these minerals are absorbed in solution by the roots; recall the names of important minerals; nitrates, phosphates, potassium and magnesium; explain simple data about plant growth in the presence or absence of these minerals. ...
... the soil, for healthy growth; state that these minerals are absorbed in solution by the roots; recall the names of important minerals; nitrates, phosphates, potassium and magnesium; explain simple data about plant growth in the presence or absence of these minerals. ...
(English, 40 pages)
... but not always, at a selective disadvantage. When successful they help transfer genes among species, thus maintaining if not increasing genetic diversity among populations. Third, the Grants have used variation in mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite regions of nuclear DNA to show that the 14 specie ...
... but not always, at a selective disadvantage. When successful they help transfer genes among species, thus maintaining if not increasing genetic diversity among populations. Third, the Grants have used variation in mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite regions of nuclear DNA to show that the 14 specie ...
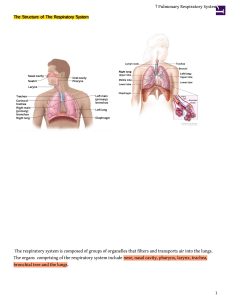
Respiratory System - Indian Hills Community College
... Pharynx – (also known as your throat) the passage way of food and air enters in from mouth to pharynx passes into the esophagus. Adenoids – consists of lymphoid tissue and are located behind the nasal cavity. Tonsils – your tonsils are also made from lymphoid tissue and are behind the mouth. You may ...
... Pharynx – (also known as your throat) the passage way of food and air enters in from mouth to pharynx passes into the esophagus. Adenoids – consists of lymphoid tissue and are located behind the nasal cavity. Tonsils – your tonsils are also made from lymphoid tissue and are behind the mouth. You may ...
Ch5
... promote venous return to heart – Pressure venous compression/squeezing – Pressure venous filling ...
... promote venous return to heart – Pressure venous compression/squeezing – Pressure venous filling ...
I CAN - Montgomery County Public Schools
... increase its numbers, (2) the genetic variability of offspring due to mutation and recombination of genes, (3) a finite supply of the resources required for life and (4) natural selection. The consequences of change over time provide a scientific explanation for the fossil record of ancient life for ...
... increase its numbers, (2) the genetic variability of offspring due to mutation and recombination of genes, (3) a finite supply of the resources required for life and (4) natural selection. The consequences of change over time provide a scientific explanation for the fossil record of ancient life for ...
Metal Complex in the Blood - Department of Chemistry, IIT Bombay
... b. Do you expect the absorbance (A) at λmax to be the same or different for the two solutions? If the absorbance is different for the two solutions, indicate which solution will have a higher absorbance. Briefly, explain your reasoning. ...
... b. Do you expect the absorbance (A) at λmax to be the same or different for the two solutions? If the absorbance is different for the two solutions, indicate which solution will have a higher absorbance. Briefly, explain your reasoning. ...
bronchi tubes - Fort Bend ISD
... * At rest, the body takes in and breathes out about 10 liters of air each minute. * The right lung is slightly larger than the left. * The highest recorded "sneeze speed" is 165 km per hour. * The surface area of the lungs is roughly the same size as a tennis court. * The capillaries in the lungs wo ...
... * At rest, the body takes in and breathes out about 10 liters of air each minute. * The right lung is slightly larger than the left. * The highest recorded "sneeze speed" is 165 km per hour. * The surface area of the lungs is roughly the same size as a tennis court. * The capillaries in the lungs wo ...
Chapter 42
... mitral valve - the valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle. It prevents the back-flow of blood from the ventricle to the atrium. pulmonary artery - the blood vessel that carries oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs. pulmonary valve - the flaps between the ...
... mitral valve - the valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle. It prevents the back-flow of blood from the ventricle to the atrium. pulmonary artery - the blood vessel that carries oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs. pulmonary valve - the flaps between the ...
Metal Complex in the Blood - Department of Chemistry | Washington
... b. Do you expect the absorbance (A) at λmax to be the same or different for the two solutions? If the absorbance is different for the two solutions, indicate which solution will have a higher absorbance. Briefly, explain your reasoning. ...
... b. Do you expect the absorbance (A) at λmax to be the same or different for the two solutions? If the absorbance is different for the two solutions, indicate which solution will have a higher absorbance. Briefly, explain your reasoning. ...
MEMBRANOGENESIS AND PLACENTAL FUNCTION LEARNING OUTCOMES
... Most of the rest is due to amino acid and lactate oxidation Rather little is from fatty acid oxidation (Notice that maternal energy metabolism is almost the mirror of this with a shift to fatty acid oxidation and a shift away from amino acids and glucose) ...
... Most of the rest is due to amino acid and lactate oxidation Rather little is from fatty acid oxidation (Notice that maternal energy metabolism is almost the mirror of this with a shift to fatty acid oxidation and a shift away from amino acids and glucose) ...
① Pulmonary Respiratory System
... The major function of lungs is exchanging of gases between the body and the external enviroment. The respiratory system offers the individual replacing O2 and removing CO2 between lung and blood. These actions occur because of ventilation and diffusion. Ventilation is the mechanical process of movin ...
... The major function of lungs is exchanging of gases between the body and the external enviroment. The respiratory system offers the individual replacing O2 and removing CO2 between lung and blood. These actions occur because of ventilation and diffusion. Ventilation is the mechanical process of movin ...
Fact Sheet 41 | CYSTIC FIBROSIS This fact sheet describes the
... the body to function normally, and are known as genetic carriers for cystic fibrosis. Genetic carriers for cystic fibrosis will not have any signs or symptoms of the condition. To be affected with cystic fibrosis, both copies of the CFTR gene must be faulty. Without a working copy of the CFTR gene, ...
... the body to function normally, and are known as genetic carriers for cystic fibrosis. Genetic carriers for cystic fibrosis will not have any signs or symptoms of the condition. To be affected with cystic fibrosis, both copies of the CFTR gene must be faulty. Without a working copy of the CFTR gene, ...
Overview of the Circulatory Pathways
... the body's organs and tissues (except for the alveoli of the lungs). Systemic arteries branch off into smaller arterioles that lead into extensive networks of systemic capillaries. Nutrients and gases are exchanged between blood and systemic tissues through the thin capillary walls. After the blood ...
... the body's organs and tissues (except for the alveoli of the lungs). Systemic arteries branch off into smaller arterioles that lead into extensive networks of systemic capillaries. Nutrients and gases are exchanged between blood and systemic tissues through the thin capillary walls. After the blood ...
Basic Theories for Introductory Biology
... [This is a companion to “Promoting Creative and Critical Thinking Skills in College Biology”, by Anton E. Lawson, Department of Biology, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287-1501. Bioscene, vol. 27(1), March 2001. This document elaborates on Table 2 in that publication. Dr. Lawson kindly contri ...
... [This is a companion to “Promoting Creative and Critical Thinking Skills in College Biology”, by Anton E. Lawson, Department of Biology, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287-1501. Bioscene, vol. 27(1), March 2001. This document elaborates on Table 2 in that publication. Dr. Lawson kindly contri ...
EXAM 3 - USD Biology
... II. Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer (2 pts each, 14 pts. total) 1. Which of the following is not true of teleost gills? a) gill septum reduced to base of filament, b) gill slits open to opercular chamber, c) water and blood flow in opposite directions at the lamellae, d) spiracle is present, ...
... II. Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer (2 pts each, 14 pts. total) 1. Which of the following is not true of teleost gills? a) gill septum reduced to base of filament, b) gill slits open to opercular chamber, c) water and blood flow in opposite directions at the lamellae, d) spiracle is present, ...
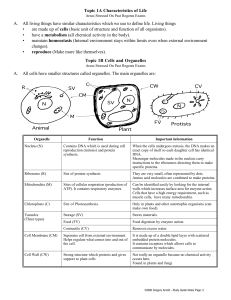
Topic 1A Characteristics of Life A. All living things have similar
... Organisms will react in ways that will maintain an internal environment allowing the chemical activities of life to occur regardless if the external environment changes. This process is known as homeostasis (steady state). For example, the heart and breathing rate will change due to various levels o ...
... Organisms will react in ways that will maintain an internal environment allowing the chemical activities of life to occur regardless if the external environment changes. This process is known as homeostasis (steady state). For example, the heart and breathing rate will change due to various levels o ...
Circulation and Respiration Revised Class Notes
... Hemoglobin releases oxygen at tissues and becomes dark red in color. It looks blue under the skin because of the way light passes through the skin. The fluid surrounding tissues and cells has a lower [O2] than blood so oxygen diffuses from the blood into the fluid surrounding the tissues This diffus ...
... Hemoglobin releases oxygen at tissues and becomes dark red in color. It looks blue under the skin because of the way light passes through the skin. The fluid surrounding tissues and cells has a lower [O2] than blood so oxygen diffuses from the blood into the fluid surrounding the tissues This diffus ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.