Circulatory system - Frank`s Hospital Workshop
... expansion : pause : contraction : pause. [...] The pulse is a movement in the heart and arteries ... which takes the form of alternate expansion and contraction."[7] In 1242, the Arabian physician, Ibn al-Nafis, became the first person to accurately describe the process of pulmonary circulation, for ...
... expansion : pause : contraction : pause. [...] The pulse is a movement in the heart and arteries ... which takes the form of alternate expansion and contraction."[7] In 1242, the Arabian physician, Ibn al-Nafis, became the first person to accurately describe the process of pulmonary circulation, for ...
13 Respiration - bloodhounds Incorporated
... Which of the following factors is (are) essential to hemoglobin saturation and the release of oxygen from the heme? A. Hydrogen concentration B. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide C. The amount of 2,3 DPG in the blood D. All of the above ...
... Which of the following factors is (are) essential to hemoglobin saturation and the release of oxygen from the heme? A. Hydrogen concentration B. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide C. The amount of 2,3 DPG in the blood D. All of the above ...
Mammals - Meade USD 226
... Mammals are unique among vertebrates in the way that they nourish their young after birth. Mammary glands located on the female’s chest or abdomen produce a nutrient-rich energy source called milk and give this class its name. Milk is rich in protein, carbohydrates (sugar lactose), and fat. It also ...
... Mammals are unique among vertebrates in the way that they nourish their young after birth. Mammary glands located on the female’s chest or abdomen produce a nutrient-rich energy source called milk and give this class its name. Milk is rich in protein, carbohydrates (sugar lactose), and fat. It also ...
32 Physiology of respiratory system. External breathing
... produce energy and is therefore essential to life. The respiratory system may be defined as the organs and tissues through which air is passed into and out of the body to allow the necessary gaseous exchanges to take place. ...
... produce energy and is therefore essential to life. The respiratory system may be defined as the organs and tissues through which air is passed into and out of the body to allow the necessary gaseous exchanges to take place. ...
Frog Dissection Lab - Mr Dolan`s Science Page
... The frog’s heart (which is part of the circulatory system) has three chambers. There are two atria and one ventricle. There is a valve within the frog's heart that directs the flow of blood to prevent the oxygen rich blood and the carbon dioxide rich blood from mixing. In addition to breathing oxyge ...
... The frog’s heart (which is part of the circulatory system) has three chambers. There are two atria and one ventricle. There is a valve within the frog's heart that directs the flow of blood to prevent the oxygen rich blood and the carbon dioxide rich blood from mixing. In addition to breathing oxyge ...
8 CYSTIC FIBROSIS FACT SHEET 33 Important points What are the
... (mutation) is found in about 75% of people affected with CF in Australia. - The common CFTR gene mutation is called the ∆F508 (deltaF508) mutation. This means that, at position 508 along the gene’s length, there is a deletion of a code word for phenylalanine, an amino acid, which is one of the build ...
... (mutation) is found in about 75% of people affected with CF in Australia. - The common CFTR gene mutation is called the ∆F508 (deltaF508) mutation. This means that, at position 508 along the gene’s length, there is a deletion of a code word for phenylalanine, an amino acid, which is one of the build ...
6.4 gas Exchange
... • Walls of alveoli very thin, consisting of a single layer of flattened cells, • Thin walls decrease the length of the diffusion path. The shorter the diffusion path the greater the rate of diffusion • Thus the respiratory path must be as thin as possible. • Walls of the alveoli have elastic propert ...
... • Walls of alveoli very thin, consisting of a single layer of flattened cells, • Thin walls decrease the length of the diffusion path. The shorter the diffusion path the greater the rate of diffusion • Thus the respiratory path must be as thin as possible. • Walls of the alveoli have elastic propert ...
Signatures of Natural Selection and Ecological Differentiation in
... how do we define and identify ecologically distinct species of bacteria (Sect. 17.2)? It then describes different models of speciation, and the importance of natural selection in these models (Sect. 17.3). The major classes of tests for natural selection in genome sequences are briefly described (Se ...
... how do we define and identify ecologically distinct species of bacteria (Sect. 17.2)? It then describes different models of speciation, and the importance of natural selection in these models (Sect. 17.3). The major classes of tests for natural selection in genome sequences are briefly described (Se ...
Advanced Biology\AB U13 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... disease (PAD) can be caused by plaque in the descending aorta or the femoral arteries, etc. Symptoms can include numbness. Unfortunately, it is often assumed that numbness in the extremities of the elderly is due to PAD. However, it is often a vitamin B12 deficiency due to low intrinsic factor neede ...
... disease (PAD) can be caused by plaque in the descending aorta or the femoral arteries, etc. Symptoms can include numbness. Unfortunately, it is often assumed that numbness in the extremities of the elderly is due to PAD. However, it is often a vitamin B12 deficiency due to low intrinsic factor neede ...
Review Mitonuclear Ecology - Oxford Academic
... for maintaining which genes, and, above all, how to coordinate genomic products to enable system function (Lane 2011a). The archaebacterial genome gave rise to the nucleus and took command of information functions of the cell including regulatory pathways and the bulk of transcription and translatio ...
... for maintaining which genes, and, above all, how to coordinate genomic products to enable system function (Lane 2011a). The archaebacterial genome gave rise to the nucleus and took command of information functions of the cell including regulatory pathways and the bulk of transcription and translatio ...
Maintaining a Balance by Arthur Huang
... oxygen, water, salts, lipids, nitrogenous waste and other products of digestion Oxygen – when blood in the lungs comes into contact with oxygen that has entered the body by diffusion, haemoglobin (in the red blood cells) bind with the oxygen and form a compound called oxyhaemoglobin. This compound g ...
... oxygen, water, salts, lipids, nitrogenous waste and other products of digestion Oxygen – when blood in the lungs comes into contact with oxygen that has entered the body by diffusion, haemoglobin (in the red blood cells) bind with the oxygen and form a compound called oxyhaemoglobin. This compound g ...
Contribution of X chromosomal and autosomal genes to species
... within the species in the wild (Aspi & Hoikkala 1995). The songs of the montana phylad species (D. kanekoi, D. ezoana, D. littoralis, D. flavomontana, D. lacicola and D. montana) can easily be distinguished from each other by the length of the sound pulses and interpulse intervals. In some of these ...
... within the species in the wild (Aspi & Hoikkala 1995). The songs of the montana phylad species (D. kanekoi, D. ezoana, D. littoralis, D. flavomontana, D. lacicola and D. montana) can easily be distinguished from each other by the length of the sound pulses and interpulse intervals. In some of these ...
chapt10_HumanBiology14e_lecture
... • The bronchi continue to branch until they are small bronchioles about 1 mm in diameter with thinner walls. • Bronchioles eventually lead to elongated sacs called alveoli. ...
... • The bronchi continue to branch until they are small bronchioles about 1 mm in diameter with thinner walls. • Bronchioles eventually lead to elongated sacs called alveoli. ...
in the Nesospiza bunting species complex and its sister
... binding region (PBR). Of the 23 alleles, 15 were found on both the islands inhabited by Nesospiza species, and seven in both Nesospiza and Rowettia; indications of shared, ancestral polymorphism. A gene tree of Nesospiza MHCIIβ alleles with several other passerine birds shows three highly supported ...
... binding region (PBR). Of the 23 alleles, 15 were found on both the islands inhabited by Nesospiza species, and seven in both Nesospiza and Rowettia; indications of shared, ancestral polymorphism. A gene tree of Nesospiza MHCIIβ alleles with several other passerine birds shows three highly supported ...
AEMT Transition - Unit 8 - Ventilation Physiology
... Figure 8-1 Respiration is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Receptors within the body measure oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen ions and send signals to the brain to adjust the rate and depth of respirations. ...
... Figure 8-1 Respiration is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Receptors within the body measure oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen ions and send signals to the brain to adjust the rate and depth of respirations. ...
StandardB1: INQUIRY, Reflection, And social implications
... All living or once living organisms are composed of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates and lipids contain many carbon-hydrogen bonds that also store energy. However, that energy must be transferred to ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to be usable by the cell. B2.5e Explai ...
... All living or once living organisms are composed of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates and lipids contain many carbon-hydrogen bonds that also store energy. However, that energy must be transferred to ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to be usable by the cell. B2.5e Explai ...
Human Body Project
... Name (in order) the respiratory structures through which air passes through when a person is breathing. 5. Excretory System/Urinary 23 Points State the purpose of the excretory system Name the major organs involved Identify the function of the organs of the excretory system Explain how the ...
... Name (in order) the respiratory structures through which air passes through when a person is breathing. 5. Excretory System/Urinary 23 Points State the purpose of the excretory system Name the major organs involved Identify the function of the organs of the excretory system Explain how the ...
02 Gas Exchange 14 F
... v O2 isn’t highly soluble in blood or body fluids. v Respiratory pigments increase the solubility of O2 in blood. No hemoglobin: 0.3 ml O2/100 ml blood Hemoglobin: 20 ml O2/100 ml blood ...
... v O2 isn’t highly soluble in blood or body fluids. v Respiratory pigments increase the solubility of O2 in blood. No hemoglobin: 0.3 ml O2/100 ml blood Hemoglobin: 20 ml O2/100 ml blood ...
Review Tribute to P. L. Lutz: respiratory ecophysiology of coral
... respirometry to determine critical oxygen concentrations ([O2]crit) in 31 species of teleost fish from several families (Nilsson and Östlund-Nilsson, 2004). [O2]crit is the lowest oxygen level where a fish is able to maintain its routine rate of oxygen consumption (Prosser and Brown, 1961), and is a ...
... respirometry to determine critical oxygen concentrations ([O2]crit) in 31 species of teleost fish from several families (Nilsson and Östlund-Nilsson, 2004). [O2]crit is the lowest oxygen level where a fish is able to maintain its routine rate of oxygen consumption (Prosser and Brown, 1961), and is a ...
Level 6 The circulatory system Jenny Dooley – V
... too. One of them is the respiratory system, which includes the lungs. So, how do the lungs help? Well, when you breathe in, oxygen travels from the tiny air sacs in the lungs into the blood. When the blood is oxygenated (full of oxygen), it travels to the heart through one of the blood vessels. At t ...
... too. One of them is the respiratory system, which includes the lungs. So, how do the lungs help? Well, when you breathe in, oxygen travels from the tiny air sacs in the lungs into the blood. When the blood is oxygenated (full of oxygen), it travels to the heart through one of the blood vessels. At t ...
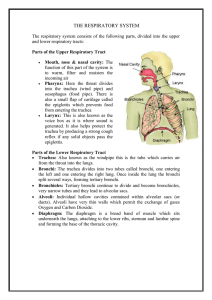
Physiology (GRPS-101) Practical notes Freshmen 2011
... Larynx: This is also known as the voice box as it is where sound is generated. It also helps protect the trachea by producing a strong cough reflex if any solid objects pass the epiglottis. ...
... Larynx: This is also known as the voice box as it is where sound is generated. It also helps protect the trachea by producing a strong cough reflex if any solid objects pass the epiglottis. ...
Chapter 22
... People cannot survive in the air at the world’s highest peaks in the Himalayan Mountains Twice a year, flocks of geese migrate over the Himalayas ...
... People cannot survive in the air at the world’s highest peaks in the Himalayan Mountains Twice a year, flocks of geese migrate over the Himalayas ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.