1 - School-Portal.co.uk
... = oxygenated blood away from heart to body tissues, Vena cava = deoxygenated blood back to heart from body tissues, Pulmonary artery = deoxygenated blood to lungs, pulmonary vein = oxygenated blood from lungs to heart. 7. What do veins and the heart both have that are not found in arteries or capill ...
... = oxygenated blood away from heart to body tissues, Vena cava = deoxygenated blood back to heart from body tissues, Pulmonary artery = deoxygenated blood to lungs, pulmonary vein = oxygenated blood from lungs to heart. 7. What do veins and the heart both have that are not found in arteries or capill ...
respiratory system
... Alveoli each alveoli has a capillary bed surrounding it. The alveoli are able to stretch. Negative pressure (drag or pull something) intercostal muscles. When we create space inside a object the air rushes in and this creates negative pressure Diaphragm muscle works on the addendum. There must alway ...
... Alveoli each alveoli has a capillary bed surrounding it. The alveoli are able to stretch. Negative pressure (drag or pull something) intercostal muscles. When we create space inside a object the air rushes in and this creates negative pressure Diaphragm muscle works on the addendum. There must alway ...
Chapter 1 - Maintaining Life
... Necessary Life functions • Responsiveness or Irritability – Ability to sense changes (stimuli) in the environment and respond to them. • Cut your hand - pull your hand away withdrawal reflex – don’t even think about it, just happens • Nervous system is mainly in charge ...
... Necessary Life functions • Responsiveness or Irritability – Ability to sense changes (stimuli) in the environment and respond to them. • Cut your hand - pull your hand away withdrawal reflex – don’t even think about it, just happens • Nervous system is mainly in charge ...
1 Bio 104 Lecture Outline Chapter 19 in Hole`s Human Anatomy and
... 1. Respiratory centers in medulla oblongata - respiratory rhythmicity center = controls basic rhythm of respiration 2. Pontine respiratory group – formally called _______________ and _____________ centers in Pons Apneustic center – lower pons ...
... 1. Respiratory centers in medulla oblongata - respiratory rhythmicity center = controls basic rhythm of respiration 2. Pontine respiratory group – formally called _______________ and _____________ centers in Pons Apneustic center – lower pons ...
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Overview of the respiratory
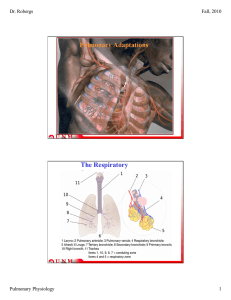
... The bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli beyond the 1° bronchi make up the lungs The right lung has 3 lobes while the left lung has 2 lobes that divide into lobules Each lung is enclosed by membranes called pleura The bronchial tree Starts with two main bronchi that lead from the trachea into t ...
... The bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli beyond the 1° bronchi make up the lungs The right lung has 3 lobes while the left lung has 2 lobes that divide into lobules Each lung is enclosed by membranes called pleura The bronchial tree Starts with two main bronchi that lead from the trachea into t ...
Download PDF
... aspects of the NDE have been reported by people who were fully conscious, and (2) hypoxic conditions give rise to mental states such as mental laziness, irritability, slowness of reasoning, and difficulty of remembering. These are contrary to the cognitive experiences regu ...
... aspects of the NDE have been reported by people who were fully conscious, and (2) hypoxic conditions give rise to mental states such as mental laziness, irritability, slowness of reasoning, and difficulty of remembering. These are contrary to the cognitive experiences regu ...
June issue (Final Notebook)
... The range of adaptation is also variable. Some reptiles can exist in a state of complete oxygen deprivation; others can survive only on drastically reduced oxygen reserves. In fact, true hibernation is seen only in small animals, whereas larger animals are often active and alert during the entire pe ...
... The range of adaptation is also variable. Some reptiles can exist in a state of complete oxygen deprivation; others can survive only on drastically reduced oxygen reserves. In fact, true hibernation is seen only in small animals, whereas larger animals are often active and alert during the entire pe ...
30.2 Respiration and Gas Exchange
... 30.2 Respiration and Gas Exchange Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. • Oxygen and carbon dioxide are carried by the blood to and from the alveoli. – oxygen diffuses from alveoli into capillary – oxygen binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells – carbon dioxide diffuses from capillary int ...
... 30.2 Respiration and Gas Exchange Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. • Oxygen and carbon dioxide are carried by the blood to and from the alveoli. – oxygen diffuses from alveoli into capillary – oxygen binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells – carbon dioxide diffuses from capillary int ...
Energy Systems Live Show
... Food is the source of energy for the human body and it also provides nutrients for growth and repair. When food is eaten, this is what happens… ...
... Food is the source of energy for the human body and it also provides nutrients for growth and repair. When food is eaten, this is what happens… ...
Chapter04 - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... • As the muscles relax, all dimensions of the thorax decrease. • Pressure in the lungs increases. ...
... • As the muscles relax, all dimensions of the thorax decrease. • Pressure in the lungs increases. ...
The Respiratory System
... 7. Most of the HCO3– diffuse into the plasma where it is carried in the bloodstream to the lungs. 8. In the HCO3– diffuse from the plasma red blood cells, combining with H+ released from hemoglobin and forming H2CO3. 9. Carbonic acid is converted back into CO2 and water. 10. CO2 formed from H2CO3 is ...
... 7. Most of the HCO3– diffuse into the plasma where it is carried in the bloodstream to the lungs. 8. In the HCO3– diffuse from the plasma red blood cells, combining with H+ released from hemoglobin and forming H2CO3. 9. Carbonic acid is converted back into CO2 and water. 10. CO2 formed from H2CO3 is ...
grade 8 released test items - pams
... mutations and can sometimes produce beneficial changes in populations. A mutant form of the normally lightcolored peppered moth is dark colored. The dark-colored moth blends in with soot-covered trees in heavily polluted areas. Why would the dark-colored mutation be beneficial in a polluted ...
... mutations and can sometimes produce beneficial changes in populations. A mutant form of the normally lightcolored peppered moth is dark colored. The dark-colored moth blends in with soot-covered trees in heavily polluted areas. Why would the dark-colored mutation be beneficial in a polluted ...
Lecture 15 - University of Idaho
... There is some effect by evaporation of saliva, but the major effect is derived from evaporation of moisture in the lungs, where blood is in close contact with surface tissues. c - Saliva -- For example, many Macropodids moisten their forearms with saliva. These regions are highly vascularized and ve ...
... There is some effect by evaporation of saliva, but the major effect is derived from evaporation of moisture in the lungs, where blood is in close contact with surface tissues. c - Saliva -- For example, many Macropodids moisten their forearms with saliva. These regions are highly vascularized and ve ...
Functions of the Circulatory System
... The Heart The muscle layer of the heart is the myocardium. Its powerful contractions pump blood through the circulatory system. The human heart has four chambers. A wall called the septum separates the right side of the heart from the left side. On each side of the septum are an upper and lower cham ...
... The Heart The muscle layer of the heart is the myocardium. Its powerful contractions pump blood through the circulatory system. The human heart has four chambers. A wall called the septum separates the right side of the heart from the left side. On each side of the septum are an upper and lower cham ...
Humans as Organisms
... The food we eat needs to be broken down into small pieces which we chew up into even smaller ones before swallowing them. Once the food gets to the stomach the food is broken down further by the stomach's muscular walls. This is known as physical digestion. Substances which our body needs cannot be ...
... The food we eat needs to be broken down into small pieces which we chew up into even smaller ones before swallowing them. Once the food gets to the stomach the food is broken down further by the stomach's muscular walls. This is known as physical digestion. Substances which our body needs cannot be ...
The Circulation And Exercise - Easymed.club
... HEART becomes LARGER and STRONGER. DECREASE in resting heart rate. Increased thickness and strength of the LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL causes an increase in the STROKE VOLUME and a lowering of the resting pulse rate. Larger stroke volume also means that there is an increase in ...
... HEART becomes LARGER and STRONGER. DECREASE in resting heart rate. Increased thickness and strength of the LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL causes an increase in the STROKE VOLUME and a lowering of the resting pulse rate. Larger stroke volume also means that there is an increase in ...
Respiratory System
... Some fish use “aquatic surface respiration” when hypoxic Swim to the surface and ventilate gills with water from the thin well-oxygenated water layer near surface Some fish can gulp air into mouth (buccal cavity) Buccal cavity highly vascularized for gas exchange ...
... Some fish use “aquatic surface respiration” when hypoxic Swim to the surface and ventilate gills with water from the thin well-oxygenated water layer near surface Some fish can gulp air into mouth (buccal cavity) Buccal cavity highly vascularized for gas exchange ...
Ch 42: Gas Exchange and the Respiratory System
... (gases, ions, pH, etc.) 3) stretching of lung tissue 4) emotional state ...
... (gases, ions, pH, etc.) 3) stretching of lung tissue 4) emotional state ...
Respiratory System Part 2
... Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3–) A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, ...
... Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3–) A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, ...
1 Bio 1B Evolution (Mishler) Practice questions Fall 2006 Answers
... B. the appearance of the leafy sea dragon (a sea horse) which looks so much like the kelp (seaweed) in which it lives that it lures prey into the seeming safety of the kelp forest and then eats them. C. the long, broad wings of the red-tailed hawk that allow it to sustain a gliding flight over open ...
... B. the appearance of the leafy sea dragon (a sea horse) which looks so much like the kelp (seaweed) in which it lives that it lures prey into the seeming safety of the kelp forest and then eats them. C. the long, broad wings of the red-tailed hawk that allow it to sustain a gliding flight over open ...
1 Bio 1B Evolution (Mishler) Practice questions Fall 2008 *Answers
... B. the appearance of the leafy sea dragon (a sea horse) which looks so much like the kelp (seaweed) in which it lives that it lures prey into the seeming safety of the kelp forest and then eats them. C. the long, broad wings of the red-tailed hawk that allow it to sustain a gliding flight over open ...
... B. the appearance of the leafy sea dragon (a sea horse) which looks so much like the kelp (seaweed) in which it lives that it lures prey into the seeming safety of the kelp forest and then eats them. C. the long, broad wings of the red-tailed hawk that allow it to sustain a gliding flight over open ...
Evolution practice questions
... B. the appearance of the leafy sea dragon (a sea horse) which looks so much like the kelp (seaweed) in which it lives that it lures prey into the seeming safety of the kelp forest and then eats them. C. the long, broad wings of the red-tailed hawk that allow it to sustain a gliding flight over open ...
... B. the appearance of the leafy sea dragon (a sea horse) which looks so much like the kelp (seaweed) in which it lives that it lures prey into the seeming safety of the kelp forest and then eats them. C. the long, broad wings of the red-tailed hawk that allow it to sustain a gliding flight over open ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.