Pharmacokinetics (Excretion of Drugs and factors affecting Excretion
... Lipid soluble drugs are not readily eliminated until they are metabolized to more polar compounds. Possible sources of excretion include: • Breath • Urine • Saliva • Perspiration • Feces • Milk • Bile • Hair ...
... Lipid soluble drugs are not readily eliminated until they are metabolized to more polar compounds. Possible sources of excretion include: • Breath • Urine • Saliva • Perspiration • Feces • Milk • Bile • Hair ...
Study of identification and assessment of drug
... As medicine become more international and different brand names in different countries and frequently have multiple brand names. The use of generic drugs decreases total count of the patients when they are available, Despite claims to the contrary; there are only a small number of examples where an ...
... As medicine become more international and different brand names in different countries and frequently have multiple brand names. The use of generic drugs decreases total count of the patients when they are available, Despite claims to the contrary; there are only a small number of examples where an ...
Comparison of Drug Approval Process in United States
... the "RMS"), it notifies this decision to other Member States (which then become the "CMS"), to whom applications have also been submitted. RMS issues a report to other states on its own findings. Generic industry is the major user of this type of drug approval procedure. This process may consu ...
... the "RMS"), it notifies this decision to other Member States (which then become the "CMS"), to whom applications have also been submitted. RMS issues a report to other states on its own findings. Generic industry is the major user of this type of drug approval procedure. This process may consu ...
Drug Myths and Facts
... make a person stop breathing, have a heart attack or go into a coma. This can happen the first time the drug is used. ...
... make a person stop breathing, have a heart attack or go into a coma. This can happen the first time the drug is used. ...
ED Toxicology
... Activated charcoal given in repeated doses also enhances the elimination of some drugs even after they have been absorbed such as carbamazepine, phenobarbitone, quinine, theophylline and dapsone. Alkalinisation of the urine for salicylate poisoning. Haemodialysis for ethylene glycol, lithium, ...
... Activated charcoal given in repeated doses also enhances the elimination of some drugs even after they have been absorbed such as carbamazepine, phenobarbitone, quinine, theophylline and dapsone. Alkalinisation of the urine for salicylate poisoning. Haemodialysis for ethylene glycol, lithium, ...
TB lecture - Mayo Clinic Center for Tuberculosis
... Patients with medical conditions that may result in abnormal pharmacokinetics of the first-line drugs (renal, liver, g-tubes, HIV with evidence of malabsorption, etc.) ...
... Patients with medical conditions that may result in abnormal pharmacokinetics of the first-line drugs (renal, liver, g-tubes, HIV with evidence of malabsorption, etc.) ...
File - Wk 1-2
... In general, the lower the potency of a drug and the higher the dose needed, the more likely it is that sites of activation other than the primary one, will assume significance associated with the appearance of unwanted side affects Therefore, no drug is ...
... In general, the lower the potency of a drug and the higher the dose needed, the more likely it is that sites of activation other than the primary one, will assume significance associated with the appearance of unwanted side affects Therefore, no drug is ...
Depressants (Downer`s)
... Interactions with other drugs – enhances the effects of other drugs sometimes leading to devastating effects -if inhibit the breakdown of other drugs, can lead to longer retention times in the body with increase effects 0.08% blood alcohol level = 80 mg/100 cm3 of blood Since it’s sufficiently volat ...
... Interactions with other drugs – enhances the effects of other drugs sometimes leading to devastating effects -if inhibit the breakdown of other drugs, can lead to longer retention times in the body with increase effects 0.08% blood alcohol level = 80 mg/100 cm3 of blood Since it’s sufficiently volat ...
Levsin Tablet PI RA - Meda Pharmaceuticals
... Levsin® is absorbed totally and completely by sublingual administration as well as oral administration. Once absorbed, Levsin® disappears rapidly from the blood and is distributed throughout the entire body. The half-life of Levsin® is 2 to 3½ hours. Levsin® is partly hydrolyzed to tropic acid and t ...
... Levsin® is absorbed totally and completely by sublingual administration as well as oral administration. Once absorbed, Levsin® disappears rapidly from the blood and is distributed throughout the entire body. The half-life of Levsin® is 2 to 3½ hours. Levsin® is partly hydrolyzed to tropic acid and t ...
MICROMEDEX? 2.0简介
... 3. You are provided with a drug consult that addresses the most recent guidelines for treating nausea and vomiting. 4. These guidelines are used as the standard of care for cancer patients and offer factual information on the incidence of nausea and vomiting due to various chemotherapeutic agents as ...
... 3. You are provided with a drug consult that addresses the most recent guidelines for treating nausea and vomiting. 4. These guidelines are used as the standard of care for cancer patients and offer factual information on the incidence of nausea and vomiting due to various chemotherapeutic agents as ...
Inhaled insulin is approved in Europe and United States
... Two of the nine members of the FDA's advisory panel on endocrinological and metabolic drugs voted against the approval of Exubera. Critics say Exubera offers no advantage in effectiveness over injected insulin and fails to control postprandial glucose concentrations as well as subcutaneous insulin. ...
... Two of the nine members of the FDA's advisory panel on endocrinological and metabolic drugs voted against the approval of Exubera. Critics say Exubera offers no advantage in effectiveness over injected insulin and fails to control postprandial glucose concentrations as well as subcutaneous insulin. ...
Adlyxin
... Hypoglycemia with concomitant use of sulfonylurea or basal insulin – consider dose reduction of basal insulin or sulfonylurea Immunogenicity – patients may develop antibodies to lixisenatide. Thyroid C-cell tumor in rats (all doses); similar to other GLP-1s Category C – Limited data in pregnan ...
... Hypoglycemia with concomitant use of sulfonylurea or basal insulin – consider dose reduction of basal insulin or sulfonylurea Immunogenicity – patients may develop antibodies to lixisenatide. Thyroid C-cell tumor in rats (all doses); similar to other GLP-1s Category C – Limited data in pregnan ...
Use of antibacterial agents in renal failure
... edema, conversion of urea to ammonia by gastric urease, antacids, or the use of alkalating agents, such as bicarbonate and citrate, decreased small bowel movement ...
... edema, conversion of urea to ammonia by gastric urease, antacids, or the use of alkalating agents, such as bicarbonate and citrate, decreased small bowel movement ...
Opioid Epidemic: Legislative Progress in Pennsylvania HR 659 Task
... Medicare/Medicaid to develop an effective approach to substance abuse. Nearly 12 percent of adults in Medicaid and 6 percent of adolescents have a Substance Use Disorder (SUD) or issue. While slower than it should be, the Pennsylvania Insurance Department is enforcing statutes that require parity of ...
... Medicare/Medicaid to develop an effective approach to substance abuse. Nearly 12 percent of adults in Medicaid and 6 percent of adolescents have a Substance Use Disorder (SUD) or issue. While slower than it should be, the Pennsylvania Insurance Department is enforcing statutes that require parity of ...
Drugs
... Cocaine use still rose during the 1920’s but then decreased in 1930’s because amphetamines became available (and at the time cost less, were more easily available AND the euphoria lasted longer) Amphetamine took over in popularity during the 1940’s – 1960’s. In 1970’s restrictions on amphetamine tig ...
... Cocaine use still rose during the 1920’s but then decreased in 1930’s because amphetamines became available (and at the time cost less, were more easily available AND the euphoria lasted longer) Amphetamine took over in popularity during the 1940’s – 1960’s. In 1970’s restrictions on amphetamine tig ...
Medication Use in the Elderly
... ADR occur due to either inhibition or induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes ...
... ADR occur due to either inhibition or induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes ...
File
... Distribution - movement of drug to various tissues of the body eg fat, muscle, and brain tissue Metabolism - chemical alteration of a drug by the body. Excretion All these factors are affected by the body system ...
... Distribution - movement of drug to various tissues of the body eg fat, muscle, and brain tissue Metabolism - chemical alteration of a drug by the body. Excretion All these factors are affected by the body system ...
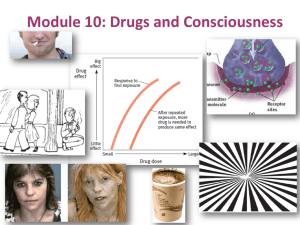
M10e Mod 10 Drugs and Consciousness
... disrupts sleep for 3-4 hours can lead to withdrawal symptoms if used daily: ...
... disrupts sleep for 3-4 hours can lead to withdrawal symptoms if used daily: ...
It`s official: high potency ecstasy makes a comeback
... ecstasy pills recovered, in 25 separate seizures, contained high levels of MDMA more common in pills made in the 1980s and 1990s. “It is rare these days to get ecstasy pills that contain MDMA, but this year we were surprised because most of the pills did,” Bunt said. The findings back up mounting an ...
... ecstasy pills recovered, in 25 separate seizures, contained high levels of MDMA more common in pills made in the 1980s and 1990s. “It is rare these days to get ecstasy pills that contain MDMA, but this year we were surprised because most of the pills did,” Bunt said. The findings back up mounting an ...
Functional Characterization
... target product profile (DTPP), designing assays in view of eventual clinical trial applications, and providing documentation in line with regulatory requirements • Design of non-standard assays to answer specific questions about therapeutic candidates In Vitro pharmacology ...
... target product profile (DTPP), designing assays in view of eventual clinical trial applications, and providing documentation in line with regulatory requirements • Design of non-standard assays to answer specific questions about therapeutic candidates In Vitro pharmacology ...
The Science of Recovery - AAP
... Parole/Probation New suspension with q30d administration should ...
... Parole/Probation New suspension with q30d administration should ...
CAL packages
... Treatment of the cardiovascular diseases described above will be discussed in terms of the assessment of risk/benefit ratios and the choice of drug, dose and route of administration. Pharmacological incompatibilities, drug interactions and their clinical significance. Evidence-based medicine includi ...
... Treatment of the cardiovascular diseases described above will be discussed in terms of the assessment of risk/benefit ratios and the choice of drug, dose and route of administration. Pharmacological incompatibilities, drug interactions and their clinical significance. Evidence-based medicine includi ...
Rebamipide - PIO Nas - Badan Pengawas Obat dan Makanan
... concentration of rebamipide peaked (at 210 ng/mL) at 2 hours. The elimination half-life in plasma was about 1.5 hours. Repeated-administration studies have shown that the drug does not accumulate in humans. The absorption of rebamipide tended to be slow when the drug was administered orally at a dos ...
... concentration of rebamipide peaked (at 210 ng/mL) at 2 hours. The elimination half-life in plasma was about 1.5 hours. Repeated-administration studies have shown that the drug does not accumulate in humans. The absorption of rebamipide tended to be slow when the drug was administered orally at a dos ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.