
the drug seeking patient - Faculty of pain medicine
... May foster better coping skills in the ‘normal world’ Easier access to illicit drugs and cues for craving • Detoxification centres: Short-stay (usually 5-10 days) in a detoxification centre offers the patient ‘time-out’ from a drug-taking and drug-seeking environment. Switch to 2-8mg Bupre ...
... May foster better coping skills in the ‘normal world’ Easier access to illicit drugs and cues for craving • Detoxification centres: Short-stay (usually 5-10 days) in a detoxification centre offers the patient ‘time-out’ from a drug-taking and drug-seeking environment. Switch to 2-8mg Bupre ...
Alcohol Effects on Inhibitory Mechanisms of Visual Attention
... Chronic effect – decreased number of dopamine transporters in basal ganglia, despite a three year abstinence from the drug (predisposition to Parkinson’s disease) ...
... Chronic effect – decreased number of dopamine transporters in basal ganglia, despite a three year abstinence from the drug (predisposition to Parkinson’s disease) ...
Driver Diagrams - Ohio Hospital Association
... alerts and overrides to redesign standardized processes Link order sets to recent lab values or other monitoring parameters ...
... alerts and overrides to redesign standardized processes Link order sets to recent lab values or other monitoring parameters ...
Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
... – The approval for clinical use is easier due to the prior experience with the original preparation – Must be pharmaceutically equivalent: same API, dose, pharmaceutical dosage form and the same route of administration as in original preparation – Must be clinically bioequivalent: i.e. it must be of ...
... – The approval for clinical use is easier due to the prior experience with the original preparation – Must be pharmaceutically equivalent: same API, dose, pharmaceutical dosage form and the same route of administration as in original preparation – Must be clinically bioequivalent: i.e. it must be of ...
Drug disposition in pregnancy MEDSCI 722 Anna Ponnampalam
... Net results • May see decreased steady state concentrations in pregnancy if a ‘usual’ dose is administered (renally eliminated drugs) • Thus a higher dose will be needed to achieve therapeutic levels • BUT - many drug-specific exceptions can occur ...
... Net results • May see decreased steady state concentrations in pregnancy if a ‘usual’ dose is administered (renally eliminated drugs) • Thus a higher dose will be needed to achieve therapeutic levels • BUT - many drug-specific exceptions can occur ...
annexure-ii
... required release rate on par with the theoretical release rate for guar gum formulations meant for twice daily administration4. 2. Shu XZ et al., developed Chitosan/Gelatin microspheres prepared by modified emulsification and ionotropic gelation. The key point of the modified process is the introduc ...
... required release rate on par with the theoretical release rate for guar gum formulations meant for twice daily administration4. 2. Shu XZ et al., developed Chitosan/Gelatin microspheres prepared by modified emulsification and ionotropic gelation. The key point of the modified process is the introduc ...
Unit 20 Self Needs Analysis: Date……………….
... Outline the role of the nurse in the safe administration of these drugs. (Discuss this with your mentor & your clinical teacher.) ...
... Outline the role of the nurse in the safe administration of these drugs. (Discuss this with your mentor & your clinical teacher.) ...
minipress package insert [pi]
... consisting of atrophy and necrosis occurred at 25 mg/kg/day (75 times the usual maximum recommended human dose). No testicular changes were seen in rats or dogs at 10 mg/kg/day (30 times the usual maximum recommended human dose). In view of the testicular changes observed in animals, 105 patients on ...
... consisting of atrophy and necrosis occurred at 25 mg/kg/day (75 times the usual maximum recommended human dose). No testicular changes were seen in rats or dogs at 10 mg/kg/day (30 times the usual maximum recommended human dose). In view of the testicular changes observed in animals, 105 patients on ...
Module 10: Drugs and Consciousness
... • Drugs that stimulate neural activity, causing speeded-up body functions (body temperature and heart rate) and associated energy and mood changes • Results in short term energy and euphoria • Originally diet drugs ...
... • Drugs that stimulate neural activity, causing speeded-up body functions (body temperature and heart rate) and associated energy and mood changes • Results in short term energy and euphoria • Originally diet drugs ...
Keeping on target – the need for more rapid and policy
... • National govt – all staff to be trained in drug issues • Political parties take up theme – call for ministers resignation • Resignation of regional director • Promise for national assessment re institutions and drugs ...
... • National govt – all staff to be trained in drug issues • Political parties take up theme – call for ministers resignation • Resignation of regional director • Promise for national assessment re institutions and drugs ...
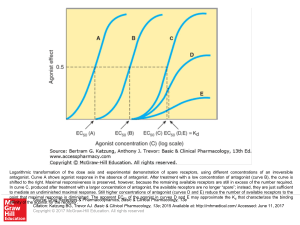
Slide ()
... Logarithmic transformation of the dose axis and experimental demonstration of spare receptors, using different concentrations of an irreversible antagonist. Curve A shows agonist response in the absence of antagonist. After treatment with a low concentration of antagonist (curve B), the curve is shi ...
... Logarithmic transformation of the dose axis and experimental demonstration of spare receptors, using different concentrations of an irreversible antagonist. Curve A shows agonist response in the absence of antagonist. After treatment with a low concentration of antagonist (curve B), the curve is shi ...
Heroin Opium, morphine and heroin are all derived from the opium
... At times it gives a feeling of happiness and well-being. Heroin, after injection, rapidly reaches the brain, thus giving an immediate effect. Because of its pain relief and "happiness" effect, heroin is potentially the most addictive drug of the narcotic/analgesic type. If the body is not supplied w ...
... At times it gives a feeling of happiness and well-being. Heroin, after injection, rapidly reaches the brain, thus giving an immediate effect. Because of its pain relief and "happiness" effect, heroin is potentially the most addictive drug of the narcotic/analgesic type. If the body is not supplied w ...
Premil Prescribing Information
... binds to specific receptors in the β cell membrane leading to the closure of ATP dependent K+ channels and the depolarisation of β cell membrane. This in turn, leads to Ca+ + influx, increased intracellular Ca ++ and the stimulation of insulin secretion. Dosage and Administration Premil has to be ta ...
... binds to specific receptors in the β cell membrane leading to the closure of ATP dependent K+ channels and the depolarisation of β cell membrane. This in turn, leads to Ca+ + influx, increased intracellular Ca ++ and the stimulation of insulin secretion. Dosage and Administration Premil has to be ta ...
Document
... Also please answer the questions from each lecturer on separate pages from those of the others. Finally, before answering the following questions, read and analyze them carefully to identify the information being requested. When you have done this, write your response, using the same organizational ...
... Also please answer the questions from each lecturer on separate pages from those of the others. Finally, before answering the following questions, read and analyze them carefully to identify the information being requested. When you have done this, write your response, using the same organizational ...
Our Genes, Our Drugs and our Future
... GDF: Rapid and slow acetylators: 15 Individuals who are rapid acetylators: Have failure rate with INH in Tx of TB Require doses of hydralazine to control HT Individuals who are slow acetylators have ...
... GDF: Rapid and slow acetylators: 15 Individuals who are rapid acetylators: Have failure rate with INH in Tx of TB Require doses of hydralazine to control HT Individuals who are slow acetylators have ...
Bacteria and mycobacteria
... • Combination therapy is used frequently for an initial severe infection in which the pathogen is unknown. • Once the pathogen is known, the appropriate drug can be administered. • Although combination therapy has many benefits, it also has many disadvantages compared with monotherapy. Drug Dose: • ...
... • Combination therapy is used frequently for an initial severe infection in which the pathogen is unknown. • Once the pathogen is known, the appropriate drug can be administered. • Although combination therapy has many benefits, it also has many disadvantages compared with monotherapy. Drug Dose: • ...
WebQuest: Drugs, and their effects on the body! Introduction: A drug
... 3. What is the world's primary source of caffeine? 4. Why does dark roast coffee have less caffeine than lighter roasts? 5. How much chocolate would you have to eat to get the same amount of caffeine found in two cups of regular coffee? 6. What happens when caffeine is used in combination with other ...
... 3. What is the world's primary source of caffeine? 4. Why does dark roast coffee have less caffeine than lighter roasts? 5. How much chocolate would you have to eat to get the same amount of caffeine found in two cups of regular coffee? 6. What happens when caffeine is used in combination with other ...
Donnatal Tablets Prescribing Information
... manifestations; and decreased sweating. Acquired hypersensitivity to barbiturates consists chiefly in allergic reactions that occur especially in persons who tend to have asthma, urticaria, angioedema, and similar conditions. Hypersensitivity reactions in this category include localized swelling, pa ...
... manifestations; and decreased sweating. Acquired hypersensitivity to barbiturates consists chiefly in allergic reactions that occur especially in persons who tend to have asthma, urticaria, angioedema, and similar conditions. Hypersensitivity reactions in this category include localized swelling, pa ...
item[`#file`]
... o vs. MDMA – “ecstasy”, not a stimulant (dopamine receptor), actually a hallucinogen (serotonin) o vs. Cocaine – same mechanism, but amphetamines last longer, and enable dopamine release Schedule II Drug – legal, but under strict control Types – include Adderal, Dexedrine, Desoxyn can be given ...
... o vs. MDMA – “ecstasy”, not a stimulant (dopamine receptor), actually a hallucinogen (serotonin) o vs. Cocaine – same mechanism, but amphetamines last longer, and enable dopamine release Schedule II Drug – legal, but under strict control Types – include Adderal, Dexedrine, Desoxyn can be given ...
Guidance regarding Psychoactive Substances
... Severe or life threatening intoxication if taken in large doses. They can affect the nervous system and lead to seizures, increased heart rate, high blood pressure, sweating, increased body temperature and agitation. ...
... Severe or life threatening intoxication if taken in large doses. They can affect the nervous system and lead to seizures, increased heart rate, high blood pressure, sweating, increased body temperature and agitation. ...
OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY
... action regardless of route of administration 2) Compartment-body space in which drug is homogeneously distributed 3) Rate constants Ka- absorption rate constant (fraction of drug entering compartment per unit time) Ke- elimination rate constant (fraction of drug eliminated from compartment pe ...
... action regardless of route of administration 2) Compartment-body space in which drug is homogeneously distributed 3) Rate constants Ka- absorption rate constant (fraction of drug entering compartment per unit time) Ke- elimination rate constant (fraction of drug eliminated from compartment pe ...
CLINICALLY IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
... Antianabolic effect of tetracycline increases urea production which is retained by the ...
... Antianabolic effect of tetracycline increases urea production which is retained by the ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.









![minipress package insert [pi]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015485945_1-c4a49eb0cb8d6643167a45b1642d1836-300x300.png)









![item[`#file`]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009481418_1-28851d674cda3ff126bbb840715e8d8b-300x300.png)


