Optimizing antifungal choice and administration
... CYP2C191. Because of this, clinically relevant potential drug–drug interactions can occur when particular triazoles are coadministered with drugs that either induce or inhibit CYP450 isoenzymes or that are substrates for them. A large list of significant drug–drug interactions have been noted with t ...
... CYP2C191. Because of this, clinically relevant potential drug–drug interactions can occur when particular triazoles are coadministered with drugs that either induce or inhibit CYP450 isoenzymes or that are substrates for them. A large list of significant drug–drug interactions have been noted with t ...
Organovo Investor Presentation
... Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“the SEC”), including those factors listed under the caption "Risk Factors" in the Company’s Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2015, filed with the SEC on June 9, 2015, as well as other filings Organovo makes with the SEC from time ...
... Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“the SEC”), including those factors listed under the caption "Risk Factors" in the Company’s Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2015, filed with the SEC on June 9, 2015, as well as other filings Organovo makes with the SEC from time ...
Anti-tuberculous drugs
... Anti-TB therapy • Multiple drugs are used to reduce the emergence of resistance • Given as combination tablets • Taken 30 min before the breakfast as absorption of rifampicin is influenced by food ...
... Anti-TB therapy • Multiple drugs are used to reduce the emergence of resistance • Given as combination tablets • Taken 30 min before the breakfast as absorption of rifampicin is influenced by food ...
POSSIBLE ALLERGIC REACTION? Contact with known/potential
... POSSIBLE ALLERGIC REACTION? Contact with known/potential trigger (drug, food allergen, insect bite) Itching Erythema of skin - painless ...
... POSSIBLE ALLERGIC REACTION? Contact with known/potential trigger (drug, food allergen, insect bite) Itching Erythema of skin - painless ...
Calcium channel blockers and drug interactions
... Diltiazem undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism, and interaction between the calcium channel blockers and drugs that alter hepatic flow are an important consideration. Therefore, diltiazem should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function. Any drug that affects hepatic ...
... Diltiazem undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism, and interaction between the calcium channel blockers and drugs that alter hepatic flow are an important consideration. Therefore, diltiazem should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function. Any drug that affects hepatic ...
Pharmacodynamics
... Theoretical concentration-effect curves for a full and partial agonist of a given receptor ...
... Theoretical concentration-effect curves for a full and partial agonist of a given receptor ...
Small Changes are Big Steps: Making Nanotechnologies Ethically
... chances of therapeutic success to about 50%. However, high adherence to HAART does not lead to the complete elimination of the virus from the host. Paediatric HIV has been almost eliminated in developed countries by limiting both maternal to fetus and breastfeeding transmission. In contrast, the sit ...
... chances of therapeutic success to about 50%. However, high adherence to HAART does not lead to the complete elimination of the virus from the host. Paediatric HIV has been almost eliminated in developed countries by limiting both maternal to fetus and breastfeeding transmission. In contrast, the sit ...
NeuroBiology
... they are 36 weeks old. (1) ci) Myelination of the nervous system leads to the development of walking. Name the cells that produce the myelin sheath (1) cii)Explain why it is important that axons are surrounded by the myelin sheath (1) 22. Use of recreational drugs can lead to drug tolerance a) Recre ...
... they are 36 weeks old. (1) ci) Myelination of the nervous system leads to the development of walking. Name the cells that produce the myelin sheath (1) cii)Explain why it is important that axons are surrounded by the myelin sheath (1) 22. Use of recreational drugs can lead to drug tolerance a) Recre ...
Pharmacologic Management
... Convert pounds to kg: 44 lb = 20 kg Determine safe dose: 20 kg x 0.5 mg = 100 mg 100 mg divided by 2 (drug is given twice a day) 5 mg is safe it meets mg / kg rule and does not exceed 40 ...
... Convert pounds to kg: 44 lb = 20 kg Determine safe dose: 20 kg x 0.5 mg = 100 mg 100 mg divided by 2 (drug is given twice a day) 5 mg is safe it meets mg / kg rule and does not exceed 40 ...
Regulatory Aspects of Ophthalmic Drug
... effectiveness issue – thus, did not require an Advisory Committee Macugen – did go through as it was first in class and route of administration for ...
... effectiveness issue – thus, did not require an Advisory Committee Macugen – did go through as it was first in class and route of administration for ...
An integrated strategy to determine the absorption, distribution
... The total clearance of [14C]-bevenopran at 360 mL/min is lower than plasma flow to the liver (812 mL/min). In the absence of any fecal excretion (<0.1%), it can be concluded that any drug product excreted via the bile would have been reabsorbed, re-circulated, and eliminated via the urine. The volum ...
... The total clearance of [14C]-bevenopran at 360 mL/min is lower than plasma flow to the liver (812 mL/min). In the absence of any fecal excretion (<0.1%), it can be concluded that any drug product excreted via the bile would have been reabsorbed, re-circulated, and eliminated via the urine. The volum ...
An Introduction to Drug Disposition: The Basic Principles of
... into tissues such as muscle. As thiopental is not tightly bound to brain lipid, its concentration in the brain changes in parallel with changes in the plasma concentration, leading to a rapid termination of anesthesia by redistribution rather than elimination. A third distributive phase for thiopent ...
... into tissues such as muscle. As thiopental is not tightly bound to brain lipid, its concentration in the brain changes in parallel with changes in the plasma concentration, leading to a rapid termination of anesthesia by redistribution rather than elimination. A third distributive phase for thiopent ...
Selected Prescription Drugs With Potential for Abuse
... **Taking drugs by injection can increase the risk of infection through needle contamination with staphylococci, HIV, hepatitis, and other organisms. ***Associated with sexual assaults. ...
... **Taking drugs by injection can increase the risk of infection through needle contamination with staphylococci, HIV, hepatitis, and other organisms. ***Associated with sexual assaults. ...
Identifying and establishing consensus on the most important safety
... There is an increasing body of evidence that errors in primary care result in harm to patients, particularly in relation to medicines management.1 Most prescribing in the United Kingdom (UK) is undertaken by general practitioners (GPs), and it is here that attention needs to be focused in order to r ...
... There is an increasing body of evidence that errors in primary care result in harm to patients, particularly in relation to medicines management.1 Most prescribing in the United Kingdom (UK) is undertaken by general practitioners (GPs), and it is here that attention needs to be focused in order to r ...
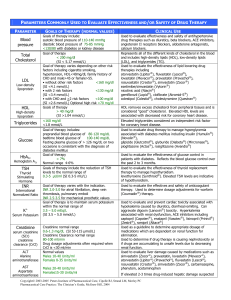
Blood pressure Total Cholesterol LDL HDL Triglycerides Glucose
... captopril (Capoten®), enalapril (Vasotec®), lisinopril (Prinivil®) (Zestril®), ramipril (Altace®) Used as a guideline to determine appropriate dosage of medications which are dependent on renal function for elimination. Used to determine if drug therapy is causing nephrotoxicity or if drugs are accu ...
... captopril (Capoten®), enalapril (Vasotec®), lisinopril (Prinivil®) (Zestril®), ramipril (Altace®) Used as a guideline to determine appropriate dosage of medications which are dependent on renal function for elimination. Used to determine if drug therapy is causing nephrotoxicity or if drugs are accu ...
Letter to the Editor - Drug Metabolism and Disposition
... McGready et al., 2003). All four drugs are reported to be CYP2C19 substrates. However, the effect of EE on their PK cannot be ascribed to CYP2C19 alone, because other cytochromes P450 are involved in metabolism (Jung et al., 1997; Yang et al., 1999; McGinnity et al., 2000; Hidestrand et al., 2001). ...
... McGready et al., 2003). All four drugs are reported to be CYP2C19 substrates. However, the effect of EE on their PK cannot be ascribed to CYP2C19 alone, because other cytochromes P450 are involved in metabolism (Jung et al., 1997; Yang et al., 1999; McGinnity et al., 2000; Hidestrand et al., 2001). ...
Express Scripts
... provide other services to help you along the process. This program not only supplies the prescribed medication and related supplies such as needles and syringes, but also provides clinical support to you to help improve compliance as well as provide convenient delivery. ...
... provide other services to help you along the process. This program not only supplies the prescribed medication and related supplies such as needles and syringes, but also provides clinical support to you to help improve compliance as well as provide convenient delivery. ...
PRESCRIBING CASCADE. A PROPOSED NEW WAY TO
... the specificity-sensibility format (low-high) and then, build a Receiver Operating Characteristic curve. This putative risk estimation should include some features of case data; for instance, number of drugs used, ADRs generated, or severity of the former disease. In this sense, low–high equate to 4 ...
... the specificity-sensibility format (low-high) and then, build a Receiver Operating Characteristic curve. This putative risk estimation should include some features of case data; for instance, number of drugs used, ADRs generated, or severity of the former disease. In this sense, low–high equate to 4 ...
Considerations for Target Selection in CNS Drug Discovery Programs
... drugged CNS targets remain exclusively within the domain of small-molecule therapeutics. The nonfenestrated endothelium of brain capillaries that constitutes the BBB physically limits the passive permeability of compounds and presents a metabolic barrier to CNS entry in the form of metabolizing enzy ...
... drugged CNS targets remain exclusively within the domain of small-molecule therapeutics. The nonfenestrated endothelium of brain capillaries that constitutes the BBB physically limits the passive permeability of compounds and presents a metabolic barrier to CNS entry in the form of metabolizing enzy ...
Inheritance and Drug Response - New England Journal of Medicine
... he promise of pharmacogenetics, the study of the role of inheritance in the individual variation in drug response, lies in its potential to identify the right drug and dose for each patient. Even though individual differences in drug response can result from the effects of age, sex, disease, or drug ...
... he promise of pharmacogenetics, the study of the role of inheritance in the individual variation in drug response, lies in its potential to identify the right drug and dose for each patient. Even though individual differences in drug response can result from the effects of age, sex, disease, or drug ...
Ch. 23-Drugs Used to Treat Thrombo
... diseases caused by clotting within blood vessels are major causes of death, they include: deep vein thrombosis myocardial infarction (MI) dysrhythmias with clot formation coronary artery spasm leading to clot formation **see box 23-1 pg. 294 for methods used to treat** ...
... diseases caused by clotting within blood vessels are major causes of death, they include: deep vein thrombosis myocardial infarction (MI) dysrhythmias with clot formation coronary artery spasm leading to clot formation **see box 23-1 pg. 294 for methods used to treat** ...
The Role of the Practice Pharmacist
... GMC recommends that GPs can prescribe unlicensed or “off license” medicines but, if you decide to do so, you must: Be satisfied that an alternative, licensed medicine would not meet the patient's needs Be satisfied that there is a sufficient evidence base and/or experience of using the medicine to d ...
... GMC recommends that GPs can prescribe unlicensed or “off license” medicines but, if you decide to do so, you must: Be satisfied that an alternative, licensed medicine would not meet the patient's needs Be satisfied that there is a sufficient evidence base and/or experience of using the medicine to d ...
MRCI Additional Instructions Walkthru
... 23. Code: If there is no code available (5 times a day) code as the next closest frequency in the tool to represent the least complex regimen (5 times a day code as “every 6hours”) 24. Code: Ni ...
... 23. Code: If there is no code available (5 times a day) code as the next closest frequency in the tool to represent the least complex regimen (5 times a day code as “every 6hours”) 24. Code: Ni ...
Torreya Insights
... drugs if appropriate regulatory steps are taken, or instead may be able to come to market sooner as socalled medical foods or even OTC products because their ingredients are regarded as safe. A drug candidate where the number of potential patients is small. There is frequently an opportunity for a h ...
... drugs if appropriate regulatory steps are taken, or instead may be able to come to market sooner as socalled medical foods or even OTC products because their ingredients are regarded as safe. A drug candidate where the number of potential patients is small. There is frequently an opportunity for a h ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.