role of phenobarbitone as an antiepileptic drug in 21st century
... pharmacokinetic profile of phenobarbitone.2 Phenobarbitone can be administered by oral, intravenous, and intramuscular routes. The oral bioavailability is approximately 95%, and the time taken to peak plasma concentrations is 0.5-4 hours and 2-8 hours respectively when phenobarbitone is given by ora ...
... pharmacokinetic profile of phenobarbitone.2 Phenobarbitone can be administered by oral, intravenous, and intramuscular routes. The oral bioavailability is approximately 95%, and the time taken to peak plasma concentrations is 0.5-4 hours and 2-8 hours respectively when phenobarbitone is given by ora ...
Chapter 4 - Skills Commons
... into a “storage chamber” where it can be more easily inhaled by the patient. The patient should be sure to rinse their mouth after administration of an MDI to prevent an oral fungal infection. Created by Jennifer Majeske, Mineral Area College ...
... into a “storage chamber” where it can be more easily inhaled by the patient. The patient should be sure to rinse their mouth after administration of an MDI to prevent an oral fungal infection. Created by Jennifer Majeske, Mineral Area College ...
Medicare Part D and Prescription Drug Utilization
... elderly that resulted from the adoption of Part D to generate new estimates the impact of prescription drug insurance coverage on drug utilization. The analysis uses detailed data on a strongly balanced panel of those 65 and older (the “elderly” as defined for this study), observed before and after ...
... elderly that resulted from the adoption of Part D to generate new estimates the impact of prescription drug insurance coverage on drug utilization. The analysis uses detailed data on a strongly balanced panel of those 65 and older (the “elderly” as defined for this study), observed before and after ...
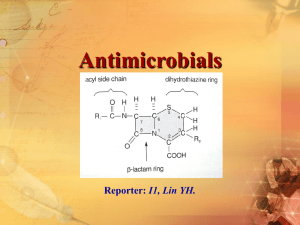
penicillins
... ulcerative colitis (as sulfasalazine), in burns (as silver sulfadiazine or mafenide), in chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum infection, and in combination with trimethoprim ...
... ulcerative colitis (as sulfasalazine), in burns (as silver sulfadiazine or mafenide), in chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum infection, and in combination with trimethoprim ...
Leflunomide - Wolverhampton Formulary
... If ALT (SGPT) elevations of 2- to 3-fold the upper limit of normal occur then the dose can be reduced from 20 mg to 10 mg and monitoring must be performed weekly. If ALT elevations of more than 2-fold the upper limit persist, or more than 3-fold the upper limit of normal are present, leflunomide tre ...
... If ALT (SGPT) elevations of 2- to 3-fold the upper limit of normal occur then the dose can be reduced from 20 mg to 10 mg and monitoring must be performed weekly. If ALT elevations of more than 2-fold the upper limit persist, or more than 3-fold the upper limit of normal are present, leflunomide tre ...
METHOD VALIDATION FOR SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC ESTIMATION OF CILNIDIPINE Research Article
... Email: [email protected] Received: 19 Mar 2012, Revised and Accepted: 30 April 2012 ABSTRACT The present study describes accurate, precise and reproducible spectrophotometric method for estimation of Cilnidipine. The method was validated by using various parameters as per ICH guidelines. Cilnidip ...
... Email: [email protected] Received: 19 Mar 2012, Revised and Accepted: 30 April 2012 ABSTRACT The present study describes accurate, precise and reproducible spectrophotometric method for estimation of Cilnidipine. The method was validated by using various parameters as per ICH guidelines. Cilnidip ...
FDA Warning Letter to Charles McKay, M.D. 2009-10-23
... intervention, and conduct of efficacy and safety-related assessments. Furthermore, the protocol required that all randomized patients be followed through to the final follow-up visit in accordance with the schedule established at the time of randomization, regardless of treatment status (i.e., perma ...
... intervention, and conduct of efficacy and safety-related assessments. Furthermore, the protocol required that all randomized patients be followed through to the final follow-up visit in accordance with the schedule established at the time of randomization, regardless of treatment status (i.e., perma ...
Drug Interaction and Food - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Phase I processes include oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis and hydration resulting in the formation of functional groups (OH, SH, NH2 or COOH) that impart the metabolite with increased polarity compared to the parent compound (Gibson and Skett, 2001). In phase I processes, the cytochrome P450 (CYP) ...
... Phase I processes include oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis and hydration resulting in the formation of functional groups (OH, SH, NH2 or COOH) that impart the metabolite with increased polarity compared to the parent compound (Gibson and Skett, 2001). In phase I processes, the cytochrome P450 (CYP) ...
Ecological Momentary Assessment of Illicit Drug Use Compared to
... used in drug treatment and employment drug testing settings [1]. The utility of these methods lies in their ability to detect metabolites of illicit drugs used within a specific window of time that varies depending on the biological specimen. Despite being the gold standard for the assessment of dru ...
... used in drug treatment and employment drug testing settings [1]. The utility of these methods lies in their ability to detect metabolites of illicit drugs used within a specific window of time that varies depending on the biological specimen. Despite being the gold standard for the assessment of dru ...
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING TABLET CONTAINING AMLODIPINE Research Article
... dispersion with PEG 4000, PVP K-30 using kneading process. Drug polymer interactions were investigated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Surface morphology of solid dispersion particles was determined by SEM study. Dissolution rate of s ...
... dispersion with PEG 4000, PVP K-30 using kneading process. Drug polymer interactions were investigated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Surface morphology of solid dispersion particles was determined by SEM study. Dissolution rate of s ...
prescription drug abuse - American College of Physicians
... suggests that drug overdose may now be the leading cause of such deaths. This paper uses the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) definition of drug abuse, which is “the intentional use of a medication without a prescription; in a way other than as prescribed; or for the experience or feeling it ...
... suggests that drug overdose may now be the leading cause of such deaths. This paper uses the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) definition of drug abuse, which is “the intentional use of a medication without a prescription; in a way other than as prescribed; or for the experience or feeling it ...
Pilocarpine E hydrochloride
... HCl: (1) Chronic simple glaucoma (especially open-angle). Chronic angle-closure glaucoma, including after iridectomy. Acute angle-closure glaucoma (alone or with other miotics, epinephrine, beta-adrenergic blocking agents, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, or hyperosmotic agents). (2) To reverse mydria ...
... HCl: (1) Chronic simple glaucoma (especially open-angle). Chronic angle-closure glaucoma, including after iridectomy. Acute angle-closure glaucoma (alone or with other miotics, epinephrine, beta-adrenergic blocking agents, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, or hyperosmotic agents). (2) To reverse mydria ...
DRUG-DRUG INTERACTIONS – FROM KNOWLEDGE BASE TO
... Some years before the MAO-inhibitor interaction was described, unexpected drug interactions causing adverse effects such as hypoglycemia in phenylbutazone (also known as butazolidine [5] and tolbutamide treated patients [6], and increased anticoagulation in phenprocoumon treated patients [7] were re ...
... Some years before the MAO-inhibitor interaction was described, unexpected drug interactions causing adverse effects such as hypoglycemia in phenylbutazone (also known as butazolidine [5] and tolbutamide treated patients [6], and increased anticoagulation in phenprocoumon treated patients [7] were re ...
Prandin
... drug levels (Cmax) occur within 1 hour (Tmax). Repaglinide is rapidly eliminated from the blood stream with a half-life of approximately 1 hour. The mean absolute bioavailability is 56%. When repaglinide was given with food, the mean Tmax was not changed, but the mean Cmax and AUC (area under the ti ...
... drug levels (Cmax) occur within 1 hour (Tmax). Repaglinide is rapidly eliminated from the blood stream with a half-life of approximately 1 hour. The mean absolute bioavailability is 56%. When repaglinide was given with food, the mean Tmax was not changed, but the mean Cmax and AUC (area under the ti ...
Antibodies to Biotherapeutics
... ■■ Application data and protocols to support pharmacokinetic (PK), anti-drug antibody (ADA) and neutralizing assays ■■ High specificity and sensitivity for optimal assay development ■■ Specialized antibodies binding to a complex of the drug and target ■■ Recommended ELISA detection antibodies availa ...
... ■■ Application data and protocols to support pharmacokinetic (PK), anti-drug antibody (ADA) and neutralizing assays ■■ High specificity and sensitivity for optimal assay development ■■ Specialized antibodies binding to a complex of the drug and target ■■ Recommended ELISA detection antibodies availa ...
Asia - INCB
... various ways, drug control efforts throughout the region of East and South-East Asia. 384. Significant bilateral efforts are being made, for example, by Myanmar and Thailand, which intend to exchange drug liaison officers, to improve contact between drug control officers along their common border an ...
... various ways, drug control efforts throughout the region of East and South-East Asia. 384. Significant bilateral efforts are being made, for example, by Myanmar and Thailand, which intend to exchange drug liaison officers, to improve contact between drug control officers along their common border an ...
Swine: Baytril® 100 is indicated for the treatment and control of
... Treatment should be repeated at 24-hour intervals for three days. Additional treatments may be given on Days 4 and 5 to animals that have shown clinical improvement but not total recovery. Single-Dose Therapy (BRD Control): Administer, by subcutaneous injection, a single dose of 7.5 mg/kg of body we ...
... Treatment should be repeated at 24-hour intervals for three days. Additional treatments may be given on Days 4 and 5 to animals that have shown clinical improvement but not total recovery. Single-Dose Therapy (BRD Control): Administer, by subcutaneous injection, a single dose of 7.5 mg/kg of body we ...
The mechanism of action of oral antidiabetic drugs: A review of
... gluconeogenesis as well as glycogenolysis, which contributes to the post-prandial plasma glucoselowering effects. Skeletal muscle and adipocytes undergo up-regulation of the insulin-sensitive GLUT4 and GLUT-1 transporters to the cell membranes, thereby increasing glucose uptake.31 Glucose metabolism ...
... gluconeogenesis as well as glycogenolysis, which contributes to the post-prandial plasma glucoselowering effects. Skeletal muscle and adipocytes undergo up-regulation of the insulin-sensitive GLUT4 and GLUT-1 transporters to the cell membranes, thereby increasing glucose uptake.31 Glucose metabolism ...
1.-Cardiology - PGXL Laboratories
... Estimated warfarin maintenance dose requirement: 3.9 mg/day‡ _ CYP2C9 Poor Metabolizer (PM): This patient’s genotype is consistent with significantly reduced CYP2C9 enzymatic activity. Reduced CYP2C9 activity leads to lower dose requirement (e.g., warfarin) due to decreased clearance, increased elim ...
... Estimated warfarin maintenance dose requirement: 3.9 mg/day‡ _ CYP2C9 Poor Metabolizer (PM): This patient’s genotype is consistent with significantly reduced CYP2C9 enzymatic activity. Reduced CYP2C9 activity leads to lower dose requirement (e.g., warfarin) due to decreased clearance, increased elim ...
to identify, evaluate, and analyze the possible drug
... Central sympatholytics Alpha+beta blockers Vasodilators Total ...
... Central sympatholytics Alpha+beta blockers Vasodilators Total ...
Presentation
... human variability in toxicokinetics (3.16) would not cater for these interactions •Results variable ; detailed analysis to classify interaction according to constant of inhibition (Ki) • In vivo database on therapeutic doses much higher than pesticide levels but only in vivo data quantifying human v ...
... human variability in toxicokinetics (3.16) would not cater for these interactions •Results variable ; detailed analysis to classify interaction according to constant of inhibition (Ki) • In vivo database on therapeutic doses much higher than pesticide levels but only in vivo data quantifying human v ...
HILIC-MS-High Resolution and Sensitivity for the
... We present examples for the different elution order of polar compounds in HILIC and RPC with UV detection and with LC–MS–MS detection. HILIC AND REVERSED PHASE SEPARATION OF PEPTIDES The selectivity of HILIC is completely different from RPC and for most samples the elution order is inversed. Figure ...
... We present examples for the different elution order of polar compounds in HILIC and RPC with UV detection and with LC–MS–MS detection. HILIC AND REVERSED PHASE SEPARATION OF PEPTIDES The selectivity of HILIC is completely different from RPC and for most samples the elution order is inversed. Figure ...
Duration of action
... • A- Potency and reliability : the first requirement of such a substance is that when administered correctly and in an adequate dosage it consistently produces effective local anesthesia . earlier agent (e.g. cocaine ) were obtained from natural sources and there was considerable variation in their ...
... • A- Potency and reliability : the first requirement of such a substance is that when administered correctly and in an adequate dosage it consistently produces effective local anesthesia . earlier agent (e.g. cocaine ) were obtained from natural sources and there was considerable variation in their ...
Heavy metal-Lead
... mouths. Children also tend to absorb lead more easily than adults do because their metabolism is faster. Lead affects the child's developing nervous system by slowing development. Children are particularly vulnerable up the age of six. The effects include hearing impairment, behavioral problems and ...
... mouths. Children also tend to absorb lead more easily than adults do because their metabolism is faster. Lead affects the child's developing nervous system by slowing development. Children are particularly vulnerable up the age of six. The effects include hearing impairment, behavioral problems and ...
4.Geetha T. S and Geetha N - International Journal of Pharmacy and
... isolated from plants are safer and have a lot of potential than the chemical drugs(1). In search of novel active compounds from plant origin, and to assess the efficient therapeutic properties with minimum side effects, application of advanced methods like computational techniques play a crucial rol ...
... isolated from plants are safer and have a lot of potential than the chemical drugs(1). In search of novel active compounds from plant origin, and to assess the efficient therapeutic properties with minimum side effects, application of advanced methods like computational techniques play a crucial rol ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.