Use of renal risk drugs in hospitalized patients with impaired renal
... of all the renal risk drugs used by the patients belonging to these stages. Loop diuretics (furosemide and bumetanide) were used by 127 (63%) patients with RI stages 3, 4 and 5, compared with 187 users (31%) in the patient group with renal function of stages 1 or 2 (P < 0.001). All but 6 patients wi ...
... of all the renal risk drugs used by the patients belonging to these stages. Loop diuretics (furosemide and bumetanide) were used by 127 (63%) patients with RI stages 3, 4 and 5, compared with 187 users (31%) in the patient group with renal function of stages 1 or 2 (P < 0.001). All but 6 patients wi ...
Drug Testing: Answers to Frequently Asked
... The CB1 receptor is located mainly in the brain and spinal cord and is responsible for the typical physiological and particularly the psychotropic effects of cannabis The CB2 receptor is located mainly in the spleen and cells of the immune system ...
... The CB1 receptor is located mainly in the brain and spinal cord and is responsible for the typical physiological and particularly the psychotropic effects of cannabis The CB2 receptor is located mainly in the spleen and cells of the immune system ...
- International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and
... damages due to mechanical trauma, chemical, physical and thermal injury, antigen antibody reactions and infections. The signs and symptoms of inflammation include redness, swelling, heat, pain and loss of function of the affected area. Pain is an unpleasant sensation that is a consequence of complex ...
... damages due to mechanical trauma, chemical, physical and thermal injury, antigen antibody reactions and infections. The signs and symptoms of inflammation include redness, swelling, heat, pain and loss of function of the affected area. Pain is an unpleasant sensation that is a consequence of complex ...
UCSF Cancer Center Phase I Protocol Template
... Provide definition of types, grades and duration of AEs that will be considered dose-limiting toxicities, or provide definitions of other endpoints that will be used to determine dose escalations. Note any definite exclusions from the DLT definition (if any rule states any grade 3/4 hematologic toxi ...
... Provide definition of types, grades and duration of AEs that will be considered dose-limiting toxicities, or provide definitions of other endpoints that will be used to determine dose escalations. Note any definite exclusions from the DLT definition (if any rule states any grade 3/4 hematologic toxi ...
72 jems august 2008
... a stretcher, they may still not say anything— even if they’ve ingested the same drug—for fear of criminal actions against them. Many long-time ALS providers may remember that during their initial training they were told it would be rare to encounter a true narcotic overdose requiring Narcan. Many we ...
... a stretcher, they may still not say anything— even if they’ve ingested the same drug—for fear of criminal actions against them. Many long-time ALS providers may remember that during their initial training they were told it would be rare to encounter a true narcotic overdose requiring Narcan. Many we ...
Drug List - Grand Saline ISD
... Chronic opioid therapy has a low risk of addiction when used appropriately. ...
... Chronic opioid therapy has a low risk of addiction when used appropriately. ...
Local anesthetics and additives
... “Importantly, the physician is free to use any drug for off-label indications as long as the use is based on sound clinical judgment and reasonable scientific rationale.” Neal J et al. RAPM 2009 ...
... “Importantly, the physician is free to use any drug for off-label indications as long as the use is based on sound clinical judgment and reasonable scientific rationale.” Neal J et al. RAPM 2009 ...
Iodine and Tyrosine
... l-tyrosine (free-form).................................................................... 500 mg. 2 capsules per day, in divided doses, with meals. ...
... l-tyrosine (free-form).................................................................... 500 mg. 2 capsules per day, in divided doses, with meals. ...
a ABBOTT
... 25. Kopple JD, Vinton NE, Laidlaw SA et al. Effect of Intmvenous Taurine Supplemenuxion on Plasma, Blood Cells and L-tie Taurine Concentrations in Adults Undergoing bmg-Term Parenteral Nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 1990; 52:846-53. 26, Roe DA, Wesron MD. Potential Significance of Free Taurine in the Die ...
... 25. Kopple JD, Vinton NE, Laidlaw SA et al. Effect of Intmvenous Taurine Supplemenuxion on Plasma, Blood Cells and L-tie Taurine Concentrations in Adults Undergoing bmg-Term Parenteral Nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 1990; 52:846-53. 26, Roe DA, Wesron MD. Potential Significance of Free Taurine in the Die ...
ANTIVIRAL AGENTS pharm
... Oral bioavailability of acyclovir ranges from 10% - 30% and decreases with increasing dose. Peak plasma concentrations average 0.4 to 0.8 µgm/l after 200mg and 1.6µg/ml 800mg doses. Following intravenous administration, peak plasma concentration average 9.8 µg/ml after 5mg/kg per 8 hrs and 20.7µg/ml ...
... Oral bioavailability of acyclovir ranges from 10% - 30% and decreases with increasing dose. Peak plasma concentrations average 0.4 to 0.8 µgm/l after 200mg and 1.6µg/ml 800mg doses. Following intravenous administration, peak plasma concentration average 9.8 µg/ml after 5mg/kg per 8 hrs and 20.7µg/ml ...
Sex differences in the vulnerability to drug abuse
... due to the ethical difficulties of studying this phase of addiction in humans, as abstinent former drug users would be likely to reinitiate drug use when exposed to priming conditions [18]. There is always the question of whether animal models adequately represent and predict human behaviors; howeve ...
... due to the ethical difficulties of studying this phase of addiction in humans, as abstinent former drug users would be likely to reinitiate drug use when exposed to priming conditions [18]. There is always the question of whether animal models adequately represent and predict human behaviors; howeve ...
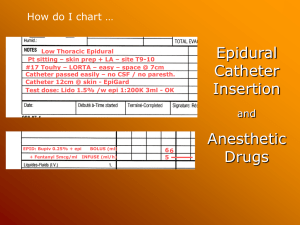
Charting Regional - Epidural Events A
... You can select Bupiv and Fentanyl separately to chart as Infusions but Anesthesia Manager will chart these infusions in the Medication Infusions & Fluids section. To keep everything together in the Medications section, it is necessary to configure the 2 drugs as a Infusion Combination: ...
... You can select Bupiv and Fentanyl separately to chart as Infusions but Anesthesia Manager will chart these infusions in the Medication Infusions & Fluids section. To keep everything together in the Medications section, it is necessary to configure the 2 drugs as a Infusion Combination: ...
Basics Pharmacology Review
... Clinical Pharmacist, Bruyere Academic Family Health Team March 2013 [email protected] (Partially adapted from slides by Marc Riachi, R.Ph.) ...
... Clinical Pharmacist, Bruyere Academic Family Health Team March 2013 [email protected] (Partially adapted from slides by Marc Riachi, R.Ph.) ...
Potassium Sparing Diuretics
... Aldosterone enhance K+ secretion by increasing Na+/K+ ATPase and the same for H+ . Therefore, Spironolactone binds to mineralocorticoid receptors “Lippincott: Spironolactone is asynthetic steroid that antagonizes aldosterone at intracellular cytoplasmic receptor sites. The spironolactone-receptor co ...
... Aldosterone enhance K+ secretion by increasing Na+/K+ ATPase and the same for H+ . Therefore, Spironolactone binds to mineralocorticoid receptors “Lippincott: Spironolactone is asynthetic steroid that antagonizes aldosterone at intracellular cytoplasmic receptor sites. The spironolactone-receptor co ...
PHASE II DRUG METABOLIZING ENZYMES Petra Jancovaa*, Pavel
... Background. Phase II biotransformation reactions (also ‘conjugation reactions’) generally serve as a detoxifying step in drug metabolism. Phase II drug metabolising enzymes are mainly transferases. This review covers the major phase II enzymes: UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, sulfotransferases, N-acet ...
... Background. Phase II biotransformation reactions (also ‘conjugation reactions’) generally serve as a detoxifying step in drug metabolism. Phase II drug metabolising enzymes are mainly transferases. This review covers the major phase II enzymes: UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, sulfotransferases, N-acet ...
Central Nervous System Activity Studies of Baptisia tinctoria (L.) R
... disorder either due to stress, depression, anxiety or any other cause [2]. Psychotherapeutics are noneffective in majority of patients with mental health problem but therapeutics having plants and plant products showed potent effect against those mental health problems [3]. The regular use of synthe ...
... disorder either due to stress, depression, anxiety or any other cause [2]. Psychotherapeutics are noneffective in majority of patients with mental health problem but therapeutics having plants and plant products showed potent effect against those mental health problems [3]. The regular use of synthe ...
Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery
... (immunotherapy) are limited by the accessibility to the tumor, the risk of operating on a vital organ, the spread of cancer cells throughout the body, and the lack of selectivity toward tumor cells. Immunotherapy is still relatively recent, and is most likely to be applied to small tumors, since its ...
... (immunotherapy) are limited by the accessibility to the tumor, the risk of operating on a vital organ, the spread of cancer cells throughout the body, and the lack of selectivity toward tumor cells. Immunotherapy is still relatively recent, and is most likely to be applied to small tumors, since its ...
PHASE II DRUG METABOLIZING ENZYMES Petra Jancovaa*, Pavel
... Background. Phase II biotransformation reactions (also ‘conjugation reactions’) generally serve as a detoxifying step in drug metabolism. Phase II drug metabolising enzymes are mainly transferases. This review covers the major phase II enzymes: UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, sulfotransferases, N-acet ...
... Background. Phase II biotransformation reactions (also ‘conjugation reactions’) generally serve as a detoxifying step in drug metabolism. Phase II drug metabolising enzymes are mainly transferases. This review covers the major phase II enzymes: UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, sulfotransferases, N-acet ...
Nitazoxanide (Alinia) - Texas Medicaid/CHIP Vendor Drug
... nitazoxanide. Only those drug-drug interactions classified as clinical significance level 1/contraindicated or those considered life-threatening which have not yet been classified will be reviewed: a) Highly Plasma Protein-Bound Medications (e.g., hydantoins, salicylates, warfarin) [clinical signifi ...
... nitazoxanide. Only those drug-drug interactions classified as clinical significance level 1/contraindicated or those considered life-threatening which have not yet been classified will be reviewed: a) Highly Plasma Protein-Bound Medications (e.g., hydantoins, salicylates, warfarin) [clinical signifi ...
km 2 4 American Medical Q Systems
... a. Mutual Cross Labeling Mutual cross labeling should be required in very limited circumstances, for instance where there is data demonstrating hazards if a very specific product is not used as part of the combination. The requirement for mutual cross labeling serves to limit the availability of adv ...
... a. Mutual Cross Labeling Mutual cross labeling should be required in very limited circumstances, for instance where there is data demonstrating hazards if a very specific product is not used as part of the combination. The requirement for mutual cross labeling serves to limit the availability of adv ...
Therapeutic uses: All types of hyperlipidemias.
... orally. Pravastatin and fluvastatin are almost completely absorbed after oral administration; Similarly, Fluvastatin and pravastatin are active as such, whereas lovastatin and simvastatin must be hydrolyzed to their acid forms. Due to first-pass metabolism, the primary action of these drugs is on th ...
... orally. Pravastatin and fluvastatin are almost completely absorbed after oral administration; Similarly, Fluvastatin and pravastatin are active as such, whereas lovastatin and simvastatin must be hydrolyzed to their acid forms. Due to first-pass metabolism, the primary action of these drugs is on th ...
3 0 M a r c h 1 6 ,
... open to the public for observation and participation. Anyone wishing to make an oral presentation should notify the contact person listed above 8s soon as possible before the meeting. The request should state the amount of time desired, the capacity in which the person will appear. and 8 brief outli ...
... open to the public for observation and participation. Anyone wishing to make an oral presentation should notify the contact person listed above 8s soon as possible before the meeting. The request should state the amount of time desired, the capacity in which the person will appear. and 8 brief outli ...
APPLICATIONS OF METABOLOMICS
... companies wanting to test the toxicity of potential drug candidates: if a compound can be eliminated before it reaches clinical trials on the grounds of adverse toxicity, it saves the enormous expense of the trials. Functional genomics. Metabolomics can be an excellent tool for determining the phe ...
... companies wanting to test the toxicity of potential drug candidates: if a compound can be eliminated before it reaches clinical trials on the grounds of adverse toxicity, it saves the enormous expense of the trials. Functional genomics. Metabolomics can be an excellent tool for determining the phe ...
Urine Drug Testing Clinical Practice
... urine sample. The drug or metabolite in the sample will compete with the labeled drug or metabolite to bind antibody to form antigen-antibody complexes. The amount of enzyme-labeled antigen that binds with the antibody has some proportional relationship to the amount of drug and/or its metabolite(s) ...
... urine sample. The drug or metabolite in the sample will compete with the labeled drug or metabolite to bind antibody to form antigen-antibody complexes. The amount of enzyme-labeled antigen that binds with the antibody has some proportional relationship to the amount of drug and/or its metabolite(s) ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.