ppt - IASA
... Nature needs to provide penetrating beams and the QGP in Au-Au collisions QGP created in Au-Au collisions as transient state for 10 fm penetrating beams created by parton scattering before QGP is formed ...
... Nature needs to provide penetrating beams and the QGP in Au-Au collisions QGP created in Au-Au collisions as transient state for 10 fm penetrating beams created by parton scattering before QGP is formed ...
Higher Physics Course Assessment Specification
... Grade description for C For the award of Grade C, learners will have demonstrated successful performance in all of the Units of the Course. In the Course assessment, learners will typically have demonstrated successful performance in relation to the mandatory skills, knowledge and understanding for ...
... Grade description for C For the award of Grade C, learners will have demonstrated successful performance in all of the Units of the Course. In the Course assessment, learners will typically have demonstrated successful performance in relation to the mandatory skills, knowledge and understanding for ...
Physcal Chemistry ERT 108 semester II 2010/2011
... difference between the system and its surroundings. It has adiabatic walls. ...
... difference between the system and its surroundings. It has adiabatic walls. ...
Rapid growth of cloud droplets by turbulence Abstract
... particles find themselves, initially, close enough for (4) to hold. And one where the point particles are distributed on a regular lattice so that (4) does not hold initially for all pairs of particles. It might be interesting to note (see figure 3) that, whilst the initial evolution of the number o ...
... particles find themselves, initially, close enough for (4) to hold. And one where the point particles are distributed on a regular lattice so that (4) does not hold initially for all pairs of particles. It might be interesting to note (see figure 3) that, whilst the initial evolution of the number o ...
101, 150406 (2008)
... respect to U=t. The gap is zero for U ¼ 0 due to the degeneracy of the ground state while with finite U the degeneracy is lifted and the gap becomes nonzero. However, the gap also approaches zero in the limit U=t ! 1 where there is no phase coherence between the atoms at different sites and the grou ...
... respect to U=t. The gap is zero for U ¼ 0 due to the degeneracy of the ground state while with finite U the degeneracy is lifted and the gap becomes nonzero. However, the gap also approaches zero in the limit U=t ! 1 where there is no phase coherence between the atoms at different sites and the grou ...
Is the electron a photon with toroidal topology?
... a \rotation horizon" and sets an upper limit on the size of the object equal to a Compton wavelength. At the same time, we can estimate a lower limit on the size from the fact that it is impossible to con ne an arbitrary wave into a box which is smaller than one half of its wavelength. Moreover, the ...
... a \rotation horizon" and sets an upper limit on the size of the object equal to a Compton wavelength. At the same time, we can estimate a lower limit on the size from the fact that it is impossible to con ne an arbitrary wave into a box which is smaller than one half of its wavelength. Moreover, the ...
In an isolated system, energy is transferred from one object to
... height of the previous hill, unless it is given a boost. It seems obvious to us that as objects move, kinetic energy is always lost. Energy is the most fundamental concept in physics. Everything that occurs in nature can be traced back to energy. The complicating factor is that there are so many for ...
... height of the previous hill, unless it is given a boost. It seems obvious to us that as objects move, kinetic energy is always lost. Energy is the most fundamental concept in physics. Everything that occurs in nature can be traced back to energy. The complicating factor is that there are so many for ...
CHAPTER 7 Kinetic Energy and Work UPI Photo/Dilip Vishwanat
... vague to be of help to us now. A looser definition might at least get us started. Energy is a number that we associate with a system of one or more objects. If a force changes one of the objects by, say, making it move, then the energy number changes. After countless experiments, scientists and engi ...
... vague to be of help to us now. A looser definition might at least get us started. Energy is a number that we associate with a system of one or more objects. If a force changes one of the objects by, say, making it move, then the energy number changes. After countless experiments, scientists and engi ...
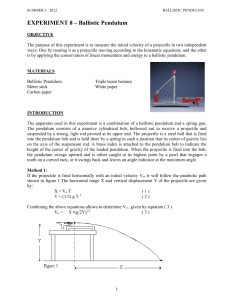
EXPERIMENT 1- Measurements and Accuracy
... 5) Remove the pendulum from the apparatus and measure its mass M and that of the ball m. Also measure the length of the pendulum R from the pivot to the center of mass (as indicated on the pendulum). 6) Reinstall the pendulum. 7) Place the ball in the shaft and cock the gun until the shaft is locked ...
... 5) Remove the pendulum from the apparatus and measure its mass M and that of the ball m. Also measure the length of the pendulum R from the pivot to the center of mass (as indicated on the pendulum). 6) Reinstall the pendulum. 7) Place the ball in the shaft and cock the gun until the shaft is locked ...
The Interacting Gluon Model: a review
... to study energy deposition, connecting it with the apparent dominance of multiparticle production processes by the gluonic content of the impinging hadrons, hence its name: Interacting Gluon Model (IGM) [11]. Its original application to the description of inelasticity [12] and multiparticle producti ...
... to study energy deposition, connecting it with the apparent dominance of multiparticle production processes by the gluonic content of the impinging hadrons, hence its name: Interacting Gluon Model (IGM) [11]. Its original application to the description of inelasticity [12] and multiparticle producti ...
Chapter 6: Work and Energy )(
... Strategy: Use the definition of work to answer the conceptual question. Solution: The calculation of work does not depend upon time or whether the slide occurs continuously. It depends only upon the force and the displacement vectors. Therefore, we conclude that the work done by gravity is exactly t ...
... Strategy: Use the definition of work to answer the conceptual question. Solution: The calculation of work does not depend upon time or whether the slide occurs continuously. It depends only upon the force and the displacement vectors. Therefore, we conclude that the work done by gravity is exactly t ...
AP Physics Pacing Curriculum
... should include uniform circular motion and projectile motion. 4.C.1 The energy of a system includes its kinetic energy, potential energy, and microscopic internal energy. Examples should include gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and kinetic energy. 4.C.1.1 The student is abl ...
... should include uniform circular motion and projectile motion. 4.C.1 The energy of a system includes its kinetic energy, potential energy, and microscopic internal energy. Examples should include gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and kinetic energy. 4.C.1.1 The student is abl ...
Chapter 6 Impulse and Momentum Continued
... 1. Decide which objects are included in the system. 2. Relative to the system, identify the internal and external forces. 3. Verify that the system is isolated. 4. Set the final momentum of the system equal to its initial momentum. Remember that momentum is a vector. ...
... 1. Decide which objects are included in the system. 2. Relative to the system, identify the internal and external forces. 3. Verify that the system is isolated. 4. Set the final momentum of the system equal to its initial momentum. Remember that momentum is a vector. ...
Oscillatory Motion
... complexity as we go. This course is meant to be directly applicable for the war-fighter. To begin with lets go back to our childhood days looking out over the calm waters of the nearby pond. When you throw a rock in the water, you create a wave on the surface. If you closely watch a leaf on the surf ...
... complexity as we go. This course is meant to be directly applicable for the war-fighter. To begin with lets go back to our childhood days looking out over the calm waters of the nearby pond. When you throw a rock in the water, you create a wave on the surface. If you closely watch a leaf on the surf ...
Conceptual Physical Science 5e — Chapter 3
... On roller blades, you toss a ball horizontally away from you. The mass of the ball is one-tenth your mass. Compared with the speed you give to the ball, your recoil speed will ideally be A. B. C. D. ...
... On roller blades, you toss a ball horizontally away from you. The mass of the ball is one-tenth your mass. Compared with the speed you give to the ball, your recoil speed will ideally be A. B. C. D. ...
Chapter 6 Impulse and Momentum Continued
... 1. Decide which objects are included in the system. 2. Relative to the system, identify the internal and external forces. 3. Verify that the system is isolated. 4. Set the final momentum of the system equal to its initial momentum. Remember that momentum is a vector. ...
... 1. Decide which objects are included in the system. 2. Relative to the system, identify the internal and external forces. 3. Verify that the system is isolated. 4. Set the final momentum of the system equal to its initial momentum. Remember that momentum is a vector. ...