File
... groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, either through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. D ...
... groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, either through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. D ...
Course 2 – Mathematical Tools and Unit Conversion Used in
... Temperature scale of the SI system is based on the ideal gas as thermometric fluid Where; R – gas constant = ave 8.3144 joules/degree mole M – Molar mass kg/mole ...
... Temperature scale of the SI system is based on the ideal gas as thermometric fluid Where; R – gas constant = ave 8.3144 joules/degree mole M – Molar mass kg/mole ...
When you drop a ball, what happens to its energy
... When you drop a ball onto the floor, what happens to its energy? Give two examples that show energy makes change. When you hold a ball above your head, does it have potential or kinetic energy? Describe how a compass works. How are sound waves and light waves different? Explain why a ball rolled wit ...
... When you drop a ball onto the floor, what happens to its energy? Give two examples that show energy makes change. When you hold a ball above your head, does it have potential or kinetic energy? Describe how a compass works. How are sound waves and light waves different? Explain why a ball rolled wit ...
Kinetic energy - Cobb Learning
... transformations of energy. • a. Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy. • b. Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. • c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electricity, mechanical motion, sound) and their char ...
... transformations of energy. • a. Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy. • b. Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. • c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electricity, mechanical motion, sound) and their char ...
(8%) Write (a) the mass-balance expression and (b) the charge-balance equation
... (i) X-ray photoelectrons, and (ii) Auger electrons. (9%) Define the following terms: a. (3%) buffer capacity b. (3%) guard column (HPLC) c. (3%) electrophoretic mobility (CE) (4%) Determine the following thermodynamic quantities extensive or intensive variables: (i) pressure (ii) entropy (iii) chemi ...
... (i) X-ray photoelectrons, and (ii) Auger electrons. (9%) Define the following terms: a. (3%) buffer capacity b. (3%) guard column (HPLC) c. (3%) electrophoretic mobility (CE) (4%) Determine the following thermodynamic quantities extensive or intensive variables: (i) pressure (ii) entropy (iii) chemi ...
Work and Energy
... 1. Levers have a rigid arm and a fulcrum. There are three classes of levers (see Figure 5 pg. 386). Ex. ...
... 1. Levers have a rigid arm and a fulcrum. There are three classes of levers (see Figure 5 pg. 386). Ex. ...
PPT version
... Thermodynamic processes… We are interested in changes in internal energy, the heat transferred to or from the system and the work done by the system - ideal the gas under piston In principle, all we need to know are the ideal gas law and the 1st law of thermodynamics: ...
... Thermodynamic processes… We are interested in changes in internal energy, the heat transferred to or from the system and the work done by the system - ideal the gas under piston In principle, all we need to know are the ideal gas law and the 1st law of thermodynamics: ...
6.1-6.3 Heat, The Nature of Energy and The First Law of
... • Potential energy – the energy associated with the position or composition of an object. • Kinetic energy – the energy associated with the motion of an object. • Thermal energy – the energy associated with the temperature of an object. • Chemical energy – the energy associated with the relative pos ...
... • Potential energy – the energy associated with the position or composition of an object. • Kinetic energy – the energy associated with the motion of an object. • Thermal energy – the energy associated with the temperature of an object. • Chemical energy – the energy associated with the relative pos ...
NOTES-Chemical energy
... -An ice cube can evaporate in the freezer (not boil) over about 2 weeks because temperature is only an average. In this case average means that some of the particles have less kinetic energy and some have more. The water molecules with the highest energy can break free from the surface of the ice cu ...
... -An ice cube can evaporate in the freezer (not boil) over about 2 weeks because temperature is only an average. In this case average means that some of the particles have less kinetic energy and some have more. The water molecules with the highest energy can break free from the surface of the ice cu ...
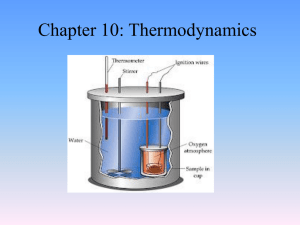
Chapter 10: Thermodynamics
... • Adiabatic process: a thermodynamic process during which heat energy is transferred to or from the system. ex: usually a fast process like filling a tank • Isobaric process: a process that takes place at a constant pressure. ex: heating an open pot of water ...
... • Adiabatic process: a thermodynamic process during which heat energy is transferred to or from the system. ex: usually a fast process like filling a tank • Isobaric process: a process that takes place at a constant pressure. ex: heating an open pot of water ...
What is Energy? - CEC
... Therefore, if one goes down, the other goes up by the same amount. We can use this when trying to create machines/technology that helps to provide an efficient means of energy. ...
... Therefore, if one goes down, the other goes up by the same amount. We can use this when trying to create machines/technology that helps to provide an efficient means of energy. ...
Examples of Kinetic Energy Problems
... This final example uses the conservation of energy. In questions like these, use both the kinetic energy and the potential energy of an object to solve the problem. It is a good idea to show your working at each step of the problem as you rearrange the equation. Example: A lump of ice falls from an ...
... This final example uses the conservation of energy. In questions like these, use both the kinetic energy and the potential energy of an object to solve the problem. It is a good idea to show your working at each step of the problem as you rearrange the equation. Example: A lump of ice falls from an ...
Forces Come in Pairs --- Newton`s Third Law Weight and Mass The
... Ch 6. Work and Energy Work done by a constant force. ...
... Ch 6. Work and Energy Work done by a constant force. ...
work and energy
... the potential energy at the top of the tall platform is 50 J, what is the potential energy at the other positions shown on the stair steps and the incline? ...
... the potential energy at the top of the tall platform is 50 J, what is the potential energy at the other positions shown on the stair steps and the incline? ...