Title: Changes in Velocity due to Potential and Kinetic Energy
... more work can be done by the rubber band. There is a connectedness, then, between potential and kinetic energy for matter. For moving objects, we can easily calculate kinetic energy using the formula: KE = (mass x velocity2)/2 or 1/2 mv2 Although mass and velocity both have great effects on kinetic ...
... more work can be done by the rubber band. There is a connectedness, then, between potential and kinetic energy for matter. For moving objects, we can easily calculate kinetic energy using the formula: KE = (mass x velocity2)/2 or 1/2 mv2 Although mass and velocity both have great effects on kinetic ...
Work, Power, and Energy Webquest
... its gravitational potential and kinetic energies a. decreases, only. b. decreases and then increases. c. increases and then decreases. d. remains the same. ...
... its gravitational potential and kinetic energies a. decreases, only. b. decreases and then increases. c. increases and then decreases. d. remains the same. ...
Chapter 6, Part IV
... height of only y = 25 m on the second hill before coming to a momentary stop. It travels a total distance d = 400 m. Calculate the work done by friction (the thermal energy produced) & calculate the average friction force on the car. ...
... height of only y = 25 m on the second hill before coming to a momentary stop. It travels a total distance d = 400 m. Calculate the work done by friction (the thermal energy produced) & calculate the average friction force on the car. ...
1 - vnhsteachers
... Scientists have categorized the universe into two general categories: mass and energy. Mass provides inertia and takes up space. Energy is any resource that provides motion to mass. ENERGY Energy is present in the universe in a variety of forms including mechanical, chemical, electromagnetic, heat, ...
... Scientists have categorized the universe into two general categories: mass and energy. Mass provides inertia and takes up space. Energy is any resource that provides motion to mass. ENERGY Energy is present in the universe in a variety of forms including mechanical, chemical, electromagnetic, heat, ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy
... The Law of Conservation of Energy states that “energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It is simply converted from one form to another.” Newton’s Cradle. The kinetic energy of the ball on the left is transferred to the next ball, which transfers the energy to the next ball, so on down the line. ...
... The Law of Conservation of Energy states that “energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It is simply converted from one form to another.” Newton’s Cradle. The kinetic energy of the ball on the left is transferred to the next ball, which transfers the energy to the next ball, so on down the line. ...
Form Of - eduScapes
... energy in substances––the vibration and movement of the atoms and molecules within substances. Motion Energy is the movement of objects and substances from one place to another. Objects and substances move when a force is applied according to Newton’s Laws of ...
... energy in substances––the vibration and movement of the atoms and molecules within substances. Motion Energy is the movement of objects and substances from one place to another. Objects and substances move when a force is applied according to Newton’s Laws of ...
Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from
... three times as much four times as much ...
... three times as much four times as much ...
1 - vnhsteachers
... inertia and takes up space. Energy is any resource that provides motion to mass. ENERGY Energy is present in the universe in a variety of forms including mechanical, chemical, electromagnetic, heat, and nuclear energy. CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Although energy can be transformed from one form to anothe ...
... inertia and takes up space. Energy is any resource that provides motion to mass. ENERGY Energy is present in the universe in a variety of forms including mechanical, chemical, electromagnetic, heat, and nuclear energy. CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Although energy can be transformed from one form to anothe ...
KEandPE
... 5.A car traveling 60 km/hr can brake to a stop within a distance of 20 m. If the car is going twice as fast, 120 km/h, what is its stopping ...
... 5.A car traveling 60 km/hr can brake to a stop within a distance of 20 m. If the car is going twice as fast, 120 km/h, what is its stopping ...
Gravitational Potential Energy
... In the above equation, m represents the mass of the object, h represents the height of the object and g represents the gravitational field strength (9.8 N/kg on Earth) - sometimes referred to as the acceleration of gravity. ...
... In the above equation, m represents the mass of the object, h represents the height of the object and g represents the gravitational field strength (9.8 N/kg on Earth) - sometimes referred to as the acceleration of gravity. ...
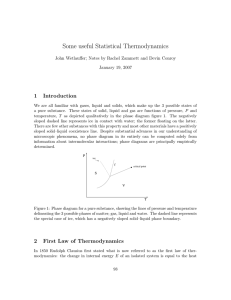
Some useful Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Introduction
... between the subsystems, and the boundary may move as a piston. The second law states that the number of accessible micro-states of an isolated system, Ω, never decreases. If we consider subsystem A to contain and ideal atomic gas, then the number of accessible micro-states of A is simply the number ...
... between the subsystems, and the boundary may move as a piston. The second law states that the number of accessible micro-states of an isolated system, Ω, never decreases. If we consider subsystem A to contain and ideal atomic gas, then the number of accessible micro-states of A is simply the number ...
Do Now
... Forms of Energy Using pg 160-167 of the textbook, fill in your Describing Wheel with the different types of energy. Include the definitions of each type and at least one example for each. ...
... Forms of Energy Using pg 160-167 of the textbook, fill in your Describing Wheel with the different types of energy. Include the definitions of each type and at least one example for each. ...
Conservation of Energy
... • Did the bowling ball smack the teacher in the chin? Did it rise higher or lower than its original height? • At what point did the bowling ball have the most gravitational potential energy? • At what point did the bowling ball have the most kinetic energy? How do we know this? ...
... • Did the bowling ball smack the teacher in the chin? Did it rise higher or lower than its original height? • At what point did the bowling ball have the most gravitational potential energy? • At what point did the bowling ball have the most kinetic energy? How do we know this? ...
Energy
... o Gravitational energy - as a result of height, PE = mgh o Electrostatic energy - potential energy of particles depends on the location and charges of particles Chemical Energy – energy stored in atoms due to their arrangement in molecules or ions ...
... o Gravitational energy - as a result of height, PE = mgh o Electrostatic energy - potential energy of particles depends on the location and charges of particles Chemical Energy – energy stored in atoms due to their arrangement in molecules or ions ...