kinetic and potential energy
... altered it, creates Potential Energy. • A yo-yo on the table, doesn’t have energy, but when picked up, it alters its position and now it has the ability (or potential) to do work. • A bow doesn’t have the capacity to do work, unless it’s held at an elevated position. ...
... altered it, creates Potential Energy. • A yo-yo on the table, doesn’t have energy, but when picked up, it alters its position and now it has the ability (or potential) to do work. • A bow doesn’t have the capacity to do work, unless it’s held at an elevated position. ...
Lect14
... • If only conservative forces are present, the total kinetic plus potential energy of a system is conserved. Mechanical Energy = Potential Energy (U) + Kinetic Energy (K) Conservative forces interchange U K (work done), but E = K + U is a constant. ΔE = ΔK + ΔU = 0 Work-kinetic energy theorem: ...
... • If only conservative forces are present, the total kinetic plus potential energy of a system is conserved. Mechanical Energy = Potential Energy (U) + Kinetic Energy (K) Conservative forces interchange U K (work done), but E = K + U is a constant. ΔE = ΔK + ΔU = 0 Work-kinetic energy theorem: ...
Unit 4 study guide
... Calculating Net Work: Can calculate work done in two ways. So choose one way. 1. Determine the net force using a free-body diagram. Then multiply the component of the net force that is parallel to the displacement by the displacement (eg. Fcosθ x d) 2. Determine the change in energy of the system. I ...
... Calculating Net Work: Can calculate work done in two ways. So choose one way. 1. Determine the net force using a free-body diagram. Then multiply the component of the net force that is parallel to the displacement by the displacement (eg. Fcosθ x d) 2. Determine the change in energy of the system. I ...
Lecture 11 (Feb 17) - West Virginia University
... An object has potential energy, because due to its location it can potentially do work. The choice of the reference level is arbitrary, since only differences of potential energies matter in the work-energy theorem: ...
... An object has potential energy, because due to its location it can potentially do work. The choice of the reference level is arbitrary, since only differences of potential energies matter in the work-energy theorem: ...
Thermal Physics Tutorial
... Note: when a bubble rises from the bottom of a beer glass, the pressure experience by this bubbles decreases. Assuming there is no change in the temperature, there will be an increase in the volume of the bubble. However, to have its volume doubled solely due to decreases in pressure, the beer glass ...
... Note: when a bubble rises from the bottom of a beer glass, the pressure experience by this bubbles decreases. Assuming there is no change in the temperature, there will be an increase in the volume of the bubble. However, to have its volume doubled solely due to decreases in pressure, the beer glass ...
Joules (J) are the units of energy
... To work out how much GPE an object gains when it is lifted up we would use the simple equation… GPE = mass (kg) × gravitational field strength × height (m) ...
... To work out how much GPE an object gains when it is lifted up we would use the simple equation… GPE = mass (kg) × gravitational field strength × height (m) ...
SMS-204: Integrative marine sciences.
... Friction is the process through which mechanical energy is converted to heat. The breaks in our car heat when we use them and so do our hands when we rub them against each other. Friction can often be an undesirable conversion of energy to heat. In that process a loss of some energy (to heat, anothe ...
... Friction is the process through which mechanical energy is converted to heat. The breaks in our car heat when we use them and so do our hands when we rub them against each other. Friction can often be an undesirable conversion of energy to heat. In that process a loss of some energy (to heat, anothe ...
Cons_of_Energy
... Conservation of Energy Try the following: A bullet of mass 10 grams leaves a gun at a velocity of 350 ms-1. If the bullet hits a stationary target which provides an average retarding force of 1234 N calculate how far into the target the bullet will penetrate before stopping. Neglect air resistance ...
... Conservation of Energy Try the following: A bullet of mass 10 grams leaves a gun at a velocity of 350 ms-1. If the bullet hits a stationary target which provides an average retarding force of 1234 N calculate how far into the target the bullet will penetrate before stopping. Neglect air resistance ...
Energy Forms and Transformations
... • There are several other types of energy that are associated with the particles of objects. ...
... • There are several other types of energy that are associated with the particles of objects. ...
Name - Net Start Class
... All objects are made of particles in constant random motion. As these particles interact, their kinetic and potential energies may change, but the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy does not change. This total energy is called the internal energy of the object. An object’s Internal Energy de ...
... All objects are made of particles in constant random motion. As these particles interact, their kinetic and potential energies may change, but the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy does not change. This total energy is called the internal energy of the object. An object’s Internal Energy de ...
HW#10b Note: numbers used in solution steps are different from
... object gets at any given time is also larger. Hence the speed is faster. Even though the distance traveled by the object within one period is doubled, its speed at any given time is also doubled, and it finish one cycle at the same T, independent of initial position or Amplitude. ...
... object gets at any given time is also larger. Hence the speed is faster. Even though the distance traveled by the object within one period is doubled, its speed at any given time is also doubled, and it finish one cycle at the same T, independent of initial position or Amplitude. ...
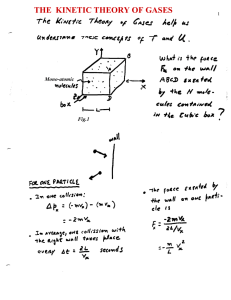
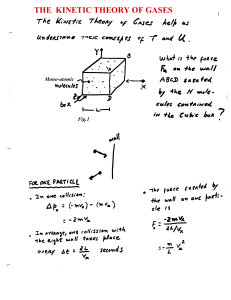
the kinetic theory of gases
... Case: Two different gases in the same container Consider a gas mixture of two types of molecules, 1 and 2, If molecules of type-1 were standing still, they would be speed by their collision with the faster moving molecules of type-2. If the type-1 molecules were to pick up too much speed, then, agai ...
... Case: Two different gases in the same container Consider a gas mixture of two types of molecules, 1 and 2, If molecules of type-1 were standing still, they would be speed by their collision with the faster moving molecules of type-2. If the type-1 molecules were to pick up too much speed, then, agai ...
Heat and Heat Transfer By Kevin Lei heat is thermal energy heat
... heat transfer through a fluid (gas or liquid) by moving circulating currents e.g. Kraft Dinner in a pot, noodles moving and heating up in convective currents, circulating from hot on bottom to cooler at top of pot o conductor a material that efficiently transfers heat e.g. metal ...
... heat transfer through a fluid (gas or liquid) by moving circulating currents e.g. Kraft Dinner in a pot, noodles moving and heating up in convective currents, circulating from hot on bottom to cooler at top of pot o conductor a material that efficiently transfers heat e.g. metal ...
Mechanical energy is conserved!
... A block of mass M is on a horizontal surface and is attached to a spring, spring constant k. If the spring is compressed an amount A and the block released from rest, how far from unstretched position will it go before stopping if there is no friction between the block and the surface? ...
... A block of mass M is on a horizontal surface and is attached to a spring, spring constant k. If the spring is compressed an amount A and the block released from rest, how far from unstretched position will it go before stopping if there is no friction between the block and the surface? ...
Notes 11 - CEProfs
... work is equal to a path independent quantity, which means adiabatic work is independent of path. • This is another form of the first law; • “For all adiabatic processes between two specified states of a closed system, the work is the same, regardless of the nature of the closed system and the detail ...
... work is equal to a path independent quantity, which means adiabatic work is independent of path. • This is another form of the first law; • “For all adiabatic processes between two specified states of a closed system, the work is the same, regardless of the nature of the closed system and the detail ...
Kinetic Energy
... Kinetic energy is energy that a moving object has because it is in motion, so kinetic energy is energy of motion. Potential energy is energy that an object has because of its position or condition. An object that is stretched or an object held in place above the ground have potential energy. ...
... Kinetic energy is energy that a moving object has because it is in motion, so kinetic energy is energy of motion. Potential energy is energy that an object has because of its position or condition. An object that is stretched or an object held in place above the ground have potential energy. ...