41Work and E TEST - Mr-Hubeny
... c. although both energies involve motion, only kinetic energy involves position. d. although both energies involve position, only potential energy involves motion. 10. Which form or forms of energy are involved in a rollercoaster ride? a. kinetic energy c. potential energy b. both potential and kine ...
... c. although both energies involve motion, only kinetic energy involves position. d. although both energies involve position, only potential energy involves motion. 10. Which form or forms of energy are involved in a rollercoaster ride? a. kinetic energy c. potential energy b. both potential and kine ...
-Energy of SHM -Comparing SHM to Circular Motion
... -Find v and a. -Show that a= - w2 x (so is this SHM?) -Find x max, v max, a max ...
... -Find v and a. -Show that a= - w2 x (so is this SHM?) -Find x max, v max, a max ...
Chapter 7
... This is a modified form of the work – kinetic energy theorem. Use this form when friction acts on an object. If friction is zero, this equation becomes the same as Conservation of Mechanical Energy. A friction force transforms kinetic energy in a system to internal energy. The increase in in ...
... This is a modified form of the work – kinetic energy theorem. Use this form when friction acts on an object. If friction is zero, this equation becomes the same as Conservation of Mechanical Energy. A friction force transforms kinetic energy in a system to internal energy. The increase in in ...
chapter-8-ap-physics-finalized
... This is a modified form of the work – kinetic energy theorem. Use this form when friction acts on an object. If friction is zero, this equation becomes the same as Conservation of Mechanical Energy. A friction force transforms kinetic energy in a system to internal energy. The increase in in ...
... This is a modified form of the work – kinetic energy theorem. Use this form when friction acts on an object. If friction is zero, this equation becomes the same as Conservation of Mechanical Energy. A friction force transforms kinetic energy in a system to internal energy. The increase in in ...
Chapter 20 - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... How much potential energy does it have when it is released? How much kinetic energy does it have just before it hits the ground? What is its speed just before impact? How much work could it do if it were to strike a nail before hitting the ground? ...
... How much potential energy does it have when it is released? How much kinetic energy does it have just before it hits the ground? What is its speed just before impact? How much work could it do if it were to strike a nail before hitting the ground? ...
Energy
... When you measure an astronomical body • You measure intensity • Intensity – amount of radiation ...
... When you measure an astronomical body • You measure intensity • Intensity – amount of radiation ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem (WKET)
... Work-kinetic energy theorem (WKET), The theorem states that the total work done by all forces acting on a system changes the total kinetic energy of the system. If more than one object makes up the system, the total kinetic energy is the algebraic sum of their individual kinetic energies. ...
... Work-kinetic energy theorem (WKET), The theorem states that the total work done by all forces acting on a system changes the total kinetic energy of the system. If more than one object makes up the system, the total kinetic energy is the algebraic sum of their individual kinetic energies. ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
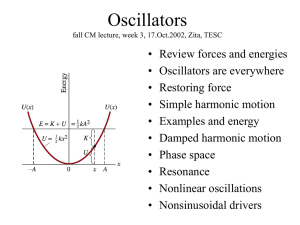
... Damped harmonic motion First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various b. Then, model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resu ...
... Damped harmonic motion First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various b. Then, model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resu ...
Kinetic and potential energy
... • Every observable change requires energy. • Energy comes in several different forms (food, electrical, solar, chemical), and can be converted from one form to another. ...
... • Every observable change requires energy. • Energy comes in several different forms (food, electrical, solar, chemical), and can be converted from one form to another. ...
Energy and Power
... Kinetic energy increase as mass increases. (golf and bowling ball) Kinetic energy increases as mass and velocity increase. ...
... Kinetic energy increase as mass increases. (golf and bowling ball) Kinetic energy increases as mass and velocity increase. ...
Energy Transformations
... 11. A 8 kg cat is running 4 m/s. How much kinetic energy does it have? ...
... 11. A 8 kg cat is running 4 m/s. How much kinetic energy does it have? ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy
... Since Potential energy is _paused_ and not in motion, think of it like _money_ in the bank. It’s there when you are ready to __spend__ it. One form of potential energy having to do with its position is called __gravitational____ potential energy. The __higher___ an object is above the Earth’s surfac ...
... Since Potential energy is _paused_ and not in motion, think of it like _money_ in the bank. It’s there when you are ready to __spend__ it. One form of potential energy having to do with its position is called __gravitational____ potential energy. The __higher___ an object is above the Earth’s surfac ...
Mechanics 105 chapter 7
... Consider the system of an object only in the earth’s gravitational field, falling from yb to ya. In free fall, the work done by gravity is mg(yb-ya), which results in a change in the kinetic energy (work-kinetic energy theorem) K. This work equals -Ug, the change in the gravitational potential ene ...
... Consider the system of an object only in the earth’s gravitational field, falling from yb to ya. In free fall, the work done by gravity is mg(yb-ya), which results in a change in the kinetic energy (work-kinetic energy theorem) K. This work equals -Ug, the change in the gravitational potential ene ...
Activity 58 "Follow the Energy"
... not belong with the others. b. Circle the word in each list that is a category that includes the others. c. Explain how the word you circled relates to the other words in the list, and how the word you crossed out does not fit in the list. ____________________________________________________________ ...
... not belong with the others. b. Circle the word in each list that is a category that includes the others. c. Explain how the word you circled relates to the other words in the list, and how the word you crossed out does not fit in the list. ____________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 12
... Grades of Energy, cont. If form A can be completely converted to form B, but the reverse is never complete, A is a higher grade of energy than B When a high-grade energy is converted to internal energy, it can never be fully recovered as high-grade energy Degradation of energy is the conversion ...
... Grades of Energy, cont. If form A can be completely converted to form B, but the reverse is never complete, A is a higher grade of energy than B When a high-grade energy is converted to internal energy, it can never be fully recovered as high-grade energy Degradation of energy is the conversion ...
Chapter 12
... Grades of Energy, cont. If form A can be completely converted to form B, but the reverse is never complete, A is a higher grade of energy than B When a high-grade energy is converted to internal energy, it can never be fully recovered as high-grade energy Degradation of energy is the conversion ...
... Grades of Energy, cont. If form A can be completely converted to form B, but the reverse is never complete, A is a higher grade of energy than B When a high-grade energy is converted to internal energy, it can never be fully recovered as high-grade energy Degradation of energy is the conversion ...
An X-ray photon of wavelength 6 pm (1 pm = 10^-12 m
... An X-ray photon of wavelength 6 pm (1 pm = 10^-12 m) makes a head-on collision with an electron, so that the scattered photon goes in a direction opposite to that of the incident photon. The electron is initially at rest. (a) How much longer is the wavelength of the scattered photon than that of the ...
... An X-ray photon of wavelength 6 pm (1 pm = 10^-12 m) makes a head-on collision with an electron, so that the scattered photon goes in a direction opposite to that of the incident photon. The electron is initially at rest. (a) How much longer is the wavelength of the scattered photon than that of the ...
Thermodynamics states that `the change in internal energy (∆ ) of a
... its kinetic energy is transformed into the thermal energy of its surroundings through friction. Similarly, a bouncing ball will decrease in height as its energy dissipates into the ground on each impact. The common trend in these examples is that ordered mechanical energy is transformed into disorde ...
... its kinetic energy is transformed into the thermal energy of its surroundings through friction. Similarly, a bouncing ball will decrease in height as its energy dissipates into the ground on each impact. The common trend in these examples is that ordered mechanical energy is transformed into disorde ...
Elements of Science Midterm Exam Review Answer Key
... 12. The energy a moving object has because of its motion is kinetic energy 13. The energy stored in an object is potential energy 14. Energy stored by something that can stretch or compress is _ elastic potential energy 15. The energy stored in chemical bonds is _ chemical potential energy _________ ...
... 12. The energy a moving object has because of its motion is kinetic energy 13. The energy stored in an object is potential energy 14. Energy stored by something that can stretch or compress is _ elastic potential energy 15. The energy stored in chemical bonds is _ chemical potential energy _________ ...