Orbital Physics Part 1: Gravitational Potential Energy Our start will be
... planet’s orbit to the Sun (perihelion) and then increases again as the planet moves away from perihelion toward aphelion again. Due to the conservation of mechanical energy, kinetic energy shows the opposite pattern: when gravitational potential energy is highest, at aphelion, kinetic energy is at ...
... planet’s orbit to the Sun (perihelion) and then increases again as the planet moves away from perihelion toward aphelion again. Due to the conservation of mechanical energy, kinetic energy shows the opposite pattern: when gravitational potential energy is highest, at aphelion, kinetic energy is at ...
Energy 1 Test Notes
... o Mechanical Kinetic energy: Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion. Mechanical kinetic energy increases as an object moves faster. A moving car has kinetic energy. If the car moves faster, it has more kinetic energy. ...
... o Mechanical Kinetic energy: Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion. Mechanical kinetic energy increases as an object moves faster. A moving car has kinetic energy. If the car moves faster, it has more kinetic energy. ...
Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work
... spring compression/tension electrostatic/magnetostatic chemical, nuclear, etc.... ...
... spring compression/tension electrostatic/magnetostatic chemical, nuclear, etc.... ...
energy
... • Bright lights have greater amplitudes (more energy) than the waves that make up dim light. • Because frequency and wavelength are related, either the wavelength or frequency of a light wave determines the color of the light. Blue light has a larger frequency and shorter wavelength than red light. ...
... • Bright lights have greater amplitudes (more energy) than the waves that make up dim light. • Because frequency and wavelength are related, either the wavelength or frequency of a light wave determines the color of the light. Blue light has a larger frequency and shorter wavelength than red light. ...
12-1 Chemical Reactions That Involve Heat
... equation would you write the term energy? 2. What is an endothermic reaction? On which side of the chemical equation would you write the term energy? 4. When clouds form water vapor (gas) turns back to liquid water. Is cloud formation exothermic or endothermic? Why do you feel cooler on a hot summer ...
... equation would you write the term energy? 2. What is an endothermic reaction? On which side of the chemical equation would you write the term energy? 4. When clouds form water vapor (gas) turns back to liquid water. Is cloud formation exothermic or endothermic? Why do you feel cooler on a hot summer ...
Motion Commotion - The Tech Museum of Innovation
... Energy: The ability to do work. Appears in many forms, all of which are either kinetic or potential. Force: A push or pull. An influence on a body or system, causing or tending to cause a change in movement or shape. Fulcrum: A lever’s pivot point. Gravitational Potential Energy: Potential energy du ...
... Energy: The ability to do work. Appears in many forms, all of which are either kinetic or potential. Force: A push or pull. An influence on a body or system, causing or tending to cause a change in movement or shape. Fulcrum: A lever’s pivot point. Gravitational Potential Energy: Potential energy du ...
Physical Science
... The student will investigate and understand changes in matter and the relationship of these changes to the Law of Conservation of Matter and Energy. Key concepts include a) physical changes; b) chemical changes; and c) nuclear reactions. ...
... The student will investigate and understand changes in matter and the relationship of these changes to the Law of Conservation of Matter and Energy. Key concepts include a) physical changes; b) chemical changes; and c) nuclear reactions. ...
Grade 8 Physical Science 2015 Unit 1
... does not change in a chemical reaction and thus mass is conserved. § Students will design and implement an experiment to verify the Law of Conservation of Mass is upheld in both physical and chemical changes. § Relate a balanced chemical equation to the Law of Conservation of Mass. ...
... does not change in a chemical reaction and thus mass is conserved. § Students will design and implement an experiment to verify the Law of Conservation of Mass is upheld in both physical and chemical changes. § Relate a balanced chemical equation to the Law of Conservation of Mass. ...
Ezio Fornero, Kinetic Theory
... Now we can pass to the meaning of absolute temperature according to kinetic theory. From the state equation of an ideal gas PV = nRT in which n are the moles and R is the ideal gas constant we can express P in function of the others variables: nRT P = V By making equal the two expressions of the pre ...
... Now we can pass to the meaning of absolute temperature according to kinetic theory. From the state equation of an ideal gas PV = nRT in which n are the moles and R is the ideal gas constant we can express P in function of the others variables: nRT P = V By making equal the two expressions of the pre ...
energy conversion
... There are two TYPES of energy: potential and kinetic The energy we use comes from many sources: Fossil fuel (coal, oil, natural gas) , nuclear power, Sun, wind, geothermal, hydropower. Most of this we convert into electricity. There are 6 forms of energy: mechanical, chemical, nuclear, electromagne ...
... There are two TYPES of energy: potential and kinetic The energy we use comes from many sources: Fossil fuel (coal, oil, natural gas) , nuclear power, Sun, wind, geothermal, hydropower. Most of this we convert into electricity. There are 6 forms of energy: mechanical, chemical, nuclear, electromagne ...
Leap Frog Solar System
... A Void type function can be used to perform tasks, such as an iterative calculation or printing data, while not providing a result to the command that called it. This way they can be used to perform a simple closed task, for which the main function does not rely on the result of this task in any way ...
... A Void type function can be used to perform tasks, such as an iterative calculation or printing data, while not providing a result to the command that called it. This way they can be used to perform a simple closed task, for which the main function does not rely on the result of this task in any way ...
Lecture Notes: Y F Chapter 23
... Wa →b = (U a − U b ) = −(U b − U a ) = − ∆U ∆U can be positive or negative ∆U positive – Work is “done” in moving from point a to point b ∆U negative – Energy is “released” in moving from point a to point b ...
... Wa →b = (U a − U b ) = −(U b − U a ) = − ∆U ∆U can be positive or negative ∆U positive – Work is “done” in moving from point a to point b ∆U negative – Energy is “released” in moving from point a to point b ...
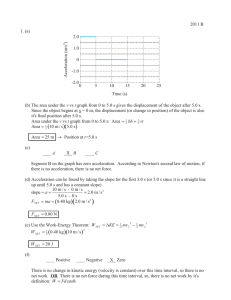
2011 B 1. (a) 2.0 0
... (b) Using the chalk, mark a starting line on the track. Using a tape metric measure or a meter stick, measure 10 m distances (marked by a chalk-line) up to, and including, 100 m (which is the finish line). Position one student, who has the starter's pistol, at the starting line. The ten other studen ...
... (b) Using the chalk, mark a starting line on the track. Using a tape metric measure or a meter stick, measure 10 m distances (marked by a chalk-line) up to, and including, 100 m (which is the finish line). Position one student, who has the starter's pistol, at the starting line. The ten other studen ...
Definition of Work Resultant Work (Net Work) Resultant Work Work
... • Energy can be transformed from one form to another & from one body to another, but the total amount remains constant. Law of Conservation of Energy • Again: Not exactly the same as the Principle of Conservation of Mechanical Energy, which holds for conservative forces only! This is a general Law ...
... • Energy can be transformed from one form to another & from one body to another, but the total amount remains constant. Law of Conservation of Energy • Again: Not exactly the same as the Principle of Conservation of Mechanical Energy, which holds for conservative forces only! This is a general Law ...
Energy - Physics
... the force constant, k. Record the value below. (Note because of the orientation of the force sensor hook, the force will register as negative and the slope of the line will be negative. The spring constant, k, is a positive number) Spring constant k A Compressed Spring Pushing the Cart Up an Incline ...
... the force constant, k. Record the value below. (Note because of the orientation of the force sensor hook, the force will register as negative and the slope of the line will be negative. The spring constant, k, is a positive number) Spring constant k A Compressed Spring Pushing the Cart Up an Incline ...
Definition and Mathematics of Work
... A hammer is a tool that uses mechanical energy to do work. The mechanical energy of a hammer gives the hammer its ability to apply a force to a nail in order to cause it to be displaced. Because the hammer has mechanical energy (in the form of kinetic energy), it is able to do work on the nail. Mech ...
... A hammer is a tool that uses mechanical energy to do work. The mechanical energy of a hammer gives the hammer its ability to apply a force to a nail in order to cause it to be displaced. Because the hammer has mechanical energy (in the form of kinetic energy), it is able to do work on the nail. Mech ...