The First Law of Thermodynamics
... The First Law of Thermodynamics A biatomic ideal gas undergoes a cycle starting at point A (2 atm, 1L). Process from A to B is an expansion at constant pressure until the volume is 2.5 L, after which is cooled at constant volume until its pressure is 1 atm. It is then compressed at constant pressur ...
... The First Law of Thermodynamics A biatomic ideal gas undergoes a cycle starting at point A (2 atm, 1L). Process from A to B is an expansion at constant pressure until the volume is 2.5 L, after which is cooled at constant volume until its pressure is 1 atm. It is then compressed at constant pressur ...
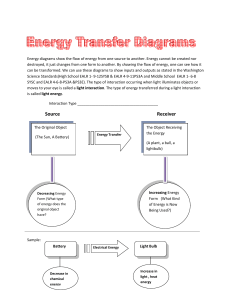
Energy Flow Introduction
... into work and heat. The work is used to carry on cell processes like growing, reproducing, moving molecules around, and getting rid of waste. The heat is a byproduct of the fuel "burning" process. Heat is always given off when fuel is burned, whether it is in a diesel engine or an animal cell. In an ...
... into work and heat. The work is used to carry on cell processes like growing, reproducing, moving molecules around, and getting rid of waste. The heat is a byproduct of the fuel "burning" process. Heat is always given off when fuel is burned, whether it is in a diesel engine or an animal cell. In an ...
Student Workbook
... a) the value of the force needed to lift the car. c) the work done by gravity. b) the work done by this lifting force. d) the net work done on the car. 7. An electron has a mass of 9.11 x 10 -31kg. A certain elephant weighs 6600-Lbs. If this elephant walked with a speed of 2.1 m/s would it be possib ...
... a) the value of the force needed to lift the car. c) the work done by gravity. b) the work done by this lifting force. d) the net work done on the car. 7. An electron has a mass of 9.11 x 10 -31kg. A certain elephant weighs 6600-Lbs. If this elephant walked with a speed of 2.1 m/s would it be possib ...
CTEnergyAnsFa06
... Answer: the same! Any journey can be thought of a series of small vertical or horizontal displacements. During any horizontal segment, the work done by gravity is zero. All upward vertical segments are cancelled by corresponding downward vertical segments, EXCEPT for the last 0.5 m between the start ...
... Answer: the same! Any journey can be thought of a series of small vertical or horizontal displacements. During any horizontal segment, the work done by gravity is zero. All upward vertical segments are cancelled by corresponding downward vertical segments, EXCEPT for the last 0.5 m between the start ...
Energy
... today. Converting one form of energy into another form always involves a loss of usable energy. Most energy transformations are not very efficient. The human body is a good example. Your body is like a machine, and the fuel for your machine is food. Food gives you the energy to move, breathe, and th ...
... today. Converting one form of energy into another form always involves a loss of usable energy. Most energy transformations are not very efficient. The human body is a good example. Your body is like a machine, and the fuel for your machine is food. Food gives you the energy to move, breathe, and th ...
Student Activity DOC
... Move to pages 4.1 and 4.2. Now you can investigate the motion of a roller coaster on a track that includes peaks and valleys. 7. Read the information on page 4.1. Page 4.2 simulates a roller coaster car moving along a track. The height and speed of the car along with the distance traveled along the ...
... Move to pages 4.1 and 4.2. Now you can investigate the motion of a roller coaster on a track that includes peaks and valleys. 7. Read the information on page 4.1. Page 4.2 simulates a roller coaster car moving along a track. The height and speed of the car along with the distance traveled along the ...
Questions 46‑47
... (D) 720,000 N (E) 1,560,000 N 20. A fan blows the air and gives it kinetic energy. An hour after the fan has been turned off, what has happened to the kinetic energy of the air? (A) it disappears (B) it turns into potential energy (C) it turns into thermal energy (D) it turns into sound energy (E) i ...
... (D) 720,000 N (E) 1,560,000 N 20. A fan blows the air and gives it kinetic energy. An hour after the fan has been turned off, what has happened to the kinetic energy of the air? (A) it disappears (B) it turns into potential energy (C) it turns into thermal energy (D) it turns into sound energy (E) i ...
1 - Learning While Doing
... measured in terms of calories and unit of work in terms of joule. These two units are still in use because it’s easier to calculate heat in calories and work in joule. We can convert calories into joule by using formula 1calorie = 4.2 joule. Power is the rate of work done or rate of energy consumed. ...
... measured in terms of calories and unit of work in terms of joule. These two units are still in use because it’s easier to calculate heat in calories and work in joule. We can convert calories into joule by using formula 1calorie = 4.2 joule. Power is the rate of work done or rate of energy consumed. ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy
... Kinetic energy is ….. energy in motion. As potential energy decreases, kinetic energy increases. So, the greatest amount of kinetic energy would be…. just before the ball hits the ...
... Kinetic energy is ….. energy in motion. As potential energy decreases, kinetic energy increases. So, the greatest amount of kinetic energy would be…. just before the ball hits the ...
5 Energy and Machines
... The SI unit for work is the joule (j), which equals one Newton • meter (N•m). For maximum work to be done, the object must move in the direction of the force. If the object is moving at an angle to the force, determine the component of the force in the direction of motion (W = FΔd cos θ) . Remember, ...
... The SI unit for work is the joule (j), which equals one Newton • meter (N•m). For maximum work to be done, the object must move in the direction of the force. If the object is moving at an angle to the force, determine the component of the force in the direction of motion (W = FΔd cos θ) . Remember, ...
Transparancies for Dynamics - University of Manchester
... • But if a system changes energy in some other way (“dissipative forces”) – Friction changes energy to heat ...
... • But if a system changes energy in some other way (“dissipative forces”) – Friction changes energy to heat ...