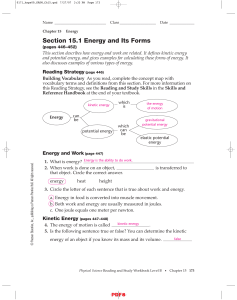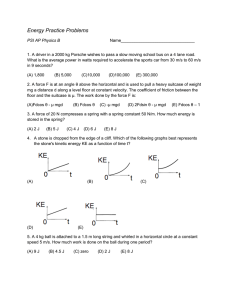
AP Physics B/C
... 1. A 50 kg block is pulled from rest by a force of 1000 N at 37° across a horizontal rough surface over a distance of 5.6 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.5. a. Draw a free-body diagram and show all the applied forces. b. How much work is done by force F? ...
... 1. A 50 kg block is pulled from rest by a force of 1000 N at 37° across a horizontal rough surface over a distance of 5.6 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.5. a. Draw a free-body diagram and show all the applied forces. b. How much work is done by force F? ...
Energy of a Tossed Ball
... When a juggler tosses a bean ball straight upward, the ball slows down until it reaches the top of its path and then speeds up on its way back down. In terms of energy, when the ball is released it has kinetic energy, KE. As it rises during its free-fall phase it slows down, loses kinetic energy, an ...
... When a juggler tosses a bean ball straight upward, the ball slows down until it reaches the top of its path and then speeds up on its way back down. In terms of energy, when the ball is released it has kinetic energy, KE. As it rises during its free-fall phase it slows down, loses kinetic energy, an ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... giving its latitude (345.6’), longitude (11742.7’), and elevation above sea level (1200 ft.). The location uniquely specified by the three coordinates is analogous to the thermodynamic state of a system. Suppose that our system in Figure 1 is gaseous helium at a low pressure and a high temperature ...
... giving its latitude (345.6’), longitude (11742.7’), and elevation above sea level (1200 ft.). The location uniquely specified by the three coordinates is analogous to the thermodynamic state of a system. Suppose that our system in Figure 1 is gaseous helium at a low pressure and a high temperature ...
Energy of a Tossed Ball
... When a juggler tosses a bean ball straight upward, the ball slows down until it reaches the top of its path and then speeds up on its way back down. In terms of energy, when the ball is released it has kinetic energy, EK. As it rises during its free-fall phase it slows down, loses kinetic energy, an ...
... When a juggler tosses a bean ball straight upward, the ball slows down until it reaches the top of its path and then speeds up on its way back down. In terms of energy, when the ball is released it has kinetic energy, EK. As it rises during its free-fall phase it slows down, loses kinetic energy, an ...
Energy Transformation on a Roller Coaster
... accord with their loss of height. The cars subsequently gain kinetic energy. Kinetic energy - the energy of motion - is dependent upon the mass of the object and the speed of the object. The train of coaster cars speeds up as they lose height. Thus, their original potential energy (due to their larg ...
... accord with their loss of height. The cars subsequently gain kinetic energy. Kinetic energy - the energy of motion - is dependent upon the mass of the object and the speed of the object. The train of coaster cars speeds up as they lose height. Thus, their original potential energy (due to their larg ...
SOLID-STATE PHYSICS II 2009 O. Entin-Wohlman
... in which the conductivity is dominated by the electrons which are excited thermally into the conductance band, and extrinsic semiconductors, whose electronic behavior is determined by the electrons contributed to the conduction band by impurities. One should keep in mind that the value of the energy ...
... in which the conductivity is dominated by the electrons which are excited thermally into the conductance band, and extrinsic semiconductors, whose electronic behavior is determined by the electrons contributed to the conduction band by impurities. One should keep in mind that the value of the energy ...
Using the “Clicker”
... A heat engine A heat engine is a device that uses heat to do work. A gasoline-powered car engine is a good example. To be useful, the engine must go through cycles, with work being done every cycle. Two temperatures are required. The higher temperature causes the system to expand, doing work, and t ...
... A heat engine A heat engine is a device that uses heat to do work. A gasoline-powered car engine is a good example. To be useful, the engine must go through cycles, with work being done every cycle. Two temperatures are required. The higher temperature causes the system to expand, doing work, and t ...
Slide 1
... • When energy changes from one form to another, the total energy remains unchanged even though many energy conversions may occur. • The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. – Energy can be converted from one form to another. – In a closed system, the amoun ...
... • When energy changes from one form to another, the total energy remains unchanged even though many energy conversions may occur. • The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. – Energy can be converted from one form to another. – In a closed system, the amoun ...
Topic 8_1__Energy degradation and power generation
... of the law: Much energy is lost or wasted. And the example of kicking the block shown next demonstrates the first part: All of the kinetic energy of the block became heat due to friction. Obviously, this heat cannot ever be used to give the block back its original kinetic energy! This loss of en ...
... of the law: Much energy is lost or wasted. And the example of kicking the block shown next demonstrates the first part: All of the kinetic energy of the block became heat due to friction. Obviously, this heat cannot ever be used to give the block back its original kinetic energy! This loss of en ...
Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation of Mechanical
... Whenever the work done by a force in moving an object from an initial point to a final point is independent of the path, then the force is called a conservative force. D.2 Potential Energy D.2.1 Change in Potential Energy Let’s consider an example in which only conservative forces are acting on a sy ...
... Whenever the work done by a force in moving an object from an initial point to a final point is independent of the path, then the force is called a conservative force. D.2 Potential Energy D.2.1 Change in Potential Energy Let’s consider an example in which only conservative forces are acting on a sy ...
Development of the Work Energy Concept in Mechanics
... Introduction. The concepts of work and energy are introduced in all beginning physics classes. At that beginning level, the student has attained a proficiency in algebra and trigonometry only, and as such, many educators believe the student is unable to appreciate or understand the development of t ...
... Introduction. The concepts of work and energy are introduced in all beginning physics classes. At that beginning level, the student has attained a proficiency in algebra and trigonometry only, and as such, many educators believe the student is unable to appreciate or understand the development of t ...
userfiles/269/my files/work energy power more info?id=1319
... The potential energy of the 100-N boulder with respect to the ground below is 200 J in each case. a. The boulder is lifted with 100 N of force. b. The boulder is pushed up the 4-m incline with 50 N of force. c. The boulder is lifted with 100 N of force up each 0.5-m stair. ...
... The potential energy of the 100-N boulder with respect to the ground below is 200 J in each case. a. The boulder is lifted with 100 N of force. b. The boulder is pushed up the 4-m incline with 50 N of force. c. The boulder is lifted with 100 N of force up each 0.5-m stair. ...
m2_CEC
... As the ball rises it loses kinetic energy and gains potential energy, but, the loss in kinetic energy is equal to the gain in potential energy. When the ball falls, it gains kinetic energy and losses potential energy, but, the gain in kinetic energy is equal to the loss in potential energy. For the ...
... As the ball rises it loses kinetic energy and gains potential energy, but, the loss in kinetic energy is equal to the gain in potential energy. When the ball falls, it gains kinetic energy and losses potential energy, but, the gain in kinetic energy is equal to the loss in potential energy. For the ...