Chapter 2
... the rug as possible, and arrive at numerical predictions about the average value of various properties such as pressure, temperature, and thermal energy. Let us illustrate this principle by considering a simple gas. The gas found in a 1 liter bottle under ordinary room conditions contains about 3x10 ...
... the rug as possible, and arrive at numerical predictions about the average value of various properties such as pressure, temperature, and thermal energy. Let us illustrate this principle by considering a simple gas. The gas found in a 1 liter bottle under ordinary room conditions contains about 3x10 ...
Energy:
... The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The greater the mass of a moving object, the more kinetic energy it ...
... The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The greater the mass of a moving object, the more kinetic energy it ...
Gas and Thermo Notes
... Specific heat (c)- the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a chemical substance by 1 ˚C. Heat Capacity (C)- the energy required to raise the temperature of an object (of a given constant mass) by 1˚C. Notice that the heat capacity is for a given object, while specific is for any obje ...
... Specific heat (c)- the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a chemical substance by 1 ˚C. Heat Capacity (C)- the energy required to raise the temperature of an object (of a given constant mass) by 1˚C. Notice that the heat capacity is for a given object, while specific is for any obje ...
Chapter 10: Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... since work is a process that involves moving random motions into more ordered ones. ...
... since work is a process that involves moving random motions into more ordered ones. ...
Chapter 5 HW – Conservation of Energy… and Springs
... 6. Two snow covered peaks are at elevations of 850 m and 750 m above the valley between them. A ski run extends from the top of one peak to the top of the other. A skier starts from rest at the top of the taller peak and goes as fast as possible down one and up the other. How fast will he be going a ...
... 6. Two snow covered peaks are at elevations of 850 m and 750 m above the valley between them. A ski run extends from the top of one peak to the top of the other. A skier starts from rest at the top of the taller peak and goes as fast as possible down one and up the other. How fast will he be going a ...
Solutions and Statistics
... vertical distance h is mgh, so ∆Ug = mgh = (2.5 kg)(9.8 m/s2 )(0.17 m) = 4.19 J = ∆Ug (c) (5 points) As the box slides across the floor and up the ramp, what energy is lost to friction (in Joules)? Solution: Energy lost to friction is the work done against friction, and work is force times distance. ...
... vertical distance h is mgh, so ∆Ug = mgh = (2.5 kg)(9.8 m/s2 )(0.17 m) = 4.19 J = ∆Ug (c) (5 points) As the box slides across the floor and up the ramp, what energy is lost to friction (in Joules)? Solution: Energy lost to friction is the work done against friction, and work is force times distance. ...
4. Classical Thermodynamics
... We need to start with a handful of definitions: • A system that is completely isolated from all outside influences is said to be contained in adiabatic walls. We will also refer to such systems as insulated. • Walls that are not adiabatic are said to be diathermal and two systems separated by a diat ...
... We need to start with a handful of definitions: • A system that is completely isolated from all outside influences is said to be contained in adiabatic walls. We will also refer to such systems as insulated. • Walls that are not adiabatic are said to be diathermal and two systems separated by a diat ...
PowerPoint Version
... Since the most time consuming part is the evaluation of the force, the raw speed of the integration algorithm is not so important It should permit the use of long time step Far more important to employ a long time step. In this way, a given period of simulation time can be covered in a modest number ...
... Since the most time consuming part is the evaluation of the force, the raw speed of the integration algorithm is not so important It should permit the use of long time step Far more important to employ a long time step. In this way, a given period of simulation time can be covered in a modest number ...
Chapter 2: Energy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis
... Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and, thus, experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. The change in the stored energy is identical to the change in internal energy for stationary systems. If KE = PE = 0, ...
... Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and, thus, experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. The change in the stored energy is identical to the change in internal energy for stationary systems. If KE = PE = 0, ...
Chapter 2: Energy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis
... Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and, thus, experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. The change in the stored energy is identical to the change in internal energy for stationary systems. If KE = PE = 0, ...
... Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and, thus, experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. The change in the stored energy is identical to the change in internal energy for stationary systems. If KE = PE = 0, ...
3. Simple Harmonic Oscillator
... So far, we have been looking at systems that we can solve completely analytically. The potential energies and Hamiltonians have been of a form that makes the Schroedinger equation solvable without any approximation techniques. What if we don’t have such a “nice” Hamiltonian. In general, one must rel ...
... So far, we have been looking at systems that we can solve completely analytically. The potential energies and Hamiltonians have been of a form that makes the Schroedinger equation solvable without any approximation techniques. What if we don’t have such a “nice” Hamiltonian. In general, one must rel ...
massachusetts institute of technology
... mass and length l . A spring of negligible mass and force constant k is connected at one end to the point mass and attached to a wall at the other end. The spring is relaxed when 0 . The pendulum is displaced a small angle 0 from the vertical and released from rest. The system oscillates. Let ...
... mass and length l . A spring of negligible mass and force constant k is connected at one end to the point mass and attached to a wall at the other end. The spring is relaxed when 0 . The pendulum is displaced a small angle 0 from the vertical and released from rest. The system oscillates. Let ...
First Law of Thermodynamics - Erwin Sitompul
... Instead, the sample may change from one phase, or state, to another, with no change in temperature. The amount of energy per unit mass that must be transferred as heat when a sample completely undergoes a phase change is called the heat of transformation L. Thus, when a sample of mass m comple ...
... Instead, the sample may change from one phase, or state, to another, with no change in temperature. The amount of energy per unit mass that must be transferred as heat when a sample completely undergoes a phase change is called the heat of transformation L. Thus, when a sample of mass m comple ...
printer-friendly version
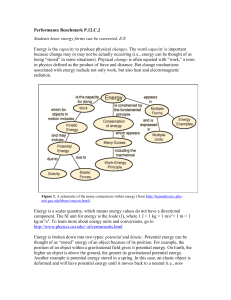
... Energy is a scalar quantity, which means energy values do not have a directional component. The SI unit for energy is the Joule (J), where 1 J = 1 kg × 1 m/s2× 1 m = 1 kg∙m2/s2. To learn more about energy units and conversions, go to http://www.physics.uci.edu/~silverma/units.html Energy is broken d ...
... Energy is a scalar quantity, which means energy values do not have a directional component. The SI unit for energy is the Joule (J), where 1 J = 1 kg × 1 m/s2× 1 m = 1 kg∙m2/s2. To learn more about energy units and conversions, go to http://www.physics.uci.edu/~silverma/units.html Energy is broken d ...
First Law of Thermodynamics - Erwin Sitompul
... Instead, the sample may change from one phase, or state, to another, with no change in temperature. The amount of energy per unit mass that must be transferred as heat when a sample completely undergoes a phase change is called the heat of transformation L. Thus, when a sample of mass m comple ...
... Instead, the sample may change from one phase, or state, to another, with no change in temperature. The amount of energy per unit mass that must be transferred as heat when a sample completely undergoes a phase change is called the heat of transformation L. Thus, when a sample of mass m comple ...
Chapter 17: Electric Potential
... Electric potential energy (Ue) is energy stored in the electric field. •Ue depends only on the location, not upon the path taken to get there (conservative force). Not a vector. •Ue = 0 at some reference point. •For two point particles take Ue = 0 at r = . kq1q2 •For the electric force U e r ...
... Electric potential energy (Ue) is energy stored in the electric field. •Ue depends only on the location, not upon the path taken to get there (conservative force). Not a vector. •Ue = 0 at some reference point. •For two point particles take Ue = 0 at r = . kq1q2 •For the electric force U e r ...