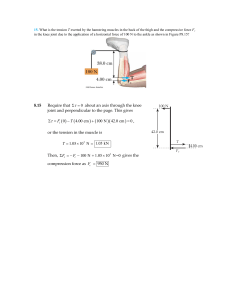
Ch 08-151
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
Exam 1
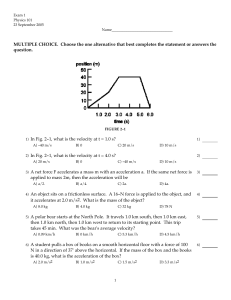
... A) Both its velocity and its acceleration are zero. B) Its velocity is zero and its acceleration is not zero. C) Neither its velocity nor its acceleration is zero. D) Its velocity is not zero and its acceleration is zero. ...
... A) Both its velocity and its acceleration are zero. B) Its velocity is zero and its acceleration is not zero. C) Neither its velocity nor its acceleration is zero. D) Its velocity is not zero and its acceleration is zero. ...
Kreutter: Dynamics 9 Lesson 9: Applying Newton`s Second Law
... magnitude and the sign of the answer, its units, and how the result changes if one of the quantities becomes zero – do these all make sense? Make sure you go back to the force and motion diagrams to make sure your answer is consistent with both. ...
... magnitude and the sign of the answer, its units, and how the result changes if one of the quantities becomes zero – do these all make sense? Make sure you go back to the force and motion diagrams to make sure your answer is consistent with both. ...
Newton`s Laws
... Mass is intrinsic property of any object Weight measures gravitational force on an object, usually due to a planet Weight depends on location of object Question 1: How does mass of a rock compare when on Earth and on moon? Question 2: How does its weight ...
... Mass is intrinsic property of any object Weight measures gravitational force on an object, usually due to a planet Weight depends on location of object Question 1: How does mass of a rock compare when on Earth and on moon? Question 2: How does its weight ...
Chapter 5
... theory of electricity and magnetism, founding the theory of electromagnetic field. At the same time, Maxwell’s theory predicted a constant which should be the speed of electromagnetic field traveling in free space. Everything was fine except for asking which inertia frame of reference is the right o ...
... theory of electricity and magnetism, founding the theory of electromagnetic field. At the same time, Maxwell’s theory predicted a constant which should be the speed of electromagnetic field traveling in free space. Everything was fine except for asking which inertia frame of reference is the right o ...
Galaxies – Island universes
... cluster. If they’re big enough to identify as having eaten several galaxies, we call them “central dominant” or “cannibal galaxies” … ...
... cluster. If they’re big enough to identify as having eaten several galaxies, we call them “central dominant” or “cannibal galaxies” … ...
Physics 50 Lecture Final Review
... b) Know how to apply Newton’s Laws of Motion to describe the motion of a system in equilibrium or moving with constant acceleration. See “ STEPS IN USING NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION” on notes on homepage. c) ALWAYS define your system when applying Newton’s Laws. d) Define a convenient SYSTEM and use a c ...
... b) Know how to apply Newton’s Laws of Motion to describe the motion of a system in equilibrium or moving with constant acceleration. See “ STEPS IN USING NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION” on notes on homepage. c) ALWAYS define your system when applying Newton’s Laws. d) Define a convenient SYSTEM and use a c ...
9-18 Consider the uniform 31 kg beam held in place by the wall and
... g2. Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the Moon. The Moon's radius is 1.74 E6 m and its mass is 7.35 E22 kg. Hint: Draw vectors to represent the position of the arbitrary point P indicated on the figure with respect to the center of the Moon (use figure g2.gif) Use definition of "accelera ...
... g2. Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the Moon. The Moon's radius is 1.74 E6 m and its mass is 7.35 E22 kg. Hint: Draw vectors to represent the position of the arbitrary point P indicated on the figure with respect to the center of the Moon (use figure g2.gif) Use definition of "accelera ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... Have All of the Necessary Variables 6. Write down the equation(s) you need to solve for the missing variables in your final equation. 7. Convert your units and solve for the missing variables. 8. Plug in those missing variables in your final equation and solve (remember to check your units!!!) ...
... Have All of the Necessary Variables 6. Write down the equation(s) you need to solve for the missing variables in your final equation. 7. Convert your units and solve for the missing variables. 8. Plug in those missing variables in your final equation and solve (remember to check your units!!!) ...
Lecture 22 - LSU Physics
... 4) A uniform spherical shell of matter attracts an object on the outside as if all the shell’s mass were concentrated at its center (note: this defines the position) mass were concentrated at its center (note: this defines the position) height = RE + h ...
... 4) A uniform spherical shell of matter attracts an object on the outside as if all the shell’s mass were concentrated at its center (note: this defines the position) mass were concentrated at its center (note: this defines the position) height = RE + h ...
Summary of lesson
... Move to pages 1.2 –1.3 and read the background information for this activity. The average acceleration of an object is equal to the change in velocity of the object over a period of time. A force is a push or pull on an object. Forces cause objects to accelerate. According to Newton's second law, th ...
... Move to pages 1.2 –1.3 and read the background information for this activity. The average acceleration of an object is equal to the change in velocity of the object over a period of time. A force is a push or pull on an object. Forces cause objects to accelerate. According to Newton's second law, th ...
hw chp5 091114
... A Newton is the force required to accelerate a 1 kg object at a rate of 1 m/s2. ...
... A Newton is the force required to accelerate a 1 kg object at a rate of 1 m/s2. ...
exam2_T102
... A small disk, tied to one end of a light string, moves with speed v in a circular path of radius r, on a horizontal, frictionless table. The string passes through a hole in the center of the table as shown in Figure 6. If the string is slowly pulled down, thereby reducing the radius of the path of t ...
... A small disk, tied to one end of a light string, moves with speed v in a circular path of radius r, on a horizontal, frictionless table. The string passes through a hole in the center of the table as shown in Figure 6. If the string is slowly pulled down, thereby reducing the radius of the path of t ...
Chapter 7
... • 1. The law of orbits: All planets move in elliptical orbits, with the Sun at one focus • 2. The law of areas: A line that connects the planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in the plane of the planet’s orbit in equal time intervals • 3. The law of periods: The square of the period of any planet ...
... • 1. The law of orbits: All planets move in elliptical orbits, with the Sun at one focus • 2. The law of areas: A line that connects the planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in the plane of the planet’s orbit in equal time intervals • 3. The law of periods: The square of the period of any planet ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.