Physics Fall Midterm Review
... Compare the momentum of different moving objects Compare the momentum of the same object moving at different velocities Identify examples of change in the momentum of an object Describe changes in momentum in terms of force and time Use the impulse-momentum theorem to calculate force, time ...
... Compare the momentum of different moving objects Compare the momentum of the same object moving at different velocities Identify examples of change in the momentum of an object Describe changes in momentum in terms of force and time Use the impulse-momentum theorem to calculate force, time ...
Forces Study Guide
... Newton’s Laws & Circular Motion (Topics are highlighted in yellow) 1. For a winter fair, some students decide to build 30.0-kg wooden pull-carts on sled skis. If two 90.0-kg passengers get in, how much force will the puller have to exert to move a pull-cart? The coefficient of maximum static frictio ...
... Newton’s Laws & Circular Motion (Topics are highlighted in yellow) 1. For a winter fair, some students decide to build 30.0-kg wooden pull-carts on sled skis. If two 90.0-kg passengers get in, how much force will the puller have to exert to move a pull-cart? The coefficient of maximum static frictio ...
Forces Study Guide
... Newton’s Laws & Circular Motion (Topics are highlighted in yellow) 1. For a winter fair, some students decide to build 30.0-kg wooden pull-carts on sled skis. If two 90.0-kg passengers get in, how much force will the puller have to exert to move a pull-cart? The coefficient of maximum static frictio ...
... Newton’s Laws & Circular Motion (Topics are highlighted in yellow) 1. For a winter fair, some students decide to build 30.0-kg wooden pull-carts on sled skis. If two 90.0-kg passengers get in, how much force will the puller have to exert to move a pull-cart? The coefficient of maximum static frictio ...
AST 207 Test 3 23 November 2009
... a. (1 pt.) At the present time, does the value of Hubble’s constant depend on the galaxy in which the observations are made? (2 pts.) Explain your reasoning. b. Simplicio erroneously believes that everything in the universe is expanding according to Hubble’s Law. At an earlier time, everything did o ...
... a. (1 pt.) At the present time, does the value of Hubble’s constant depend on the galaxy in which the observations are made? (2 pts.) Explain your reasoning. b. Simplicio erroneously believes that everything in the universe is expanding according to Hubble’s Law. At an earlier time, everything did o ...
Gravity Basics The Power of Attraction
... Since the Sun is such a massive object, Earth and all the other planets in the solar system are attracted to it. You may be wondering why the planets don’t fall into the Sun directly. The only factor preventing this from happening is the speed at which the planets are traveling. ...
... Since the Sun is such a massive object, Earth and all the other planets in the solar system are attracted to it. You may be wondering why the planets don’t fall into the Sun directly. The only factor preventing this from happening is the speed at which the planets are traveling. ...
6th Grade Science Chapter 19 Jeopardy Game
... What is a very bright, star-like object that generates immense energy? a. b. c. d. ...
... What is a very bright, star-like object that generates immense energy? a. b. c. d. ...
Division I students, START HERE.
... A thermally insulating container has a membrane separating the container into two equal parts. In one part is a vacuum. In the other part is an ideal gas of temperature T and internal energy U. The membrane is punctured and the gas rushes into the region which was vacuum. After the system has return ...
... A thermally insulating container has a membrane separating the container into two equal parts. In one part is a vacuum. In the other part is an ideal gas of temperature T and internal energy U. The membrane is punctured and the gas rushes into the region which was vacuum. After the system has return ...
WS Circular Motion Problem Sheet 1 Horiz Circles
... d) If the period of revolution is half as large, but all other quantities remain the same, what would be the effect on the velocity, acceleration and force? ...
... d) If the period of revolution is half as large, but all other quantities remain the same, what would be the effect on the velocity, acceleration and force? ...
Ch33
... • Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other particle. • A particle is a piece of matter, small enough in size to be regarded as having no volume. In practice we use the particle model even for larger bodies • The Law of Universal Gravitation is an example of an inverse ...
... • Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other particle. • A particle is a piece of matter, small enough in size to be regarded as having no volume. In practice we use the particle model even for larger bodies • The Law of Universal Gravitation is an example of an inverse ...
Chapter 2 Lessons 1 - 3 slides
... Kinematics in 1 dimension with constant acceleration Lesson Objective: The ‘suvat’ equations Consider a point mass moving along a line with a constant acceleration. What does its velocity time graph look like? ...
... Kinematics in 1 dimension with constant acceleration Lesson Objective: The ‘suvat’ equations Consider a point mass moving along a line with a constant acceleration. What does its velocity time graph look like? ...
lecture1
... are not time-invariant – Hubble’s measurement of galaxy redshifts showed that the Universe is not static – High speed motions of stars in galaxies show that either we do not understand gravity or that there is a large amount of “dark matter”, i.e. different stuff that the ones that makes you and me ...
... are not time-invariant – Hubble’s measurement of galaxy redshifts showed that the Universe is not static – High speed motions of stars in galaxies show that either we do not understand gravity or that there is a large amount of “dark matter”, i.e. different stuff that the ones that makes you and me ...
Full text in PDF form
... equations he had formulated proved to him that electromagnetic fields spread in the form of polarized waves and with the speed of light! To few men in the world has such an experience been vouchsafed. At that thrilling moment he surely never guessed that the riddling nature of light, apparently so c ...
... equations he had formulated proved to him that electromagnetic fields spread in the form of polarized waves and with the speed of light! To few men in the world has such an experience been vouchsafed. At that thrilling moment he surely never guessed that the riddling nature of light, apparently so c ...
assignments
... the gas is kept at a constant. This is a very unusual thermometer in that it requires only one temperature for calibration if the temperature is referred to absolute zero; i.e. need to use the Kelvin scale. From the information in the question we know that at 0 C or 273 K, the pressure in the therm ...
... the gas is kept at a constant. This is a very unusual thermometer in that it requires only one temperature for calibration if the temperature is referred to absolute zero; i.e. need to use the Kelvin scale. From the information in the question we know that at 0 C or 273 K, the pressure in the therm ...
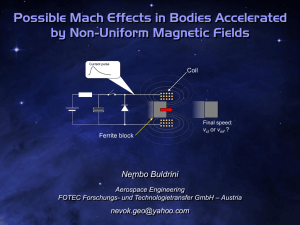
v mf - Yimg
... Efficiency of Mach Effects Given the last experimental results, the question why the magnitude of the recorded effect is so low compared to the one predicted by the theoretical model ...
... Efficiency of Mach Effects Given the last experimental results, the question why the magnitude of the recorded effect is so low compared to the one predicted by the theoretical model ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.