THE PARAMETRIC STUDY OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FOR
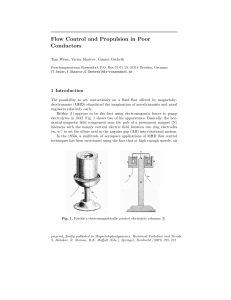
... In electromagnetic-energy harvesting, a magnetic field converts mechanical energy to electrical. Methods to increase the amount of electricity and to induce voltage include by increasing the number of turns of the coil and increasing the permanent magnetic field. Both of the methods can affect the p ...
... In electromagnetic-energy harvesting, a magnetic field converts mechanical energy to electrical. Methods to increase the amount of electricity and to induce voltage include by increasing the number of turns of the coil and increasing the permanent magnetic field. Both of the methods can affect the p ...
X - GWU`s SEAS - The George Washington University
... This work is concerned with the determination of both macroscopic and microscopic deformations, motions, stresses, as well as electromagnetic fields developed in the material body due to external loads of thermal, mechanical, and electromagnetic origins. The balance laws of mass, microinertia, linea ...
... This work is concerned with the determination of both macroscopic and microscopic deformations, motions, stresses, as well as electromagnetic fields developed in the material body due to external loads of thermal, mechanical, and electromagnetic origins. The balance laws of mass, microinertia, linea ...
Rotational Equilibrium
... and under what circumstances an object moves. If the object is initially motionless it will remain motionless unless acted on by a net force. Similarly if the object is in motion it will move at a constant velocity (in the same direction at the same speed) unless acted on by a net force. The ultimat ...
... and under what circumstances an object moves. If the object is initially motionless it will remain motionless unless acted on by a net force. Similarly if the object is in motion it will move at a constant velocity (in the same direction at the same speed) unless acted on by a net force. The ultimat ...
Introduction to PHY008: Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... main ways; (i) as a convenient unit of energy, and (ii) to calculate the velocity of a charged particle passing through an electric field. Definition: The change in energy E of a charged particle q as it moves through a potential difference V is given by . 1 electron-volt =1eV =1.6×10-19×1 = 1.6×10- ...
... main ways; (i) as a convenient unit of energy, and (ii) to calculate the velocity of a charged particle passing through an electric field. Definition: The change in energy E of a charged particle q as it moves through a potential difference V is given by . 1 electron-volt =1eV =1.6×10-19×1 = 1.6×10- ...