Harmonic Oscillators and Sound Quiz
... a. Increasing the distance between the speakers b. Increasing the temperature of the air c. Increasing the wavelength emitted sound d. (a-c) e. None of the above ...
... a. Increasing the distance between the speakers b. Increasing the temperature of the air c. Increasing the wavelength emitted sound d. (a-c) e. None of the above ...
Numerical Simulation of Electromagnetic Forming Process
... somewhat artificial infinite boundary condition. On the other hand, the main disadvantage of the BEM is that it generates full dense matrices in place of the sparse FEM matrices. This causes an a priori high memory requirement as well as longer CPU time to solve the linear systems. In order to impro ...
... somewhat artificial infinite boundary condition. On the other hand, the main disadvantage of the BEM is that it generates full dense matrices in place of the sparse FEM matrices. This causes an a priori high memory requirement as well as longer CPU time to solve the linear systems. In order to impro ...
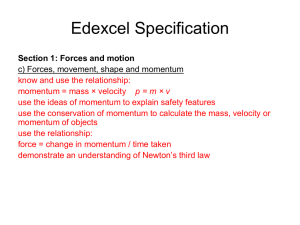
Momentum
... thus at the same speed. Although both of these situations conserve momentum, they differ in whether they conserve kinetic energy. The two particles that stick together and come to rest clearly have lost their kinetic energy, giving it up to other forms of energy such as sound and heat, because we kn ...
... thus at the same speed. Although both of these situations conserve momentum, they differ in whether they conserve kinetic energy. The two particles that stick together and come to rest clearly have lost their kinetic energy, giving it up to other forms of energy such as sound and heat, because we kn ...
Momentum, Impulse and Recoil
... • The momentum, mv, is the amount gained before the cord begins to stretch. Ft is the impulse the cord supplies to reduce the momentum to zero. • Because the rubber cord stretches for a long time, a large time interval t ensures that a small average force F acts on the jumper. • The cord typically s ...
... • The momentum, mv, is the amount gained before the cord begins to stretch. Ft is the impulse the cord supplies to reduce the momentum to zero. • Because the rubber cord stretches for a long time, a large time interval t ensures that a small average force F acts on the jumper. • The cord typically s ...
James Clerk Maxwell (1831 - 1879)
... is described by the Lorentz force law (8.5 with given E and B background fields. This approximation scheme decouples the set of differential equations into two separate, more tractable, sets. In this text, we focus on the second problem: the mechanics of probe charges in the background of given elec ...
... is described by the Lorentz force law (8.5 with given E and B background fields. This approximation scheme decouples the set of differential equations into two separate, more tractable, sets. In this text, we focus on the second problem: the mechanics of probe charges in the background of given elec ...
Chapters 1–5 Schedule of Crisis Centre
... The momentum of the water is changed due to the force applied to it by the turbine blade. ∆p ∆v In 1 s, m = 30 kg of water hits the blade and F = =m changes speed from vo = 16 m/s to vf = –16 m/s. ∆t ∆t So, F = 30 × (−16 − 16) = −960 N Friday, October 20, 2006 ...
... The momentum of the water is changed due to the force applied to it by the turbine blade. ∆p ∆v In 1 s, m = 30 kg of water hits the blade and F = =m changes speed from vo = 16 m/s to vf = –16 m/s. ∆t ∆t So, F = 30 × (−16 − 16) = −960 N Friday, October 20, 2006 ...
Experiment P25: Kinetic Friction (Smart Pulley)
... The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study how the coefficient of kinetic friction for an object depends on the mass of the object, the area of contact between the object and a surface, the type of material making contact, and the speed of the object. THEORY The block of mass M is placed on ...
... The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study how the coefficient of kinetic friction for an object depends on the mass of the object, the area of contact between the object and a surface, the type of material making contact, and the speed of the object. THEORY The block of mass M is placed on ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
... i. The gravitational mass of an object determines the amount of force exerted on the object by a gravitational field. ii. Near the Earth’s surface, all objects fall (in a vacuum) with the same acceleration, regardless of their inertial mass. d. A vector field gives, as a function of position (and p ...
... i. The gravitational mass of an object determines the amount of force exerted on the object by a gravitational field. ii. Near the Earth’s surface, all objects fall (in a vacuum) with the same acceleration, regardless of their inertial mass. d. A vector field gives, as a function of position (and p ...