PSI AP Physics I
... Object 2 has a mass of 2.8 kg with a velocity of 15 m/s south. What is the momentum of the system? 28. Three objects in a system are moving as follows: Object 1 has a mass of 5.5 kg with a velocity of 12 m/s east; Object 2 has a mass of 2.2 kg with a velocity of 15 m/s west; and Object 3 has a mass ...
... Object 2 has a mass of 2.8 kg with a velocity of 15 m/s south. What is the momentum of the system? 28. Three objects in a system are moving as follows: Object 1 has a mass of 5.5 kg with a velocity of 12 m/s east; Object 2 has a mass of 2.2 kg with a velocity of 15 m/s west; and Object 3 has a mass ...
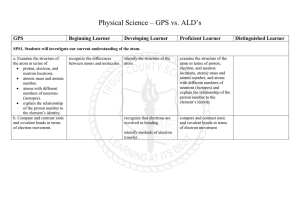
Physical Science ALDs Organized by GPS
... predict outcomes given series and parallel circuits explain magnetism and/or its relationship to the movement of electrical charge as it relates to electromagnets, including simple motors and permanent magnets ...
... predict outcomes given series and parallel circuits explain magnetism and/or its relationship to the movement of electrical charge as it relates to electromagnets, including simple motors and permanent magnets ...
Electromagnetic force computation with the Eggshell method
... Table I shows the average torque computed with various choices of the evaluation domain S (EVAL) and the summation domain Y (SUM). Line 1 corresponds to the case where the nodal forces have been evaluated at all nodes of the mesh, (S is the whole domain occupied by the machine) and the summation has ...
... Table I shows the average torque computed with various choices of the evaluation domain S (EVAL) and the summation domain Y (SUM). Line 1 corresponds to the case where the nodal forces have been evaluated at all nodes of the mesh, (S is the whole domain occupied by the machine) and the summation has ...
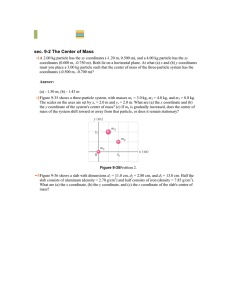
Halliday 9th chapter 9
... Particle 1 of mass m1 = 5.00 g is shot directly along the x axis on a frictionless floor, with constant speed 10.0 m/s. Particle 2 of mass m2 = 3.00 g is shot with a velocity of magnitude 20.0 m/s, at an upward angle such that it always stays directly above particle 1. (a) What is the maximum height ...
... Particle 1 of mass m1 = 5.00 g is shot directly along the x axis on a frictionless floor, with constant speed 10.0 m/s. Particle 2 of mass m2 = 3.00 g is shot with a velocity of magnitude 20.0 m/s, at an upward angle such that it always stays directly above particle 1. (a) What is the maximum height ...
Ch12 Motion Notes and Practice problems with explanations
... Fortunately, the way that we use the word momentum in everyday life is consistent with the definition of momentum in physics. For example, we say that a BMW driving 20 miles per hour has less momentum than the same car speeding on the highway at 80 miles per hour. Additionally, we know that if a lar ...
... Fortunately, the way that we use the word momentum in everyday life is consistent with the definition of momentum in physics. For example, we say that a BMW driving 20 miles per hour has less momentum than the same car speeding on the highway at 80 miles per hour. Additionally, we know that if a lar ...
General relativity in a (2+1)-dimensional space
... solutions and simple cosmological solutions. In the present paper, we will present an exact electrically charged solution to the combined Einstein-MaxweU equations. Studies of general relativity in a ( 2 + 1)dimensional space-time carried out by a number of authors [1-5] have proven instructive in a ...
... solutions and simple cosmological solutions. In the present paper, we will present an exact electrically charged solution to the combined Einstein-MaxweU equations. Studies of general relativity in a ( 2 + 1)dimensional space-time carried out by a number of authors [1-5] have proven instructive in a ...
Temperature rise in the human body exposed to
... carried out via Galerkin-Bubnov boundary element method, explained in details in [11] and [12]. In this work, the human body is represented as a cylinder with thermal properties of the muscle. The model based on infinite and finite length cylinder case of infinite and finite length cylinder is used. ...
... carried out via Galerkin-Bubnov boundary element method, explained in details in [11] and [12]. In this work, the human body is represented as a cylinder with thermal properties of the muscle. The model based on infinite and finite length cylinder case of infinite and finite length cylinder is used. ...
Qualification Exam: Classical Mechanics
... A system consists of a point particle of mass m and a streight uniform rod of length l and mass m on a frictionless horizontal table. A rigid frictionless vertical axle passes through one end of the rod. The rod is originally at rest and the point particle is moving horizontally toward the end of th ...
... A system consists of a point particle of mass m and a streight uniform rod of length l and mass m on a frictionless horizontal table. A rigid frictionless vertical axle passes through one end of the rod. The rod is originally at rest and the point particle is moving horizontally toward the end of th ...
Newton's Second Law
... In this section, the acceleration of the cart on a flat track will be measured experimentally several times and averaged to obtain the average acceleration. The mass of the hanging weight will be varied, and the resulting acceleration measured repeatedly to obtain the average acceleration. 1. Use th ...
... In this section, the acceleration of the cart on a flat track will be measured experimentally several times and averaged to obtain the average acceleration. The mass of the hanging weight will be varied, and the resulting acceleration measured repeatedly to obtain the average acceleration. 1. Use th ...
THE MASS SPECTROMETER….How it works The basic principle If
... The atom is ionized by knocking one or more electrons off to give a positive ion. This is true even for things which you would normally expect to form negative ions (chlorine, for example) or never form ions at all (argon, for example). Mass spectrometers always work with positive ions. Stage 2: Acc ...
... The atom is ionized by knocking one or more electrons off to give a positive ion. This is true even for things which you would normally expect to form negative ions (chlorine, for example) or never form ions at all (argon, for example). Mass spectrometers always work with positive ions. Stage 2: Acc ...
Perfect fluids in special relativity
... We will introduce the relativistic description of a fluid with the simplest one: ‘dust’ is defined to be a collection of particles, all of which are at rest in some one Lorentz frame. It isn’t very clear how this usage of the term ‘dust’ evolved from the other meaning as that substance which is at r ...
... We will introduce the relativistic description of a fluid with the simplest one: ‘dust’ is defined to be a collection of particles, all of which are at rest in some one Lorentz frame. It isn’t very clear how this usage of the term ‘dust’ evolved from the other meaning as that substance which is at r ...