Chapter 6, Week 6.
... Equation 6.10 says that the local acceleration of gravity, g, near the Earth’s surface is known at a given value. We will use the standard approximation of g as an appropriate value for this problem. Equation 6.11 says that there is no heat transfer between the cart and it surroundings. As is clear ...
... Equation 6.10 says that the local acceleration of gravity, g, near the Earth’s surface is known at a given value. We will use the standard approximation of g as an appropriate value for this problem. Equation 6.11 says that there is no heat transfer between the cart and it surroundings. As is clear ...
Physics Syllabus, Grade 9
... to adjust the timer to one second intervals, though 2 second intervals is easier to capture data. Error rates increase with smaller intervals. Students create several Dot Plots of accelerated or decelerated motion. They transfer these to notebooks and then to tables of data. Then they calculate the ...
... to adjust the timer to one second intervals, though 2 second intervals is easier to capture data. Error rates increase with smaller intervals. Students create several Dot Plots of accelerated or decelerated motion. They transfer these to notebooks and then to tables of data. Then they calculate the ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics
... (1) heat: Energy can also leave or enter the gas as heat. For example, collisions between a molecule in the gas and the atoms in the wall will in general be inelastic, i.e., energy will be exchanged (see Fig. 1.1). The walls and the gas will be said to be in thermal equilibrium when, if we average o ...
... (1) heat: Energy can also leave or enter the gas as heat. For example, collisions between a molecule in the gas and the atoms in the wall will in general be inelastic, i.e., energy will be exchanged (see Fig. 1.1). The walls and the gas will be said to be in thermal equilibrium when, if we average o ...
The Sabatier Principle Illustrated by Catalytic H2
... activities predicted by our model corresponds well with the observed activities. That is, the metals that bind OH too strongly are poor catalysts and thus lie on the left side of the volcano. These metals are inherently unstable in an oxidizing environment; indeed, these metals will form oxides afte ...
... activities predicted by our model corresponds well with the observed activities. That is, the metals that bind OH too strongly are poor catalysts and thus lie on the left side of the volcano. These metals are inherently unstable in an oxidizing environment; indeed, these metals will form oxides afte ...
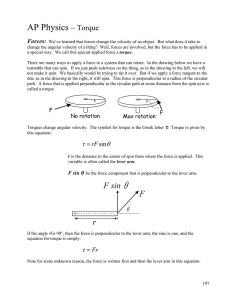
AP Physics – Applying Forces
... We’ve learned that forces change the velocity of an object. But what does it take to change the angular velocity of a thing? Well, forces are involved, but the force has to be applied in a special way. We call this special applied force a torque. There are many ways to apply a force to a system that ...
... We’ve learned that forces change the velocity of an object. But what does it take to change the angular velocity of a thing? Well, forces are involved, but the force has to be applied in a special way. We call this special applied force a torque. There are many ways to apply a force to a system that ...
Energy - mrgriecophysics
... sitting on the table, it has no kinetic energy since it is not moving. When you push it (add work to the system), that work changes into kinetic energy and the object starts to move. Elastic potential energy is also easy to observe. In addition to the rubber band and chalk experiment explained above ...
... sitting on the table, it has no kinetic energy since it is not moving. When you push it (add work to the system), that work changes into kinetic energy and the object starts to move. Elastic potential energy is also easy to observe. In addition to the rubber band and chalk experiment explained above ...
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY
... Thus, the sled's kinetic energy would increase by 18 % . ______________________________________________________________________________ 20. REASONING Since the person has an upward acceleration, there must be a net force acting in the upward direction. The net force ΣFy is related to the acceleratio ...
... Thus, the sled's kinetic energy would increase by 18 % . ______________________________________________________________________________ 20. REASONING Since the person has an upward acceleration, there must be a net force acting in the upward direction. The net force ΣFy is related to the acceleratio ...
Document
... Within a system, energy can be transformed from one type to another. The total energy of the system is not changed by these transformations. This is the law of conservation of energy. Energy can also be transferred from one system to another. The mechanical transfer of energy to a system v ...
... Within a system, energy can be transformed from one type to another. The total energy of the system is not changed by these transformations. This is the law of conservation of energy. Energy can also be transferred from one system to another. The mechanical transfer of energy to a system v ...
Ch#7 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q3. A single force acts on a 5.0 kg object in such a way that the position of the object as a function of time is given by x=10.0 t -5.0 t2 with x is in meters and t is in seconds. Find the work done on the object from t = 0 to t = 4.0 s. (Ans: 2000 J) Q4. A 2000 kg elevator moves 20 m upward in 4. ...
... Q3. A single force acts on a 5.0 kg object in such a way that the position of the object as a function of time is given by x=10.0 t -5.0 t2 with x is in meters and t is in seconds. Find the work done on the object from t = 0 to t = 4.0 s. (Ans: 2000 J) Q4. A 2000 kg elevator moves 20 m upward in 4. ...
ENTROPY
... we postpone any further statistical interpretation of entropy until Chapter 7: Mixtures, and restrict for the moment entropy measurements to the physical derivatives mentioned. Joining (2.4) and (2.5) one gets the differential form for the entropy as a function of internal energy, volume and amount ...
... we postpone any further statistical interpretation of entropy until Chapter 7: Mixtures, and restrict for the moment entropy measurements to the physical derivatives mentioned. Joining (2.4) and (2.5) one gets the differential form for the entropy as a function of internal energy, volume and amount ...
Chapter 7 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q4. A 2000 kg elevator moves 20 m upward in 4.9 sec at a constant speed. At what average rate does the force from the cable do the work on the elevator? (Ans: 80000 W) 062: Q1. A 10.0 kg box slides with a constant speed a distance of 5.00 m downward along a rough slope that makes an angle of 30.0° ...
... Q4. A 2000 kg elevator moves 20 m upward in 4.9 sec at a constant speed. At what average rate does the force from the cable do the work on the elevator? (Ans: 80000 W) 062: Q1. A 10.0 kg box slides with a constant speed a distance of 5.00 m downward along a rough slope that makes an angle of 30.0° ...
Energy is transferred when work is done.
... the ramp. You will place the ball at the top of the ramp, so calculate the ball’s potential energy at the top of the ramp using mass and height. 3 Mark a line on the floor with tape 30 cm from the bottom of the ramp. 4 Place the ball at the top of the ramp and release it without pushing. Time how ...
... the ramp. You will place the ball at the top of the ramp, so calculate the ball’s potential energy at the top of the ramp using mass and height. 3 Mark a line on the floor with tape 30 cm from the bottom of the ramp. 4 Place the ball at the top of the ramp and release it without pushing. Time how ...
ch10
... The box rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The spring is stretched to x=A and released. When the box is passing through x=0, a second box of the same mass is attached to it. Discuss what happens to the (a) maximum speed (b) amplitude (c) angular frequency. ...
... The box rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The spring is stretched to x=A and released. When the box is passing through x=0, a second box of the same mass is attached to it. Discuss what happens to the (a) maximum speed (b) amplitude (c) angular frequency. ...
Appendix D. Hints and Answers to Exercises
... Newton’s or anyone else’s. It is probably not appropriate to memorize a particular statement of any of the laws we will study. However, your wording should contain the same important components of the law. In this case, these would be: (a) The law applies to “free” objects, those which have no force ...
... Newton’s or anyone else’s. It is probably not appropriate to memorize a particular statement of any of the laws we will study. However, your wording should contain the same important components of the law. In this case, these would be: (a) The law applies to “free” objects, those which have no force ...
You can calculate the kinetic energy of a moving particle, and the
... You can calculate the work done by a force when its point of application moves by using the following formula A packing case is pulled across a horizontal floor by a horizontal rope. The case moves at a constant speed and there is a constant resistance to motion of magnitude R Newtons. When the case ...
... You can calculate the work done by a force when its point of application moves by using the following formula A packing case is pulled across a horizontal floor by a horizontal rope. The case moves at a constant speed and there is a constant resistance to motion of magnitude R Newtons. When the case ...
Summary - CED Engineering
... One additional law attributed to Newton concerns mutual attractive forces between two bodies. It is known as the universal law of gravitation and is stated as follows. "Each and every mass in the universe exerts a mutual, attractive gravitational force on every other mass in the universe. For any tw ...
... One additional law attributed to Newton concerns mutual attractive forces between two bodies. It is known as the universal law of gravitation and is stated as follows. "Each and every mass in the universe exerts a mutual, attractive gravitational force on every other mass in the universe. For any tw ...
Solutions to Chapter 6 Problems
... equal. However, the energy is proportional to the square of the speed. It takes four times as much energy to accelerate the car from rest to 60 km/h as it takes to accelerate the car from rest to 30 km/h. Therefore, it takes three times the energy to accelerate the car from 30 km/h to 60 km/h as it ...
... equal. However, the energy is proportional to the square of the speed. It takes four times as much energy to accelerate the car from rest to 60 km/h as it takes to accelerate the car from rest to 30 km/h. Therefore, it takes three times the energy to accelerate the car from 30 km/h to 60 km/h as it ...