File
... at an angle of 60° to the left of the negative y- axis. While the cart moves a horizontal distance of 10.0 m, what is the work done by the shopper on the shopping cart? Fa = 8.9 N at an angle of 60° to the left of the negative y- axis ...
... at an angle of 60° to the left of the negative y- axis. While the cart moves a horizontal distance of 10.0 m, what is the work done by the shopper on the shopping cart? Fa = 8.9 N at an angle of 60° to the left of the negative y- axis ...
Conservative and Non-conservative Forces F
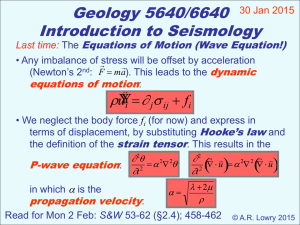
... depends on the relative position(s) of the object(s). This stored energy is also called potential energy, because there is the potential to do work. The difference in stored (potential) energies between two object positions is the amount of work required to move the object from one position to the ...
... depends on the relative position(s) of the object(s). This stored energy is also called potential energy, because there is the potential to do work. The difference in stored (potential) energies between two object positions is the amount of work required to move the object from one position to the ...
SHM MC Packet
... Which of the following is true for a system consisting of a mass oscillating on the end of an ideal spring? (A) The kinetic and potential energies are equal to each other at all times. (B) The kinetic and potential energies are both constant. (C) The maximum potential energy is achieved when the mas ...
... Which of the following is true for a system consisting of a mass oscillating on the end of an ideal spring? (A) The kinetic and potential energies are equal to each other at all times. (B) The kinetic and potential energies are both constant. (C) The maximum potential energy is achieved when the mas ...
Nonconservative Forces
... Energy stored in a compressed or extended spring. Us = ½ kx2 k is the spring constant. x is the distance the spring is compressed or stretched. ...
... Energy stored in a compressed or extended spring. Us = ½ kx2 k is the spring constant. x is the distance the spring is compressed or stretched. ...
PPT
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i.e. zero displac ...
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i.e. zero displac ...
Powerpoint Slide
... When is the velocity maximum? V = - xMAX sin(t) velocity is max. when sin(t) is max (i.e. equals 1), this happens when (t) = /2 What are we doing today? 2 experiments. The first will allow us to measure the spring constant, k, of our spring. You will hang the spring, measure the equilibrium l ...
... When is the velocity maximum? V = - xMAX sin(t) velocity is max. when sin(t) is max (i.e. equals 1), this happens when (t) = /2 What are we doing today? 2 experiments. The first will allow us to measure the spring constant, k, of our spring. You will hang the spring, measure the equilibrium l ...
Engineering Concepts Chapter 1 Terms
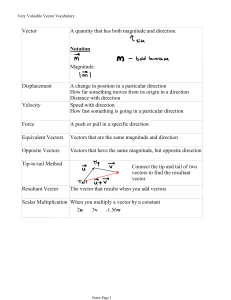
... magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of the second object acting upon the first. ...
... magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of the second object acting upon the first. ...
PPP- Review for Semester Exam
... force pushes a 15 kg object against a force of friction. If the object is accelerating at 5 m/s2, what is the net force? ...
... force pushes a 15 kg object against a force of friction. If the object is accelerating at 5 m/s2, what is the net force? ...