2.0 Circular Motion An object moves in a straight line if the net force
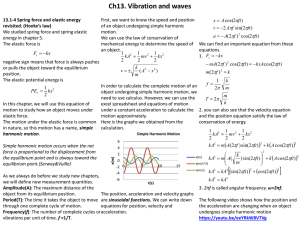
... one complete oscillation). Frequency F (the number of cycles in a unit time). In general, the period T and frequency F are related by F = in Hz Now consider an object at the end of a coil spring, when displaced from its equilibrium position and released, the resulting oscillating motion is referred ...
... one complete oscillation). Frequency F (the number of cycles in a unit time). In general, the period T and frequency F are related by F = in Hz Now consider an object at the end of a coil spring, when displaced from its equilibrium position and released, the resulting oscillating motion is referred ...
Consider a rod BC of length L and uniform cross-sectional... x which is characteristics of the rod BC.
... amount Δmax. The energy of the falling block is transformed momentarily into axial strain energy in the post and bending strain energy in the beam. Although vibrations are established in each member after impact, they will tend to dissipate as time passes. In order to determine the deformation Δmax, ...
... amount Δmax. The energy of the falling block is transformed momentarily into axial strain energy in the post and bending strain energy in the beam. Although vibrations are established in each member after impact, they will tend to dissipate as time passes. In order to determine the deformation Δmax, ...
PF1.5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
... spring to pull back (or extend) to its original length, is in the opposite direction to the applied force. ...
... spring to pull back (or extend) to its original length, is in the opposite direction to the applied force. ...
Kepler*s Laws and Gravity
... • Momentum (of a body in motion) the product of its mass and velocity. • net force -The combination of all the forces that act on an object. • Acceleration -The amount by which a speed or velocity increases (and so a scalar quantity or a vector quantity). ...
... • Momentum (of a body in motion) the product of its mass and velocity. • net force -The combination of all the forces that act on an object. • Acceleration -The amount by which a speed or velocity increases (and so a scalar quantity or a vector quantity). ...
Work, Power, Energy Multiple Choice PSI Physics
... 24. A truck drives slams on the brakes of a moving truck with a constant velocity v, as a result of his action the truck stops after traveling a distance d. If the driver had been traveling with twice the velocity, what would be the stopping distance compared to the distance in the first trial? A. T ...
... 24. A truck drives slams on the brakes of a moving truck with a constant velocity v, as a result of his action the truck stops after traveling a distance d. If the driver had been traveling with twice the velocity, what would be the stopping distance compared to the distance in the first trial? A. T ...